injury
Deltoid ligament injury
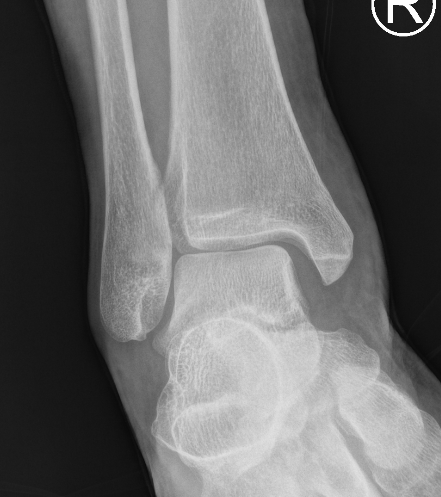
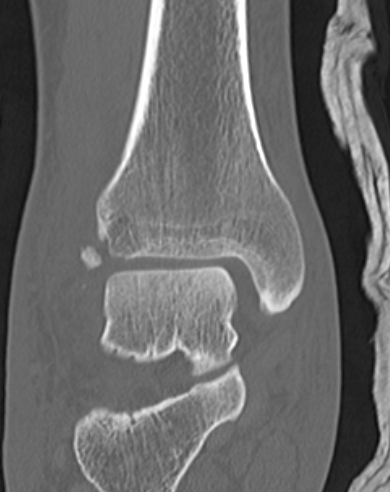
Etiology
Ankle sprain
- eversion / external rotation
Ankle fractures
Atlas / C1 Fractures
3 types
1. Posterior Arch
Mechanism
- axial compression with hyperextension
Associations
- 50% incidence other C1/2 fracture
- i.e. ondontoid fracture
Management
- stable
- soft / philadelphia collar
2. Isolated lateral mass fracture
Mechanism
- asymmetrical axial compression / lateral bend
Injury
Classification Leffert "OCRO"
I Open
II Closed
A Supraclavicular
- Preganglionic / Avulsion of Roots
- Postganglionic / Rupture of Trunks
B Infraclavicular
- cords & branches
C. Post anaesthetic
III Radiation / Other
Tumour
TFCC tears
Definition
Present with pain but not instability
Types
Traumatic
Degenerative
Different treatment algorithms for each
History
Ulna side wrist pain
- may be worse with rotation
- opening doors and jars
History of trauma
Examination
Local tenderness DRUJ
Ulna collateral ligament injury
Aetiology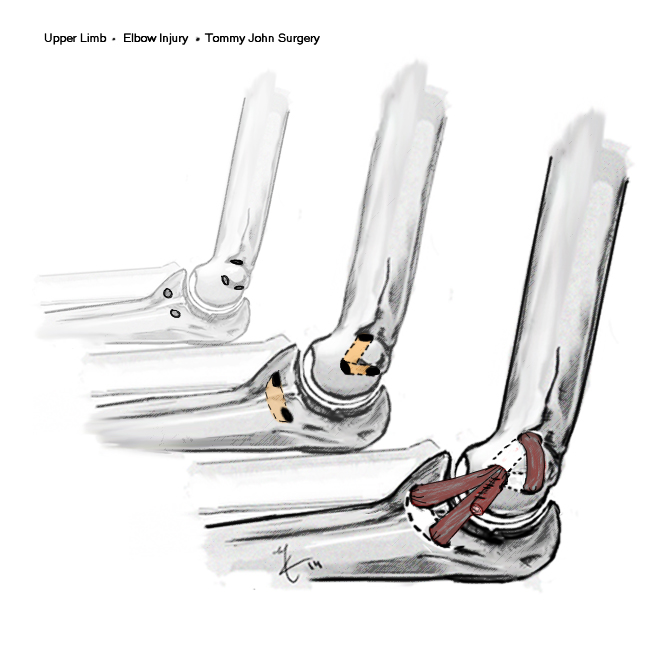
Throwing injury
