Hoffa fracture
Definition
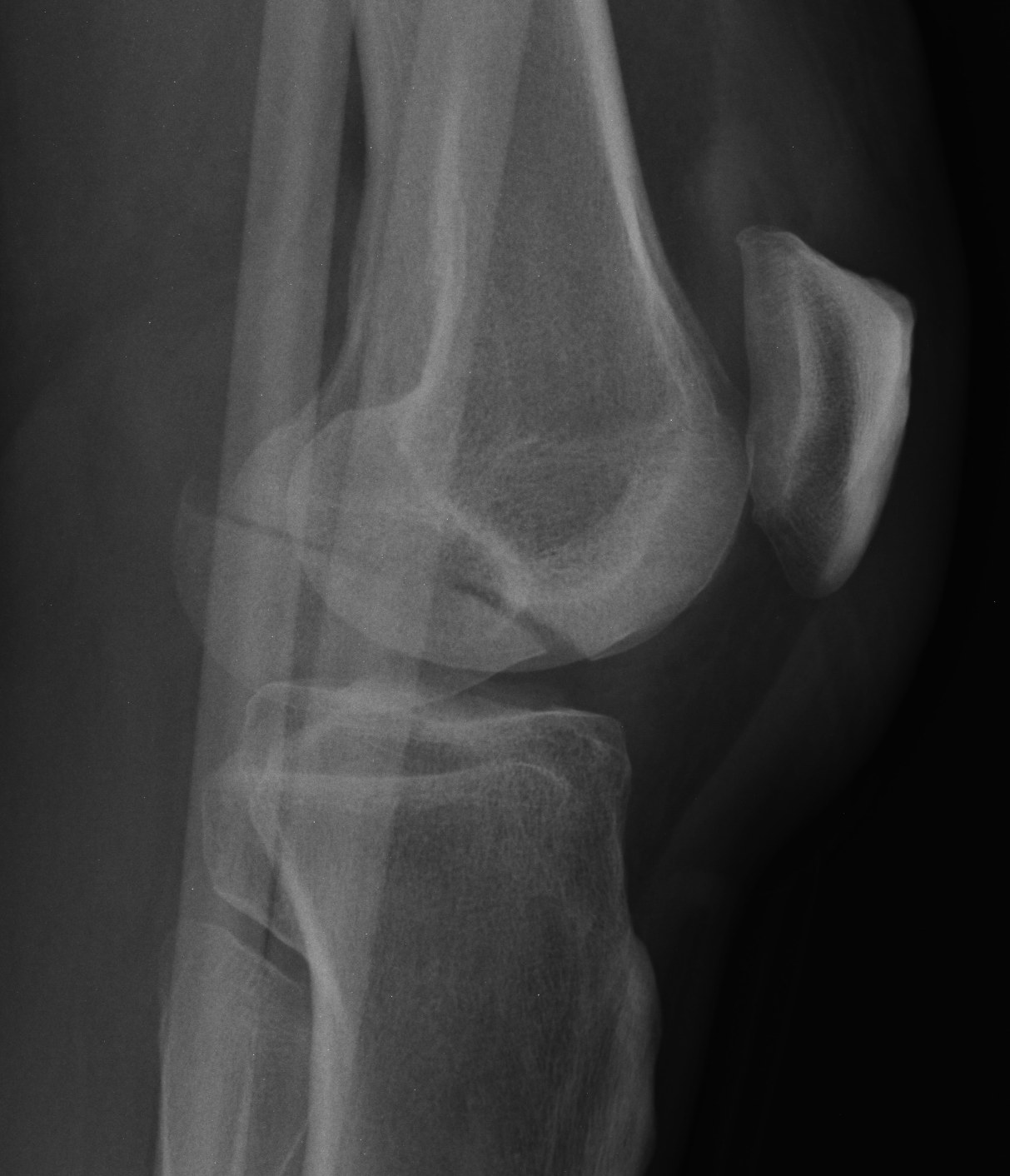
Coronal plane fracture of distal femoral condyle
- intra-articular
- often only attachment is posterior capsule
Epidemiology
Rare
Mechanism
Usually a severe valgus trauma
Xray

Coronal plane fracture of distal femoral condyle
- intra-articular
- often only attachment is posterior capsule
Rare
Usually a severe valgus trauma
Education regarding shoe wear
- extra wide / large toe box
Insoles
- longitudinal arch support
- pre MT dome for metatarsalgia
