fracture
Os Peroneum
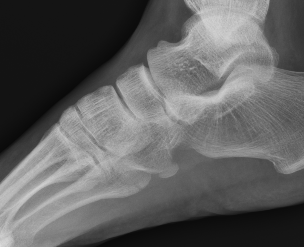
Os peroneum
Location
Posterior process fractures
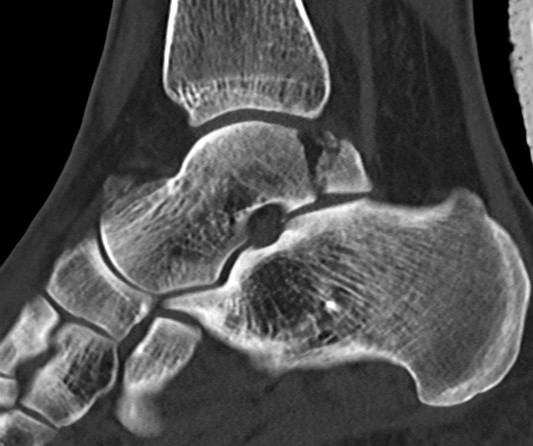
Anatomy
Posterolateral & Posteromedial tubercles
- separated by sulcus for FHL
- lateral larger than medial
PL tubercle
- size variable
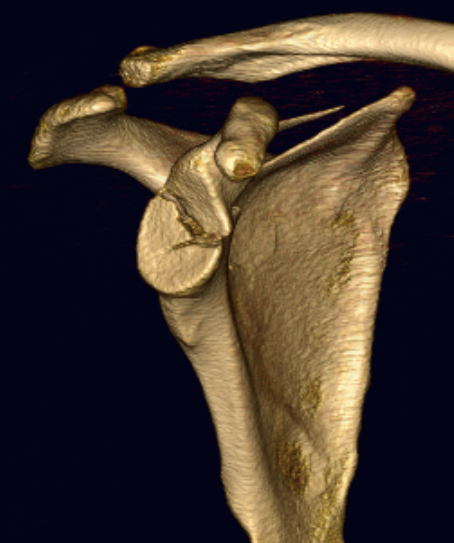
Talar head fractures
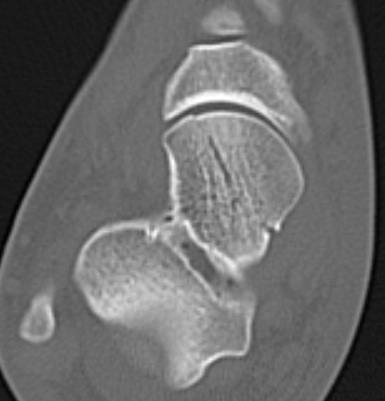
Epidemiology