- seen in the throwing athlete
- repetitive microtrauma / valgus stress
- develop laxity
History
Initially
- lose velocity / accuracy
Develop medial pain
40% ulna nerve symptoms
Scapholunate Ligament Injury / DISI
Definition
Dorsal Intercalated Segmental Instability / CID
Anatomy
Scapholunate joint
- C shaped
- 2-3 mm thick dorsally with transverse fibres
- thin palmar
Dorsal extrinsic ligaments
- V shaped, onto trapezium
Axillary Nerve Lesions
Anatomy
Terminal branch of the posterior cord
- lateral to radial nerve
- behind axillary artery
- runs over inferolateral border of SSC
- enters quadrangular space
Quadrangular space
- SSC superiorly anterior
- T major inferior
- T minor superiorly posterior
- long head triceps and humerus
Divides into anterior and posterior branches
Acute PLC Background
Anatomy
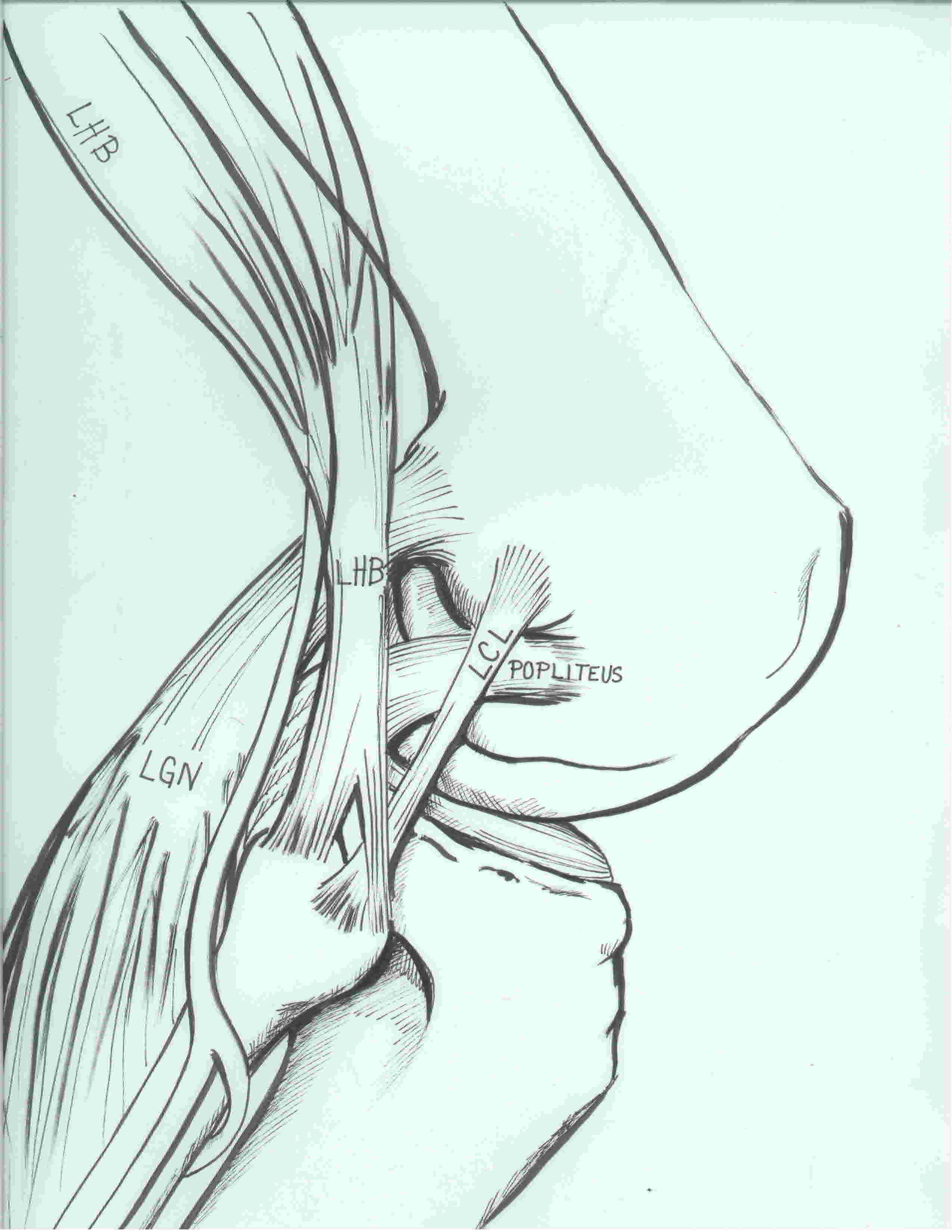
3 primary stabilizers (plus posterolateral capsule)
LCL / Popliteus / Popliteofibular ligament
Laprade et al. AJSM 2003
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14623649/
1. Lateral collateral ligament
Femoral attachment