osteotomy
Background
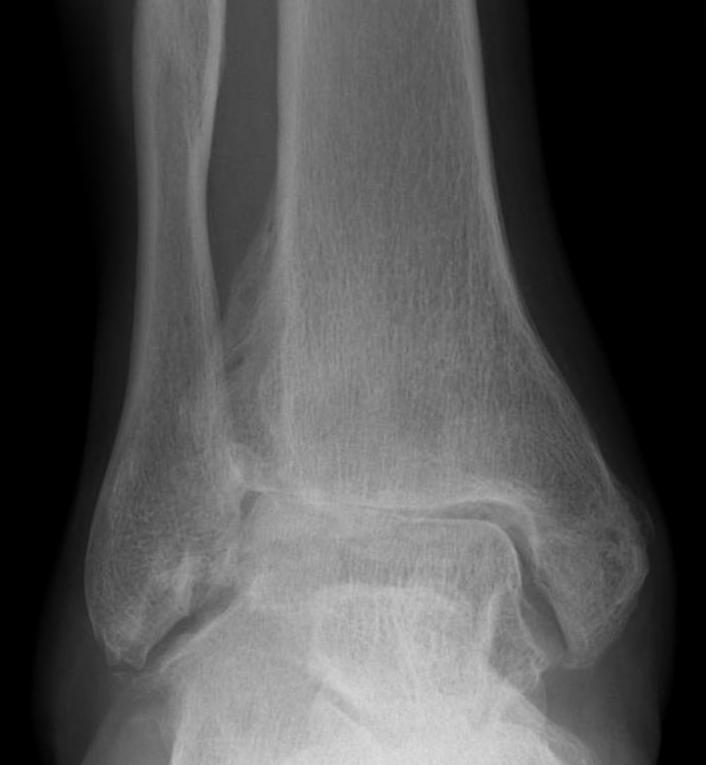
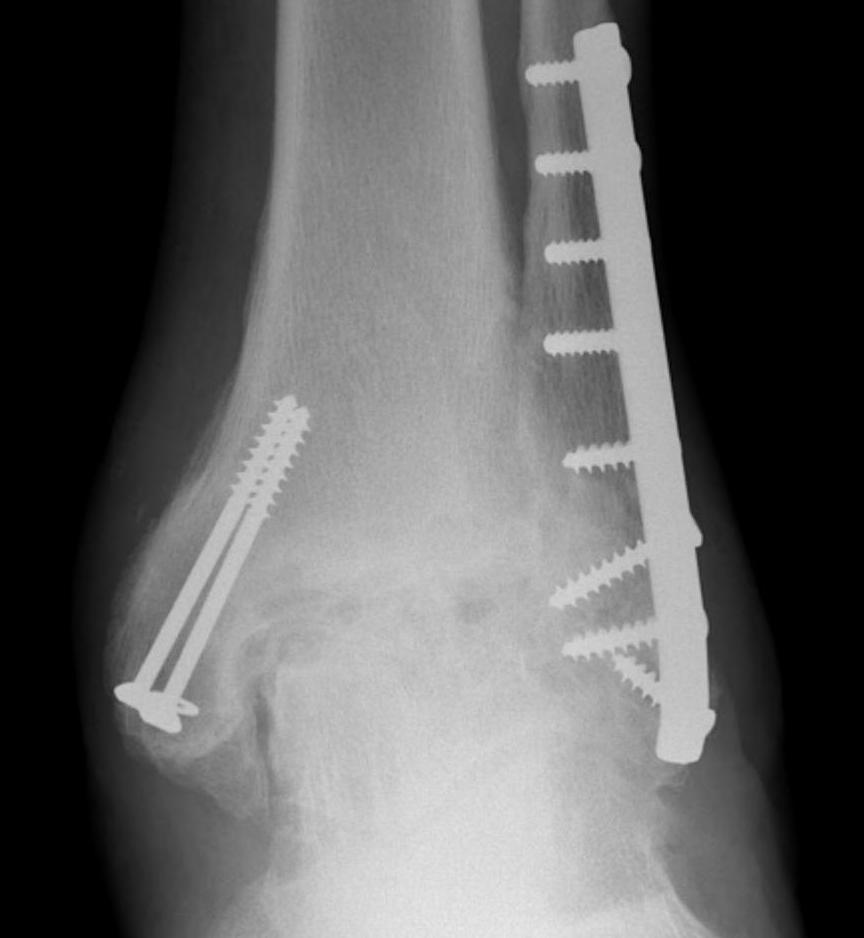
Epidemiology
Much less common than hip and knee OA
Patients tend to be younger
Distal femoral varus osteotomy (DFVO)
Aetiology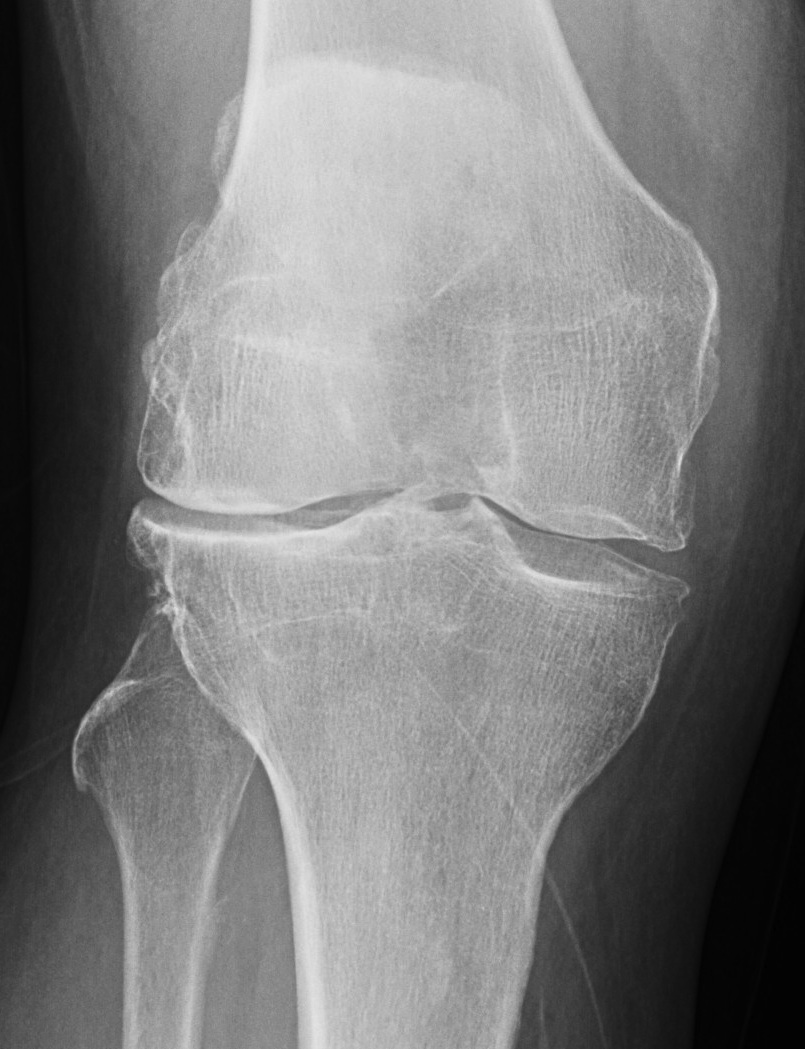
Trauma
RA
Rickets / osteomalacia
Issues
Horizontal joint line important
- < 10° tilt acceptable
> 10o joint line tilt / due to femoral valgus
- continues to overload lateral compartment
Management
Management Summary
Stage 0
Natural history mixed
- depends on size of lesion and diagnosis
- treat if becomes asymptomatic
- may benefit from bisphosphonates
Stage 1 / Normal X-ray, abnormal MRI
Forage: 80% G/E
Bisphosphonates
Stage 2 / Abnormal X-ray with cysts and sclerosis
A: As for Stage I
Extra-articular Deformity
Causes of Deformity
Metabolic Bone Disease
Paget's
Fracture Malunion
Previous Osteotomy
Options
1. Intra-articular correction
2. Simultaneous osteotomy and TKR
3. Staged correction and TKR
1. Intra-articular correction