- podiatry to attend to callosities
Toe spacers
Analgesia
1. Continued pain and discomfort
2. Difficulties with shoe wear
Return to Sport
Shelbourne et al. Am J Sports Med 1999
- 133 patients with isolated PCL injuries followed for mean of 5 years
- 1/2 returned to sport at same level of play
- 1/3 returned to sport at lower level of play
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10352760/
Agolley et al. Bone Joint J 2017
Fracture below lesser trochanter / proximal 5 cm femur
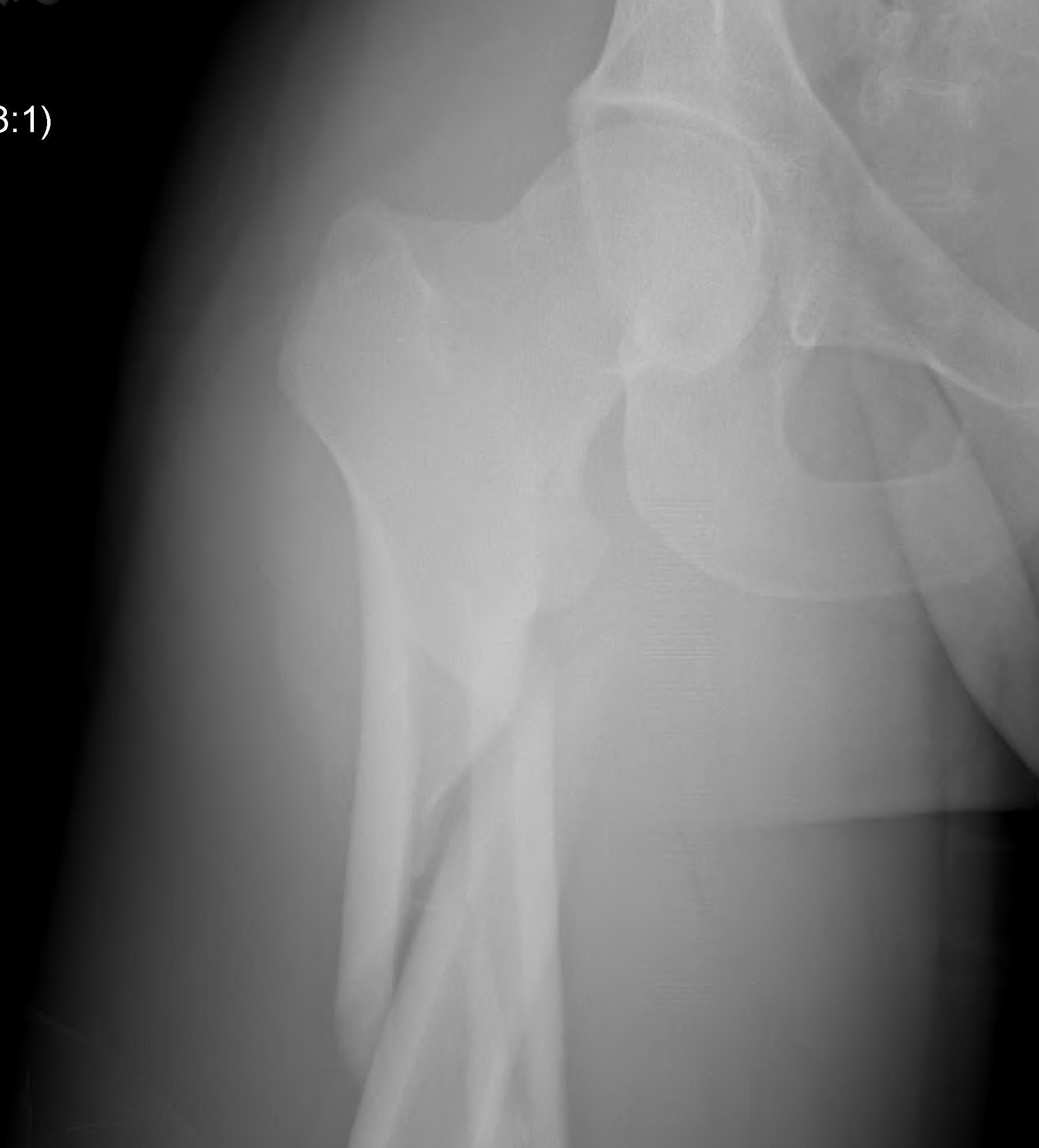
