Background
Aim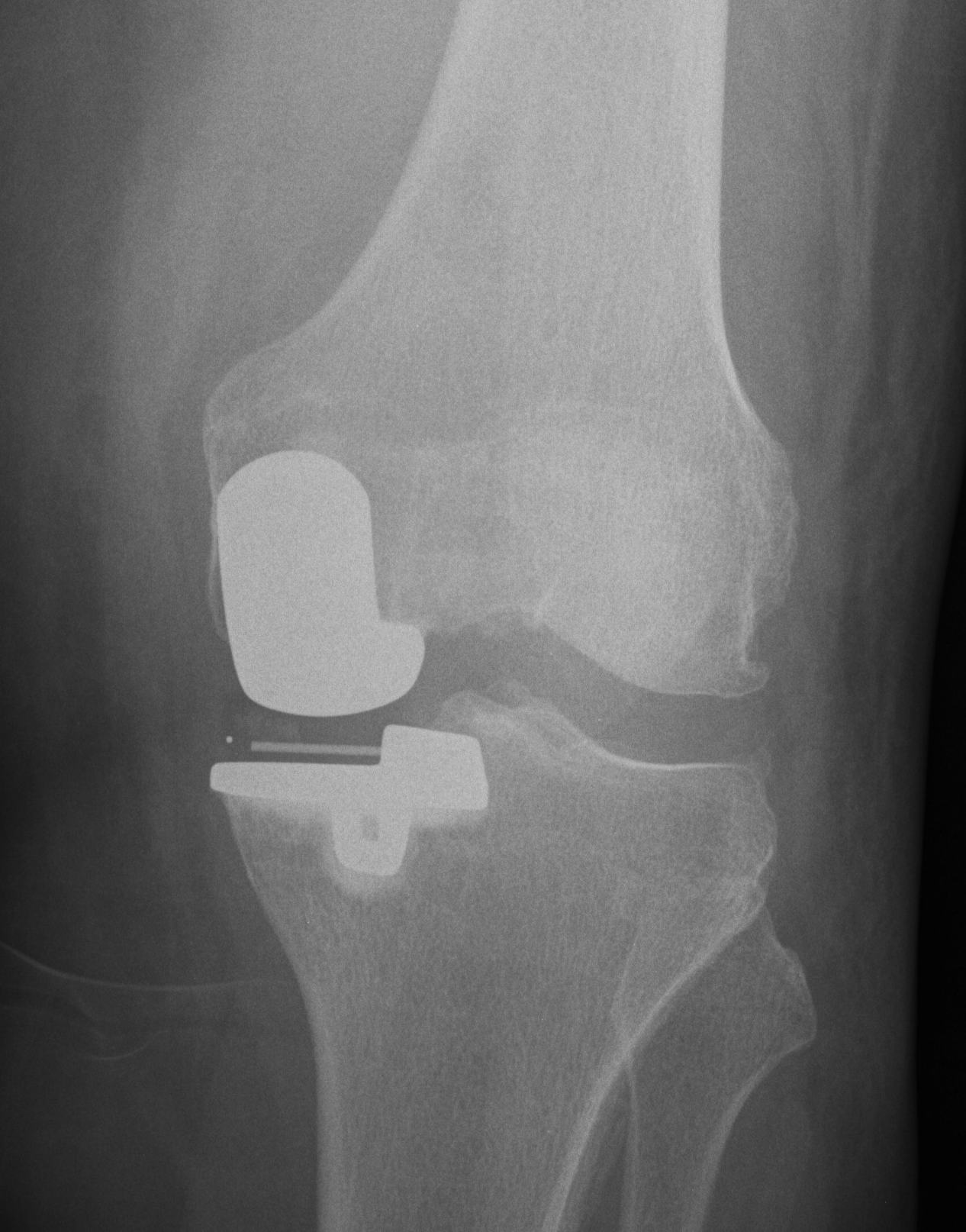
UKA is intended to be load sharing
- correct to neutral or slight varus
HTO is a load-shifting / load-sparing procedure
- over correct into valgus
UKA v TKR
Advantages UKA
1. Rapid rehabilation

UKA is intended to be load sharing
- correct to neutral or slight varus
HTO is a load-shifting / load-sparing procedure