Indications
Femur
- draw line of mechanical axis of femur
Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy
Definition
Inflammation of achilles tendon; insertional or noninsertional
Spectrum
Tendonitis / Tendonosis / Rupture
Anatomy
Triceps surae
- medial and lateral gastrocnemius
- soleus
- surrounded by paratenon which allows gliding and supplies nutrition
Inserts middle 1/3 calcaneal tuberosity
- 2 x 2 cm area
- 90o rotation distally
Retrocalcaneal bursa (x2)
Freiberg's
Definition
Crushing osteochondritis of metatarsal head
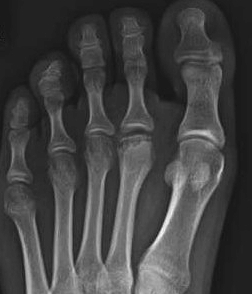
Epidemiology
Usually 2nd metatarsal (80%)
- occasionally third
- can occur in any
Age 10-15 years
- peak 15 year old girls
- F:M = 3:1
- occurs during the growth spurt at puberty
Bilateral in 6%
Aetiology
Metatarsalgia
Definition
Pain in the forefoot in the region of the MT heads
3 groups
1. Localised
Morton's neuroma
Freiberg's
Stress fracture
Infection / tumour
Plantar Keratosis
Plantar Wart
2. Systemic disease
RA