< 10% of all talus fractures
Rare and often missed
Types
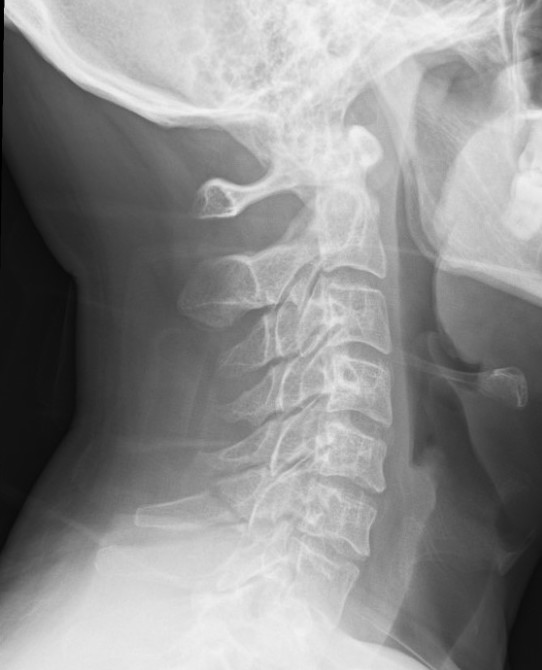
Clay-shovelers
Definition
Spinous process avulsion
- typically C7
- can be seen in thoracic spine
Mechanism
Spinous process avulsion secondary to ligamentum nuchae
Sudden single overload
Complications
Complications
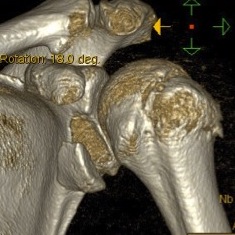
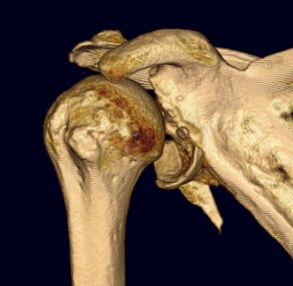