- over correct into valgus
Advantages UKA
1. Rapid rehabilation
Position
- patient supine on radiolucent table
- place ECG lead and artery clip over centre of femoral head
- useful to put II ipsilateral to leg, and place knee on cassette
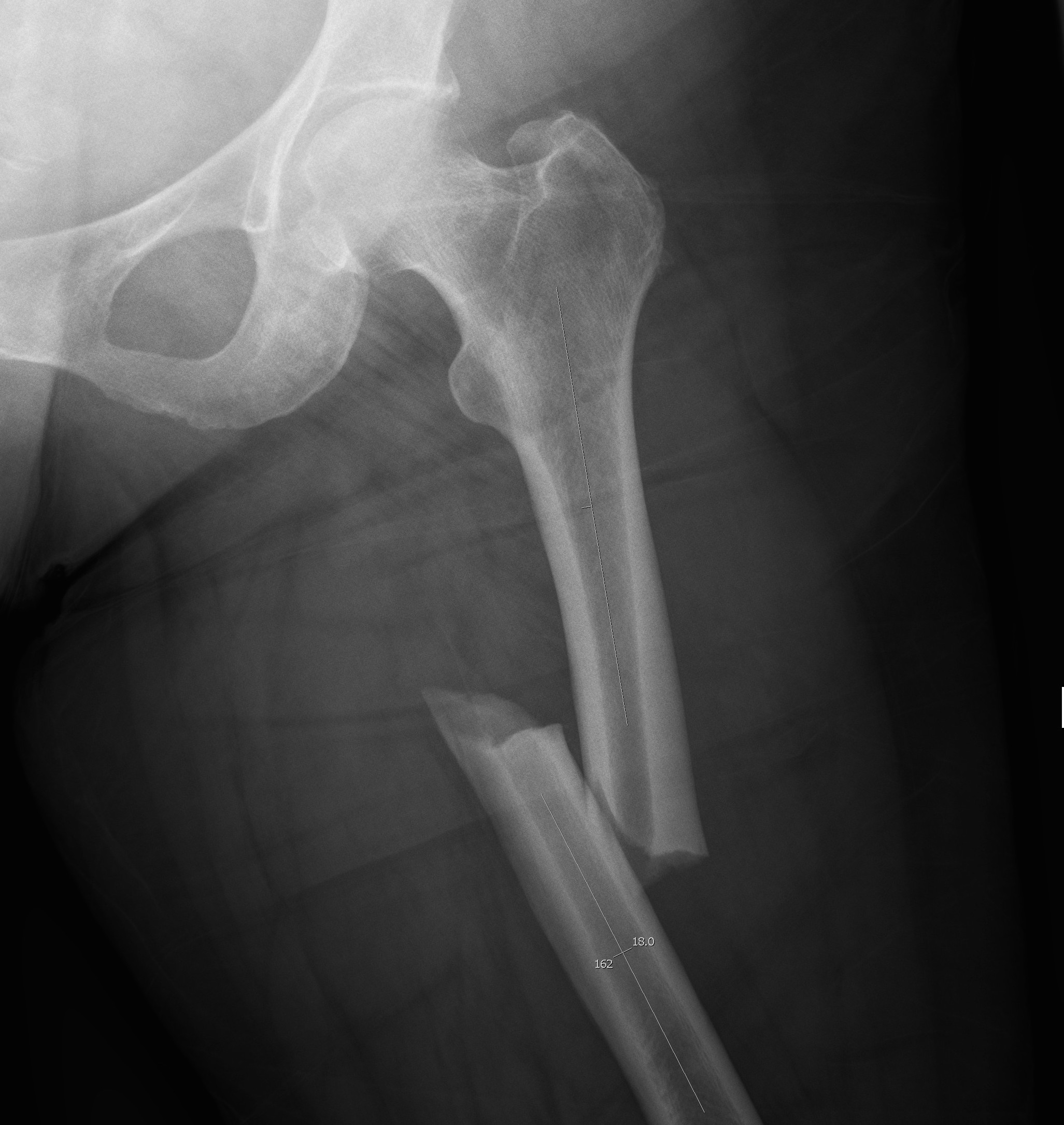
Usually young patients
- 15 - 40
15% compound
High velocity injury