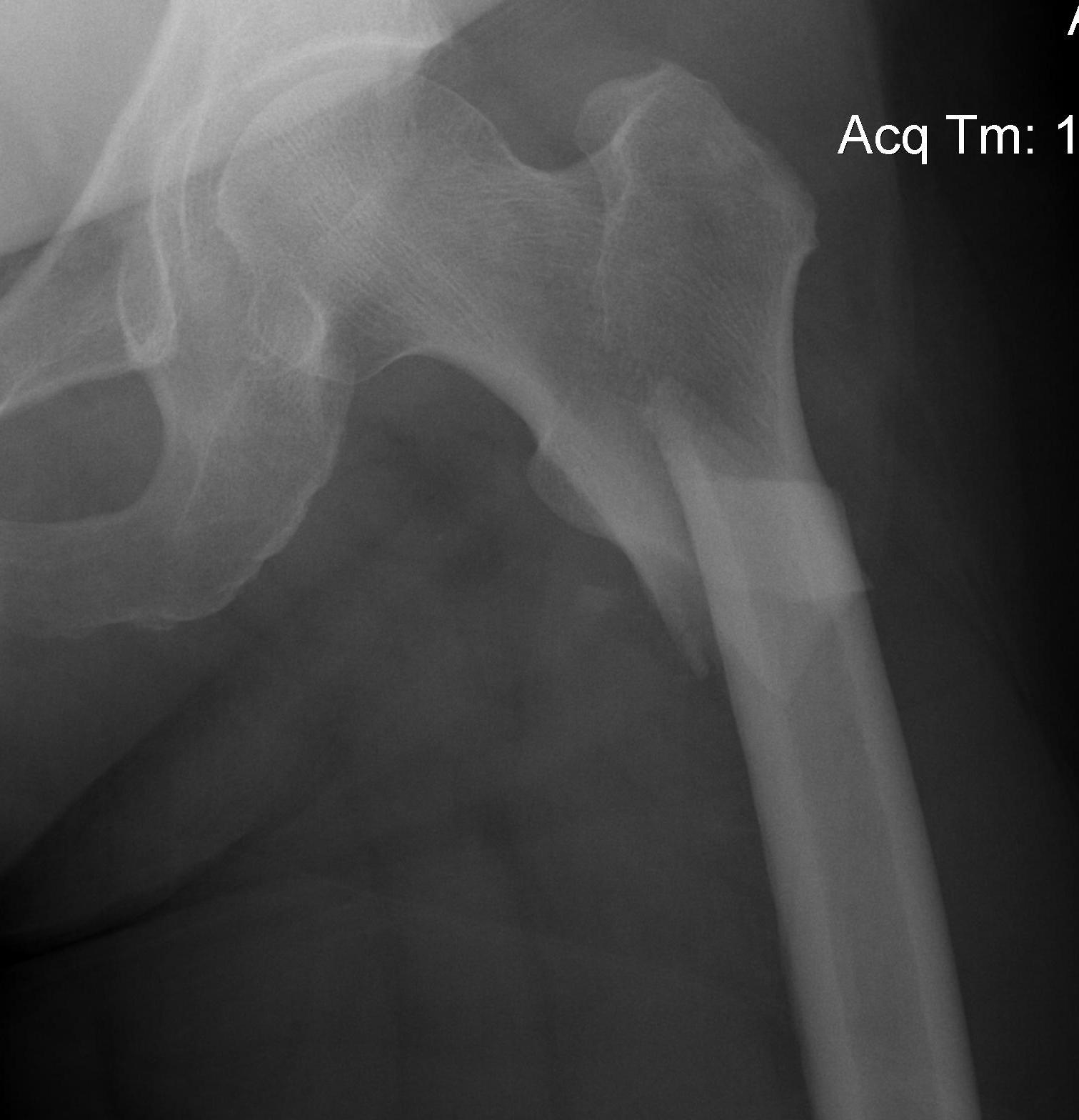
Young patients / high velocity injuries
Old patients / osteoporosis
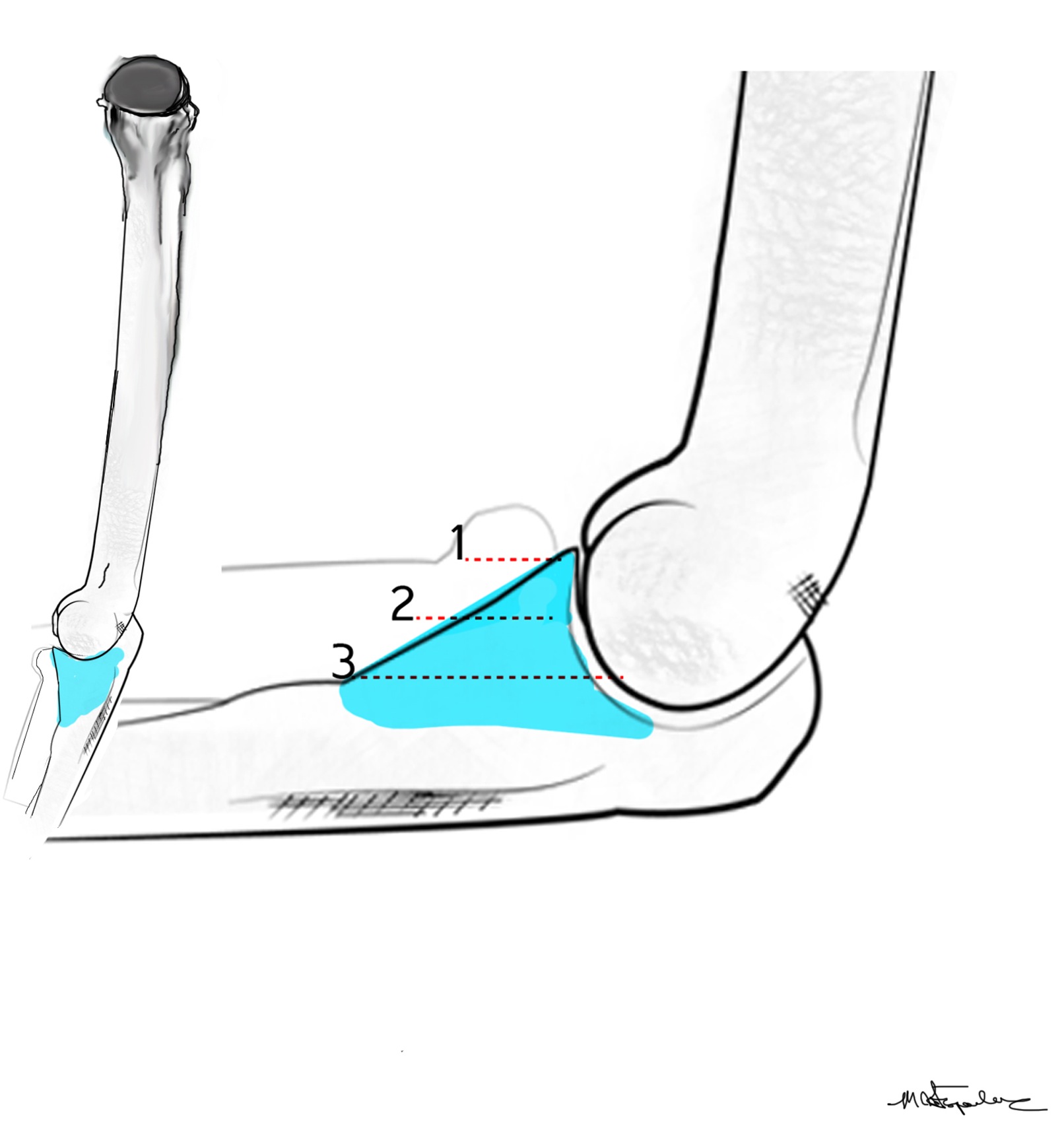
The coronoid is the most important portion of ulno-humeral articulation
Reasons
1. Provides anterior buttress
2. Anterior capsule and brachialis attach to coronoid
2. Anterior band of the MCL attaches to it
- distally and medially on sublime tubercle
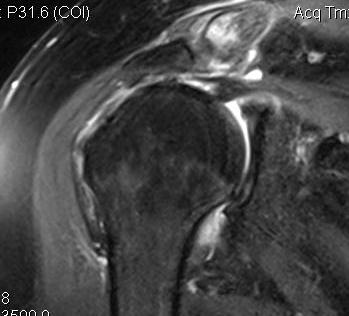
Massive tear
1. > 5cm
- retracted to humerus / glenoid margin
2. At least 2 complete tendons
