open
Greater trochanter pain syndrome
Greater trochanteric pain syndrome
Definition
Chronic lateral trochanteric pain
- abductor tendon tendonitis
- trochanteric bursitis
Epidemiology
Women 40 - 60 years old
Mechanism
? repetitive friction of iliotibial tract over GT
Symptoms
Pain over upper lateral thigh with activity
- often related to hip flexion
TFCC tears
Definition
Present with pain but not instability
Types
Traumatic
Degenerative
Different treatment algorithms for each
History
Ulna side wrist pain
- may be worse with rotation
- opening doors and jars
History of trauma
Examination
Local tenderness DRUJ
PVNS
Definition
Pigmented Villo-Nodular Synovitis
- benign inflammatory process that arises in synovial tissues
- contains significant amounts of hemosiderin
Epidemiology
Age: 20 - 50
Sex: M > F
Types
A. Diffuse
- throughout joint synovium
- more difficult to treat / excise fully
Latarjet / Bristow
Bristow
Concept
Non-anatomical bony block
- transfer of coracoid process through subscapularis
- dynamic anteroinferior musculotendinous sling
- provides subscapularis tenodesis
- preventing lower portion from displacing proximally as arm abducted
- when shoulder in vulnerable position abduction and ER
Subtalar and Triple Arthodesis
Biomechanics
Able to achieve relatively high level of function after STJ fusion
- previously believed that isolated STJ fusion should not be performed
- believed that triple arthrodesis was operation of choice for hindfoot
- STJ fusion has superior result with less stress on AJ
Average loss of DF 30% / PF 10%
Position of hindfoot determines flexibility of transverse tarsal (CCJ & TNJ) joints
- imperative that fusion be positioned in ~ 5o valgus
Full thickness tears
Surgical Options
1. Open antero-lateral approach
Large / Massive Cuff Tear
2. Deltopectoral approach
Large Subscapularis tear
3. Arthroscopic Assisted Mini-open
Indication
- Small / Moderate Cuff Tear < 3cm
- no retraction
Technique
- arthroscopic SAD
De Quervain syndrome
Definition
Stenosing tenosynovitis of the first dorsal compartment of wrist
Epidemiology
Most are middle aged women
Aetiology
Repetitive thumb movements
- abduction & extension
- combined with RD & UD movements
Any mechanical irritation
- foreign body
- prominent bony surface
- restricted fascial compartment
Sternoclavicular joint
Epidemiology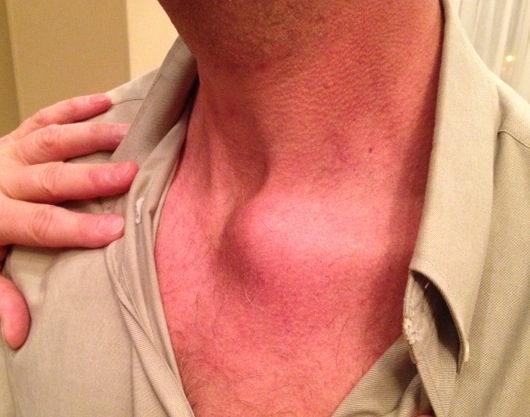
Extremely uncommon
Stability provided by joint capsule /costoclavicular & interclavicular ligaments
Recurrent instability uncommon
Many apparent dislocations in adolescents may be growth plate injuries
-will remodel without treatment
If OA from chronic dislocation may resect SCJ