- MBA
- MVA
- pedestrian v car
- fall from height
EMST principles
- need for transfusion not uncommon
Resuscitation
EMST
Neurovascular assessment
Investigations - exclude Pipkin, NOF
Emergent reduction / skeletal stabilisation
Assess stability
Re-evaluate sciatic nerve
Indications
- displaced acetabular fracture
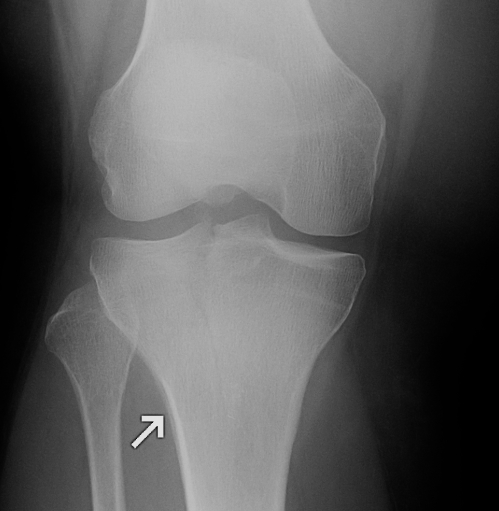
I. Lateral Spilt
- seen in young patient
- lateral meniscus can be incarcerated in fracture
II. Lateral Split Depression
- often seen in young patients with high energy injuries
- vary in severity
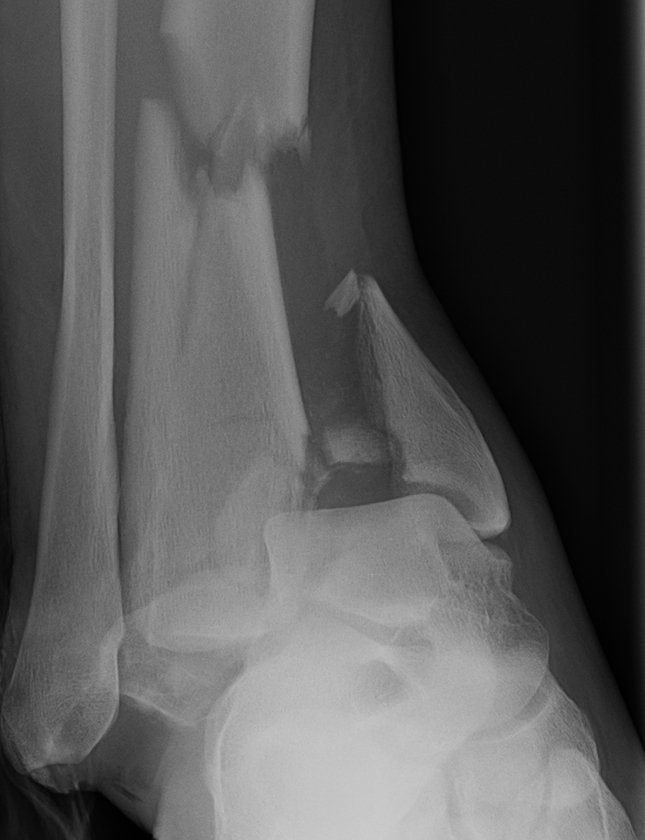
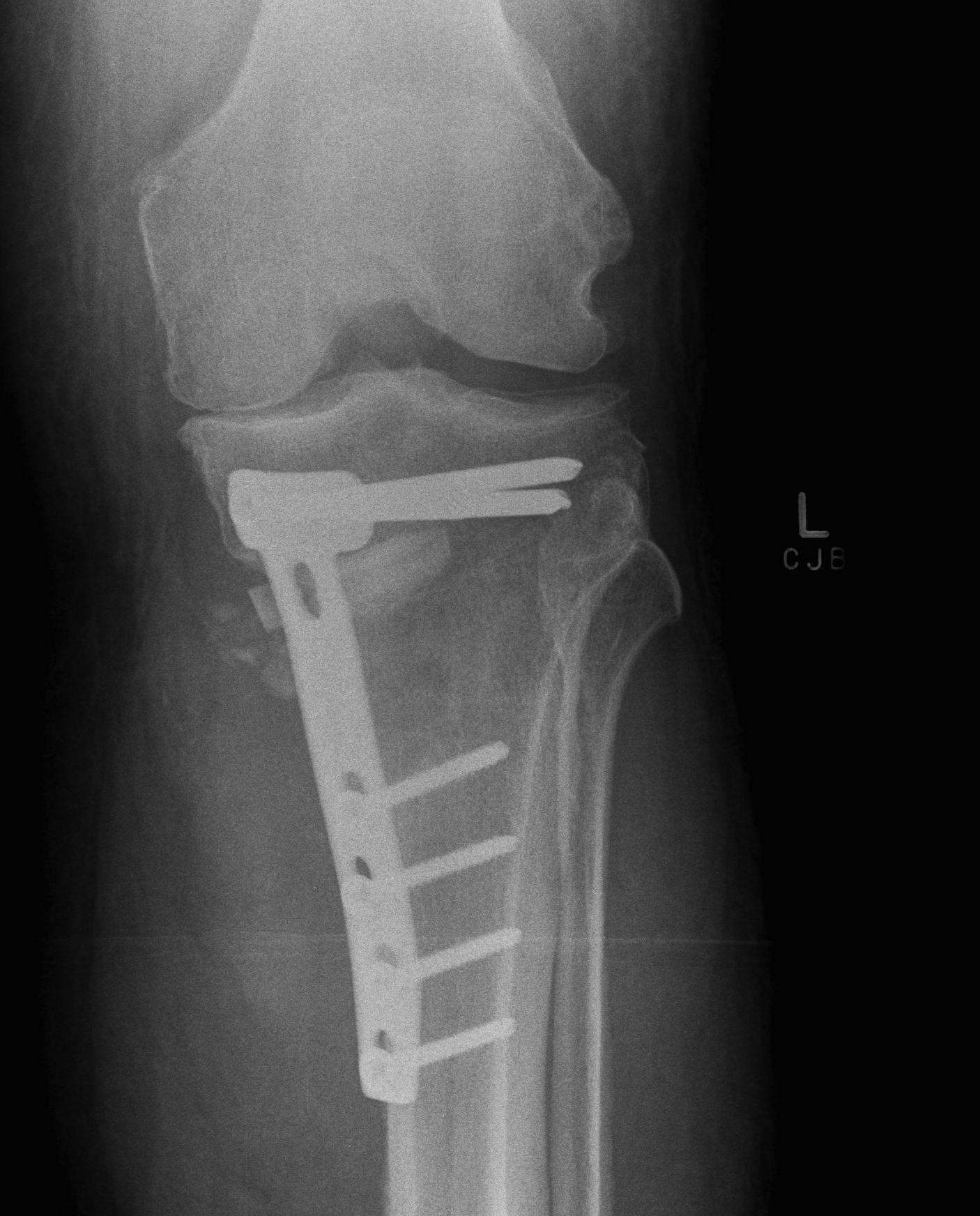
Complex / high energy injuries
Management of soft tissues critical