- lose SS / IS or SS / SC
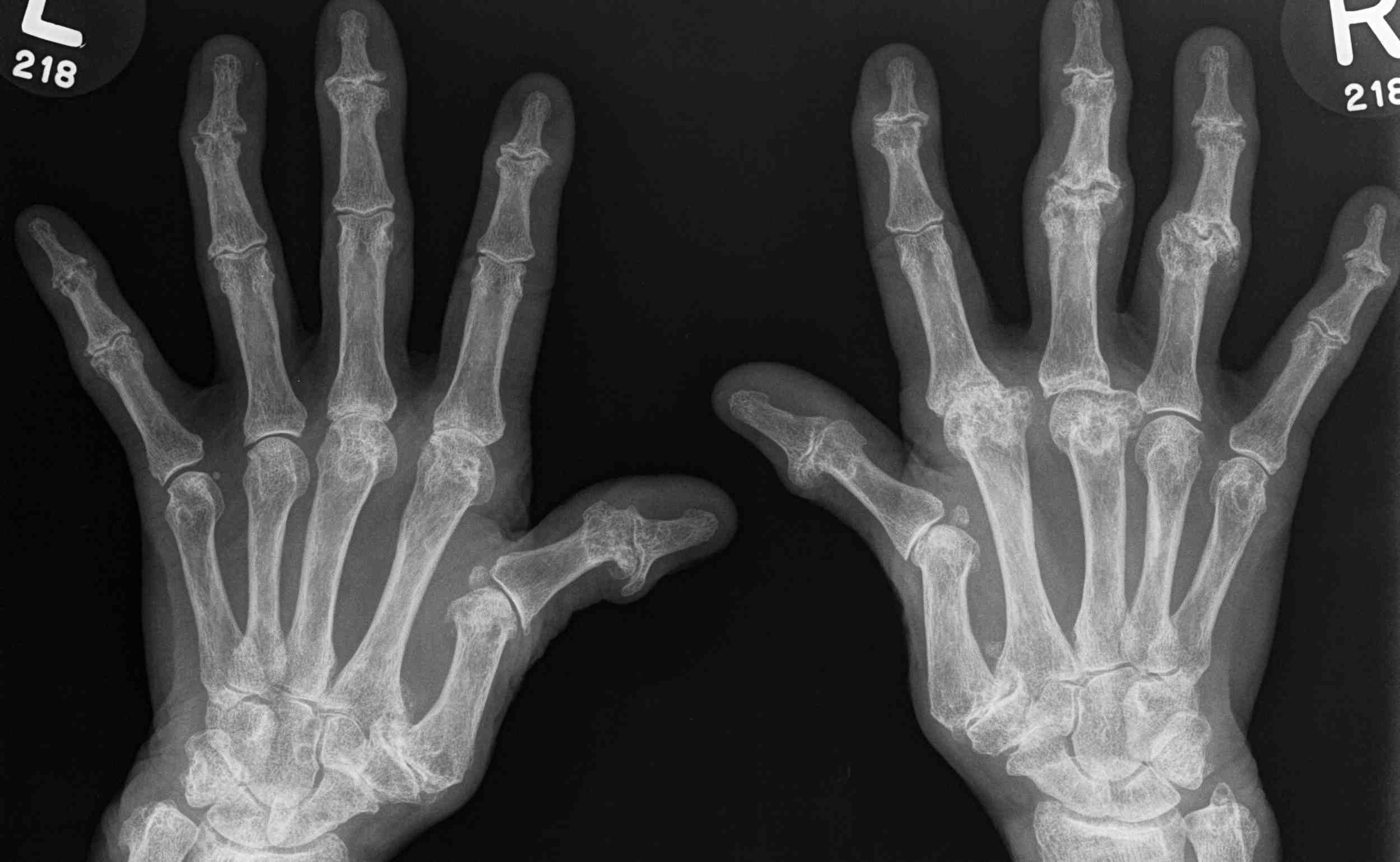
1987 American College of Rheumatology
Need 4/7 (MAX RANS)
1. Morning Stiffness
2. Arthritis of 3 areas > 6/52
3. Xray changes
4. Rh factor
5. Arthritis of Hand > 6/52
6. Nodules
7. Symmetric Arthritis > 6/52
Natural History of ACL deficient knee is variable
- functional instability 15% - 90%
- progression to OA is variable
Depends on level of patient demands / activity
1. Late meniscal injury in ACL deficient knee
15-25%
2. Function
Daniels Am J Sports Med 1994
- 292 ACL defecients knees
Crushing osteochondritis of metatarsal head
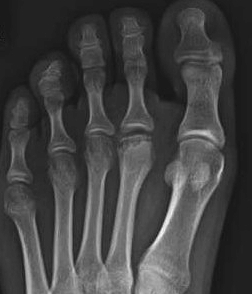
Usually 2nd metatarsal (80%)
- occasionally third
- can occur in any
Age 10-15 years
- peak 15 year old girls
- F:M = 3:1
- occurs during the growth spurt at puberty
Bilateral in 6%
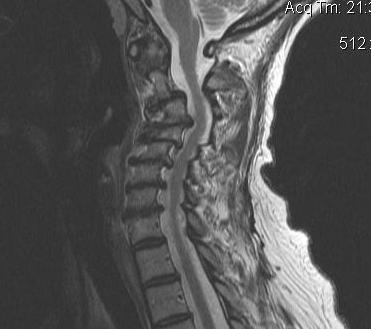
Spinal cord dysfunction
- extrinsic compression of the cord or its vascular supply
- caused by degenerative disease of spine
Most common spinal cord dysfunction in patients > 55 years old
C5/6 commonest level