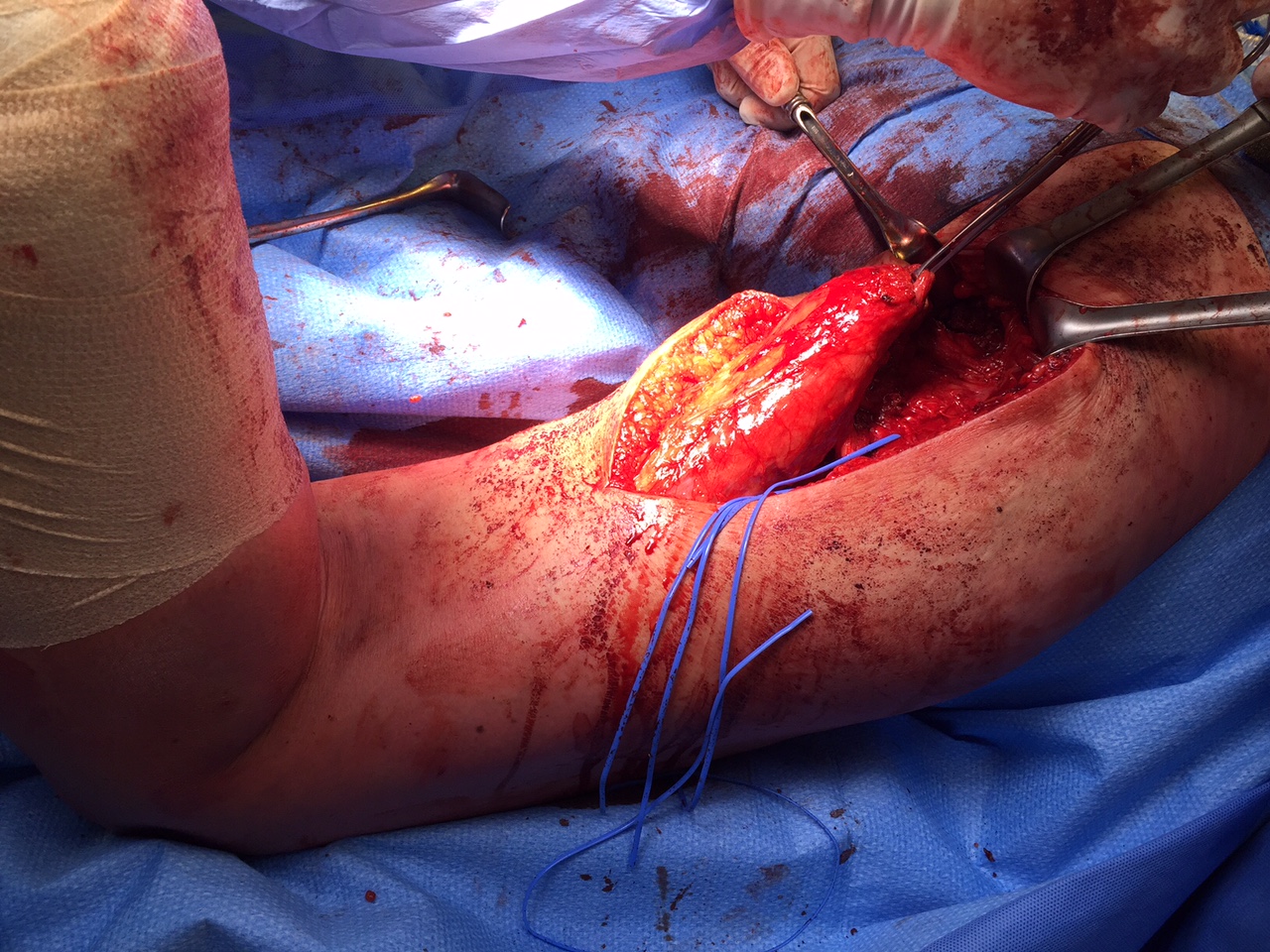
Plantar fascia rupture
Etiology
Plantar fasciitis / cortisone injections
Athletes - soccer players, NFL
Mosca et al Foot Ankle Spec 2022
- systematic review of 155 feet
- 8% spontaneous
- 89% associated with plantar fasciitis
- 84% associated with cortisone injection
History
Sudden onset acute during athletics
Examination
Focal tenderness