- restore length with external fixation
- await for swelling to reduce
Restoration of alignment & joint surface imperative
Outcome guarded
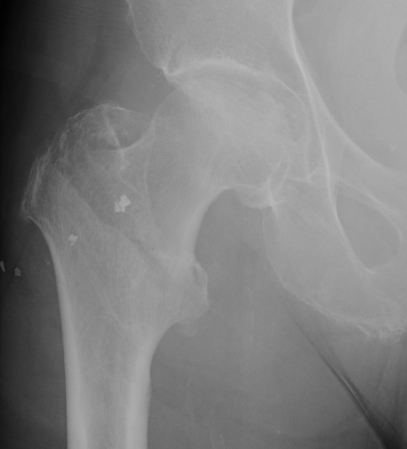
Fracture which extends between the trochanters of the proximal femur
- lower limit is inferior border of lesser tuberosity
Extra capsular / well vascularized
The key to stability is the posteromedial cortex
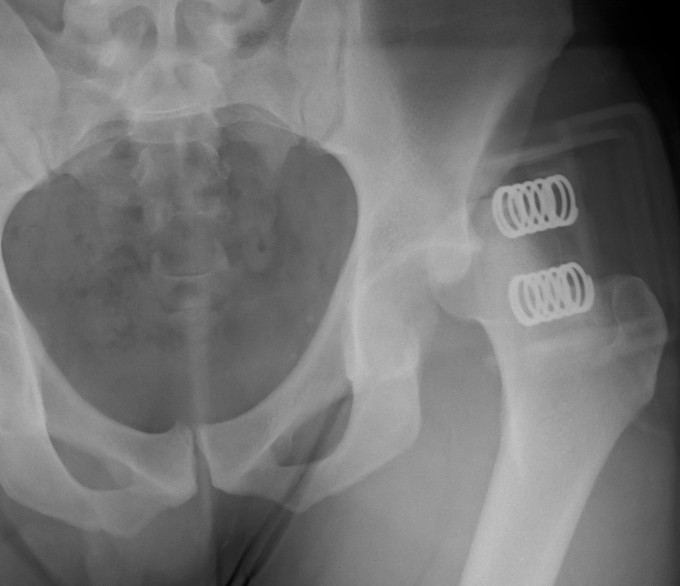
Young men
Posterior / Anterior 9:1
High velocity injury
- head direction at impact decides direction of dislocation
Anterior Dislocation
Externally rotated & abducted leg
- flexion = inferior dislocation
Viewing portal
- 1cm lateral to patella tendon
- 1cm above joint line
- 1 cm below inferior pole patella
