Postoperative discitis
Symptoms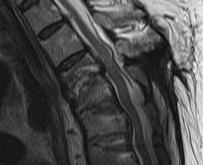
Period of pain relief after disc surgery
- followed by increasing back pain & occasional leg pain
Pain may be disproportionate to physical findings
Low grade fever common
SLR & femoral stretch tests elicit pain in some cases
Bloods