Subscapularis failure
Rotator cuff failure
Instability
Infection
Periprosthetic fracture
Aseptic loosening
Neurological injury
Incidence
Parada et al. J Should Elbow Surg 2021
- 2224 aTSA complication rate 11%, revision rate 5.6%
Background
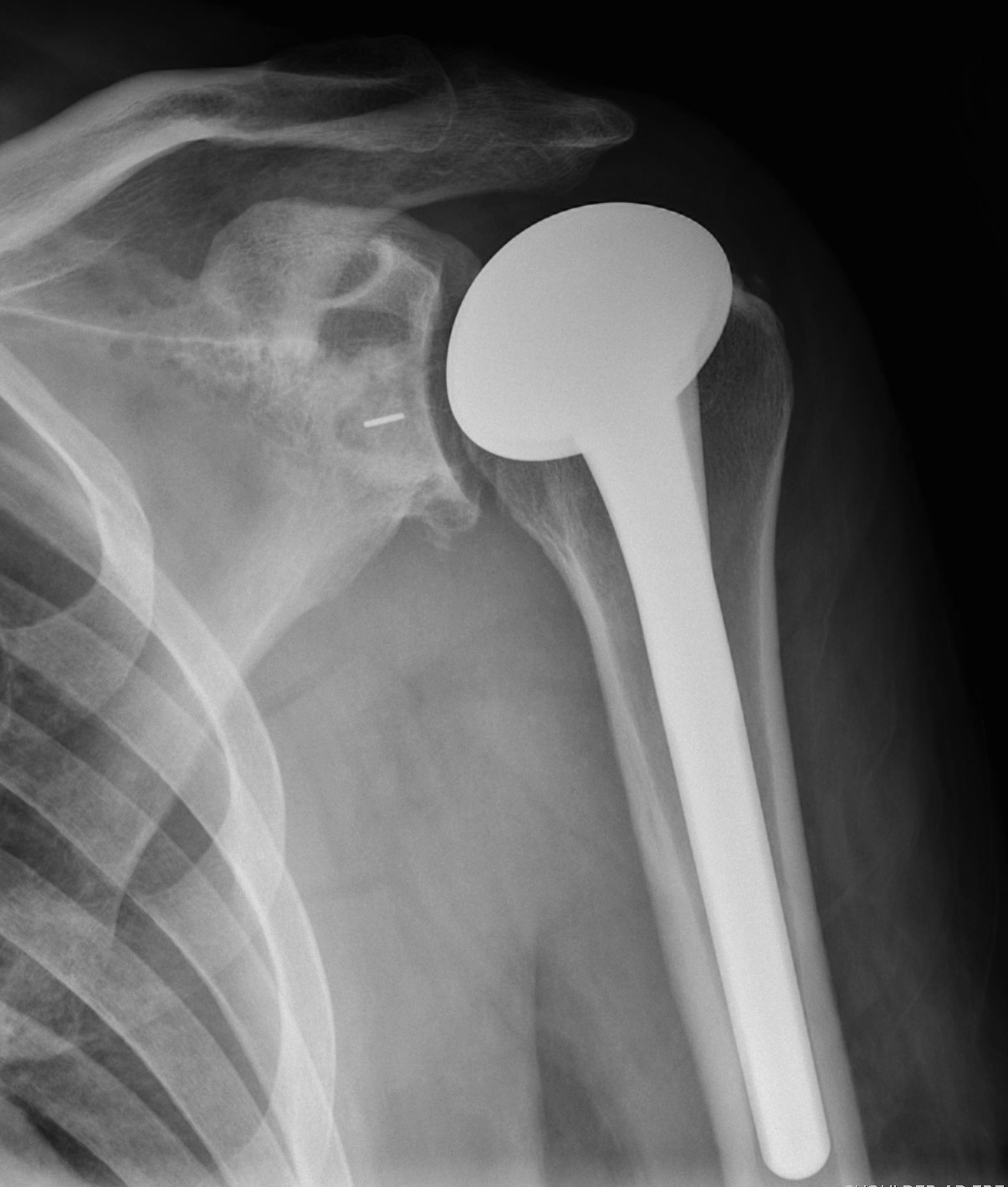
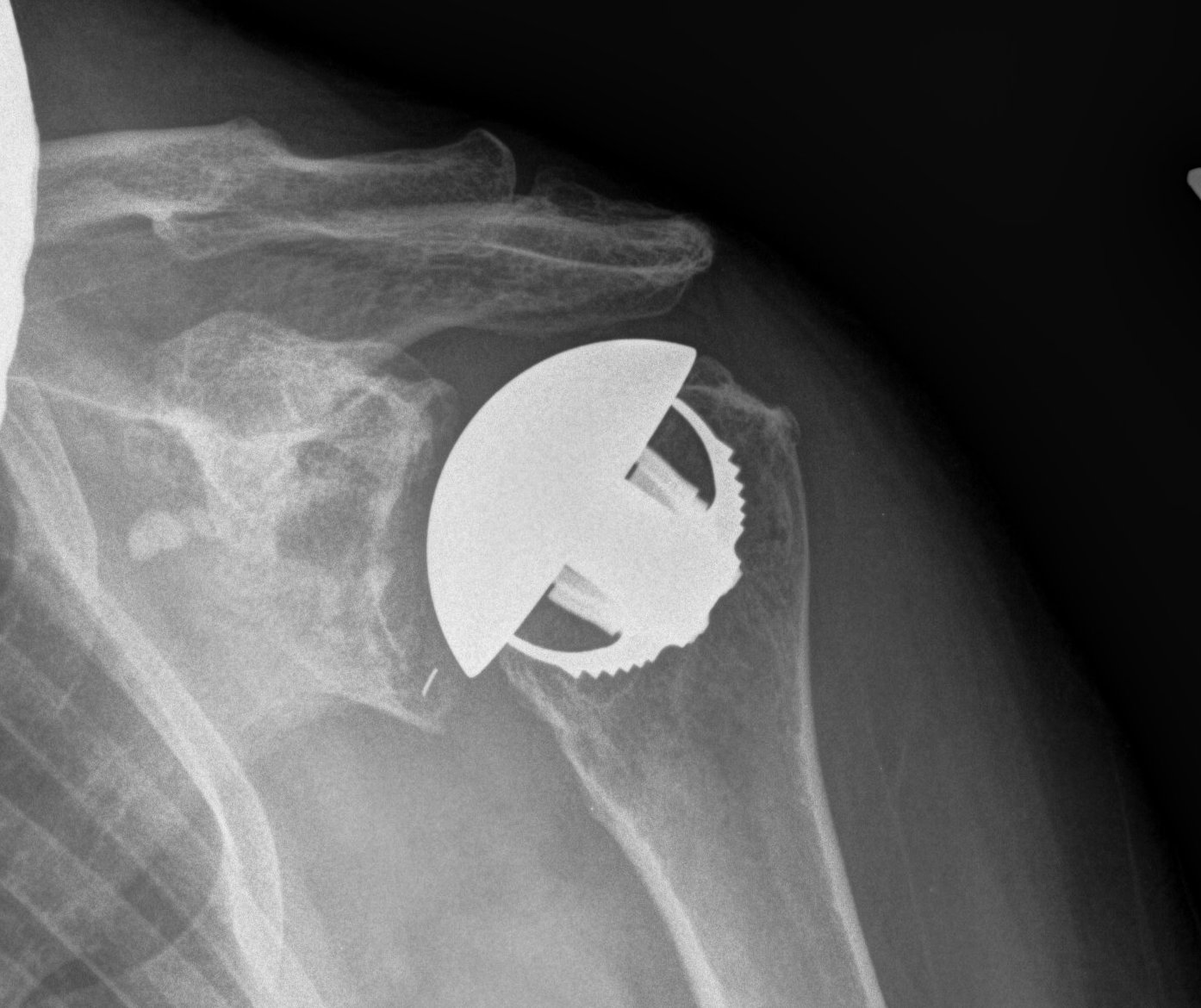
Indications
Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Avascular necrosis