Problems
- too medial, in fat pad
- too high, limitation by patella, difficult to see posterior horns
- too low, damage anterior horn meniscus
Limitations
- PCL
- anterior horn LM
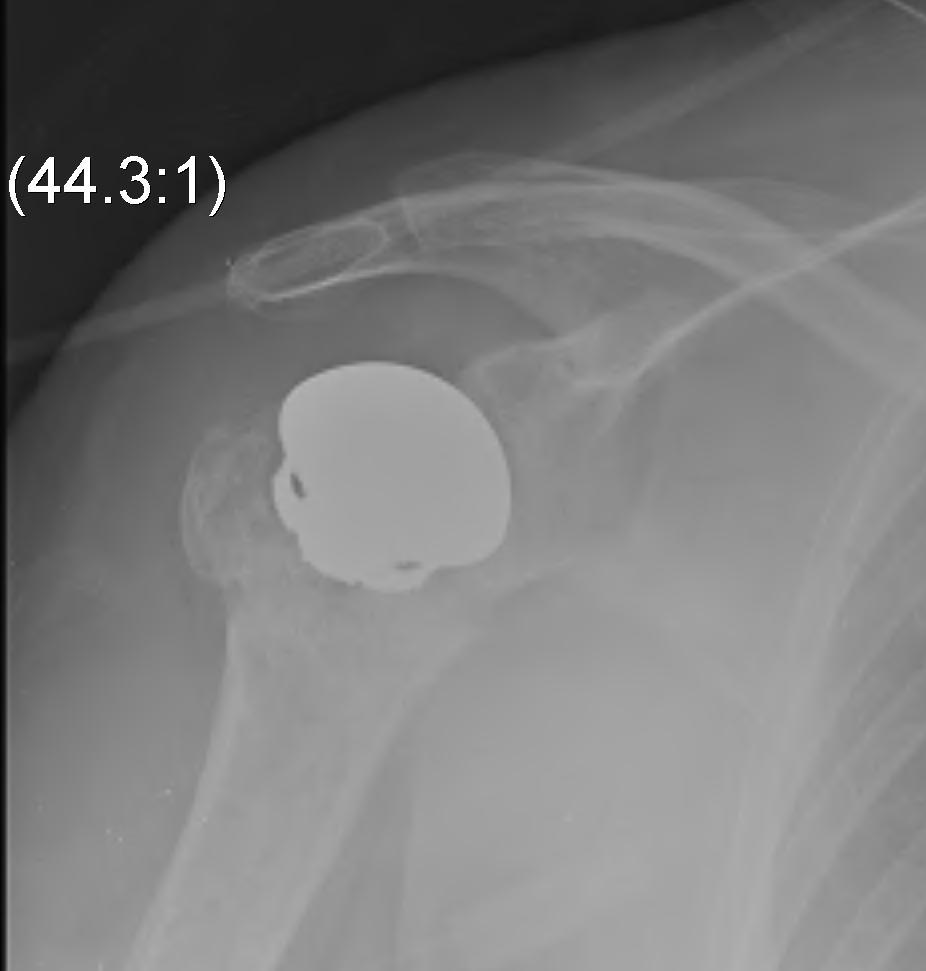
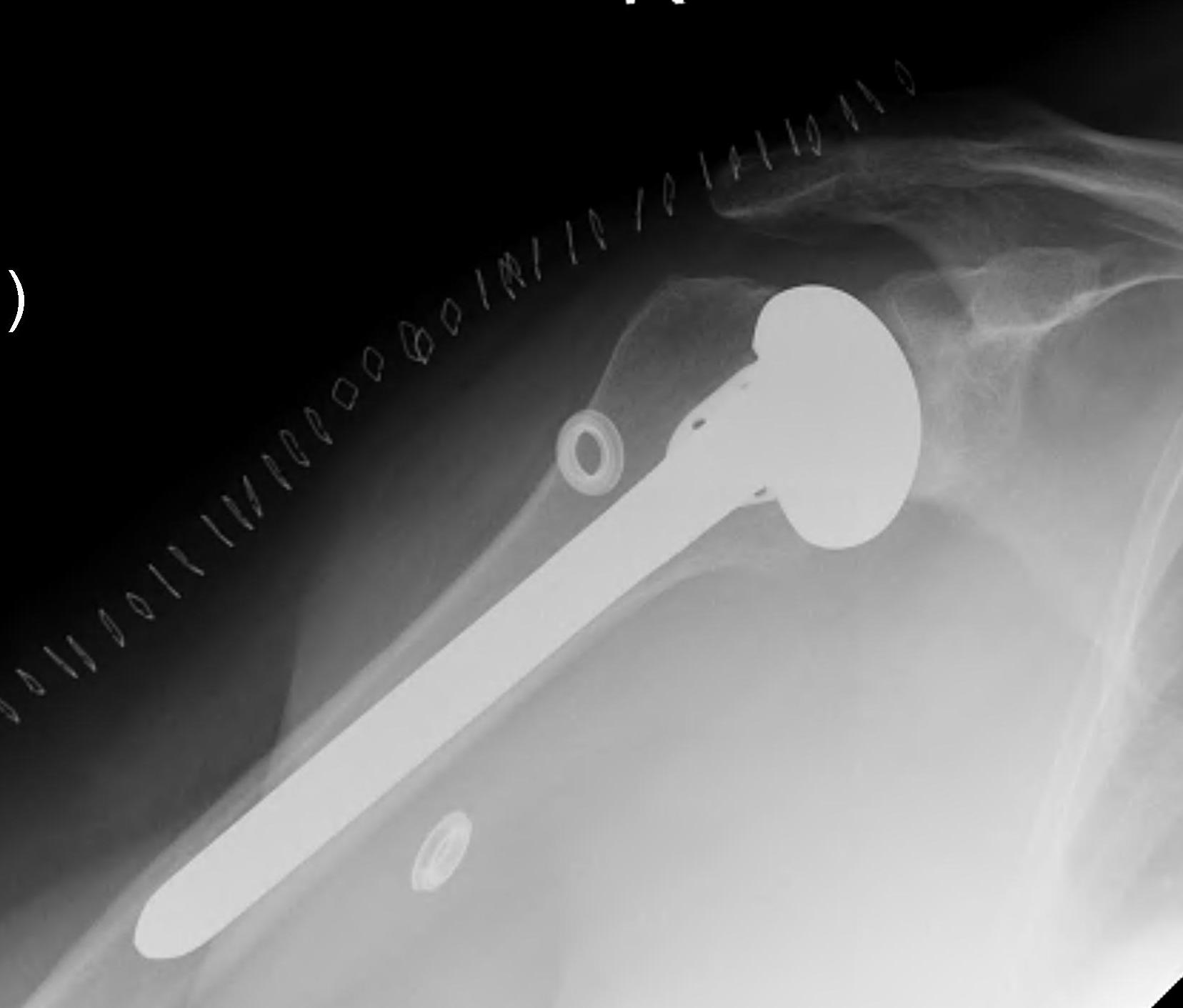
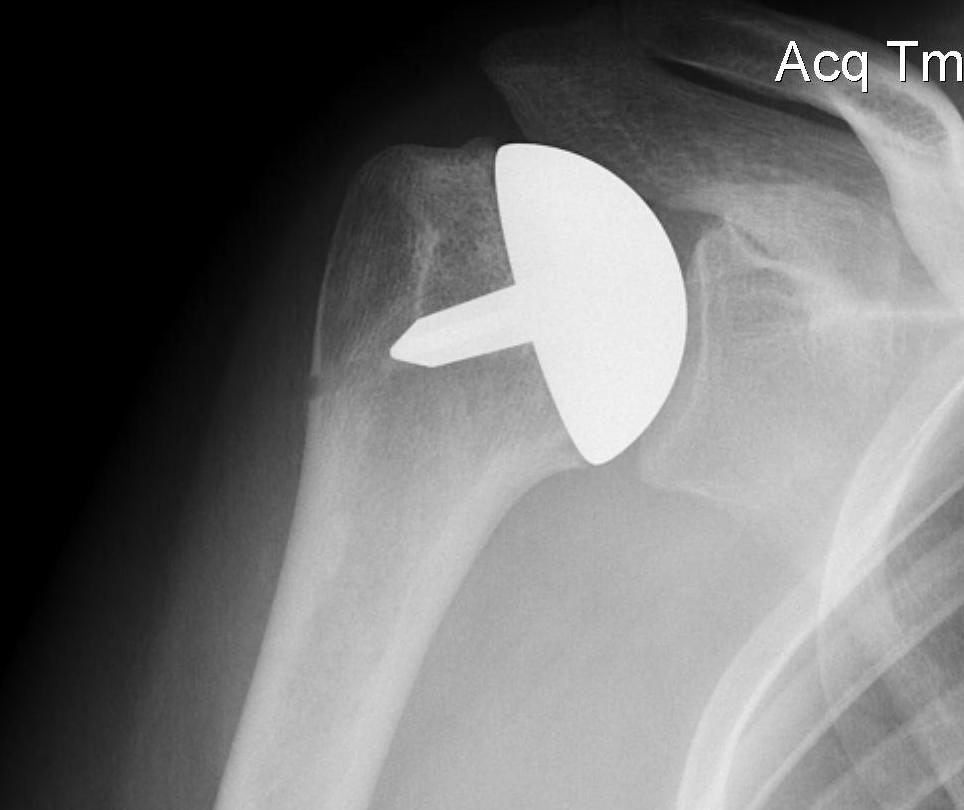
Fewer complications than TSR
Simpler procedure