Definition
Arrest in development of normal bone with weak fibro-osseous bone
Pathophysiology
Caused by somatic activating mutations in GNAS
Types
Spectrum of disease
- Monostotic (75%) - single bone affected
- Polyostotic (25%) - multiple bones affected
- McCune-Albright Syndrome
McCune - Albright Syndrome
Triad
1. Fibrous Dysplasia
2. Cafe-au-Lait Spots
- irregular "Coast of Maine"
3. Hyperfunctioning endocrinopathies
- precocious puberty
- hyperthyroidism
- growth hormone excess
Malignant transformation
Osteosarcoma / fibrosarcoma / MFH / Chondrosarcoma
Increased risk in polyostotic disease / McCune-Albright Syndrome
- 15 / 542 (3%) cases of FD had malignant transformation
Inheritance
Usually non genetic inheritance
Natural history
Usually diagnosed in children and adolescents
Remains relatively unchanged throughout life
Clinical
Bone pain
Long bones
- pathological fracture
- deformity / bowing
- limp
- leg length discrepancy
Craniofacial involvment
- slow growing painless masses
- cosmetic deformity / dental problems / vision and hearing loss
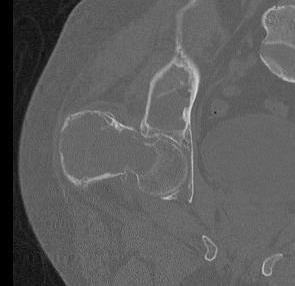
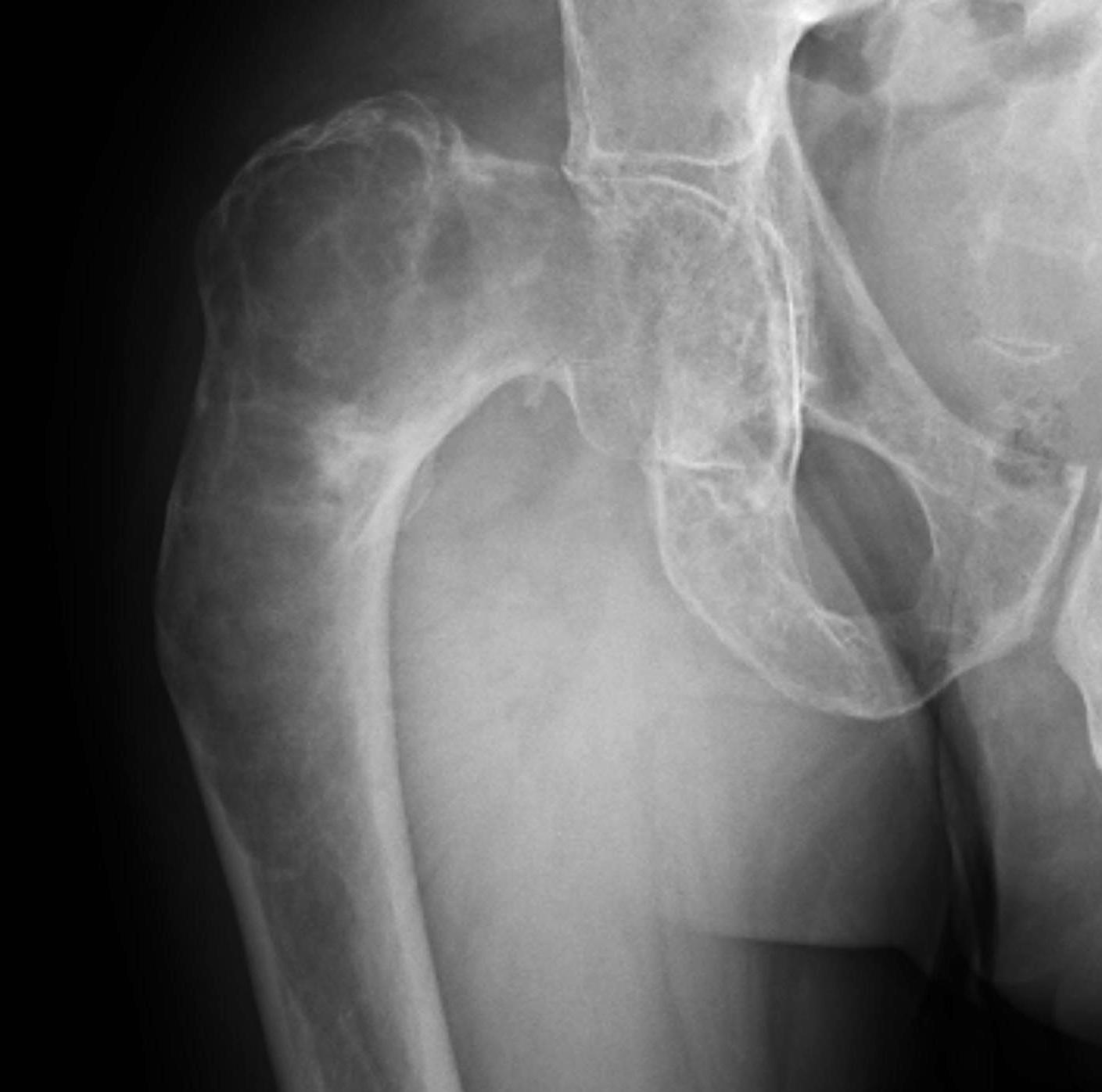
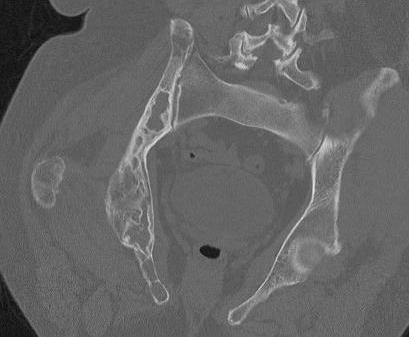
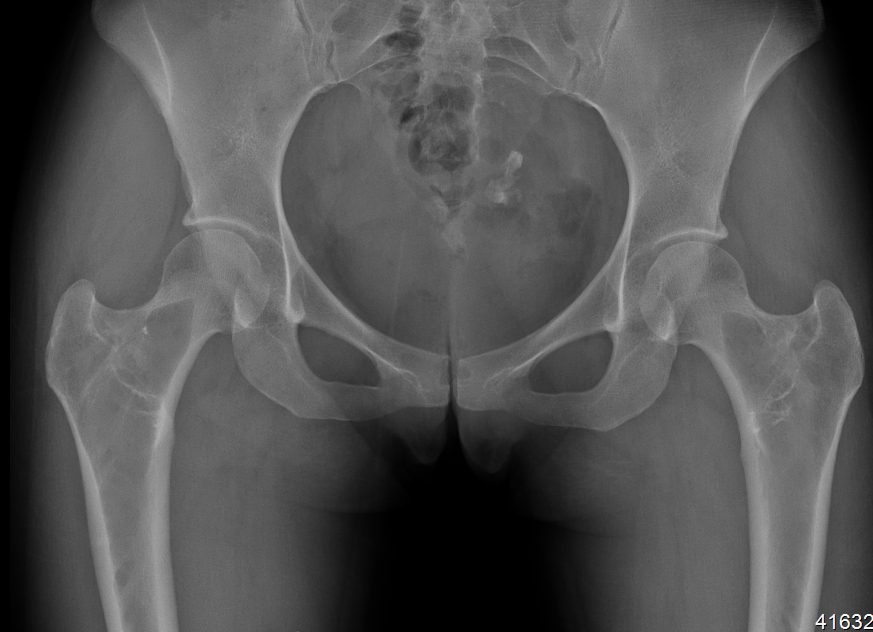
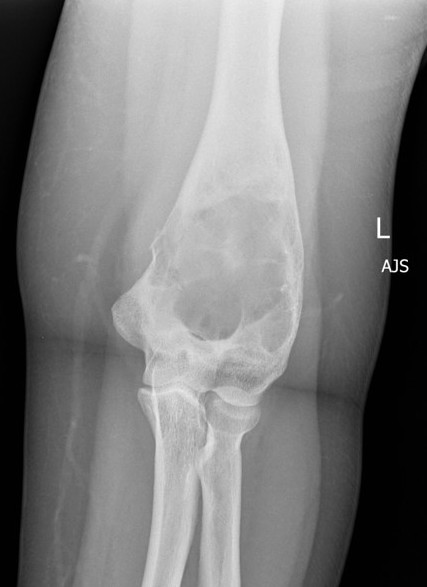
X-ray
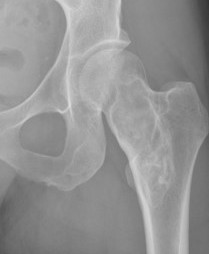
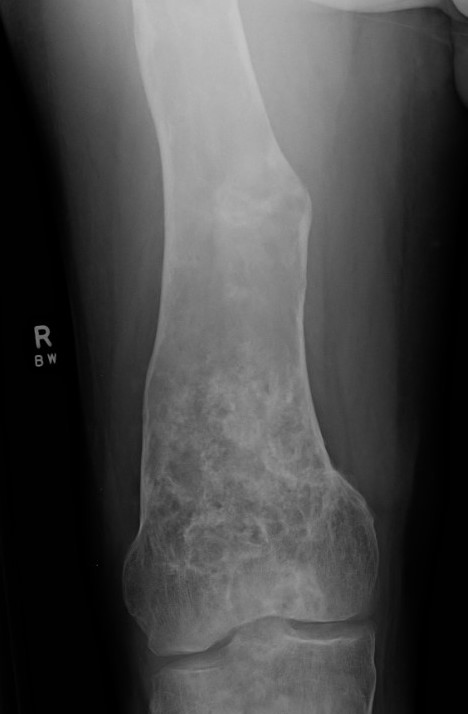
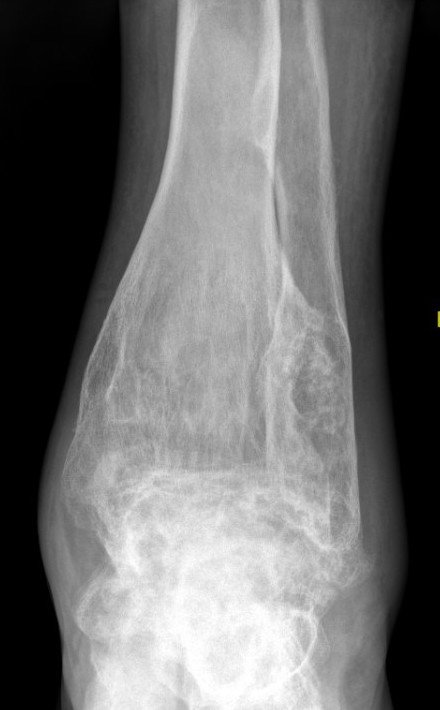
Intramedullary lucent diaphyseal lesion with 'ground glass appearance'
- thinned, slightly bulged cortex
- ± endosteal scalloping
- may have angular deformity / bowing
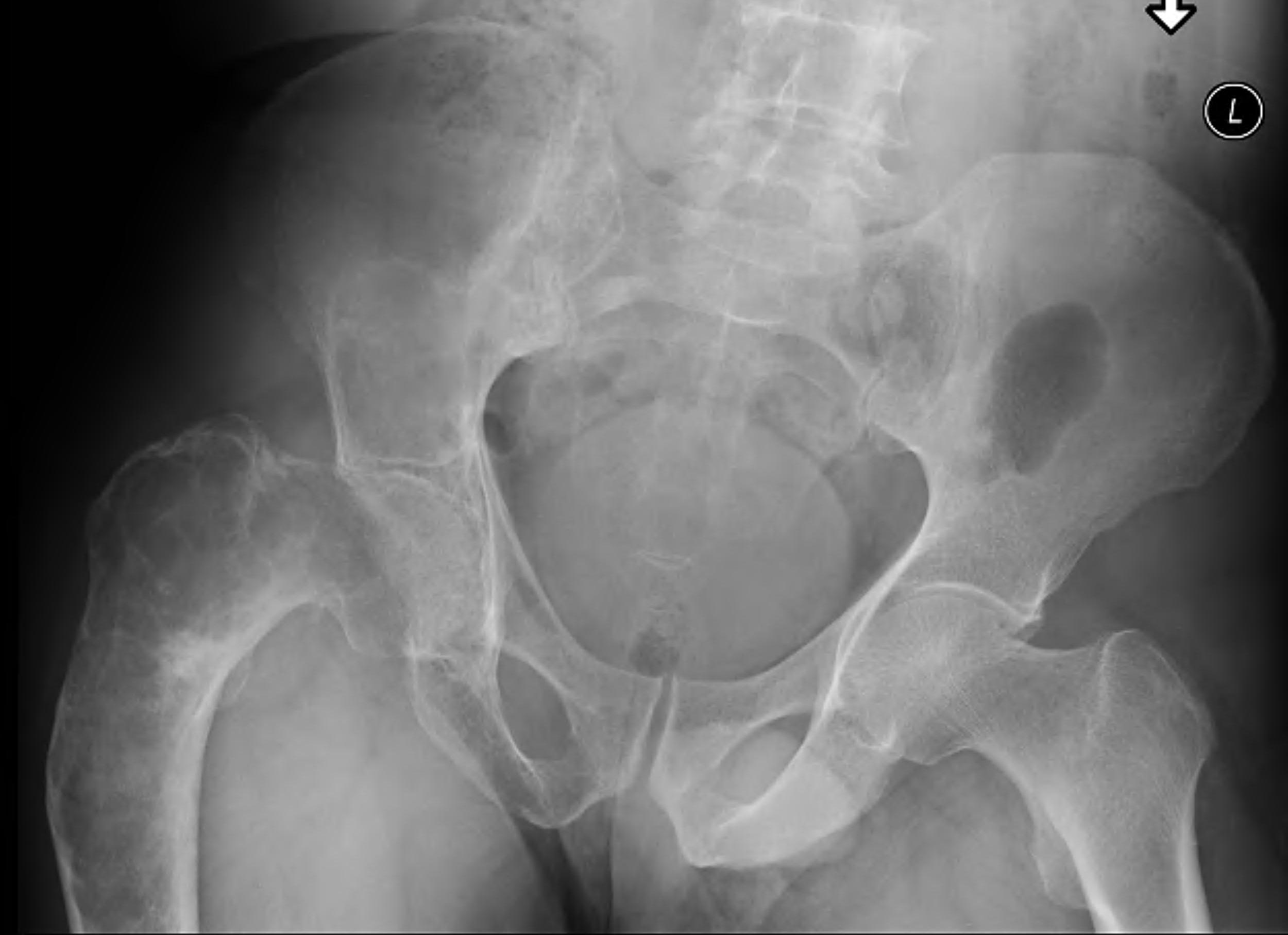
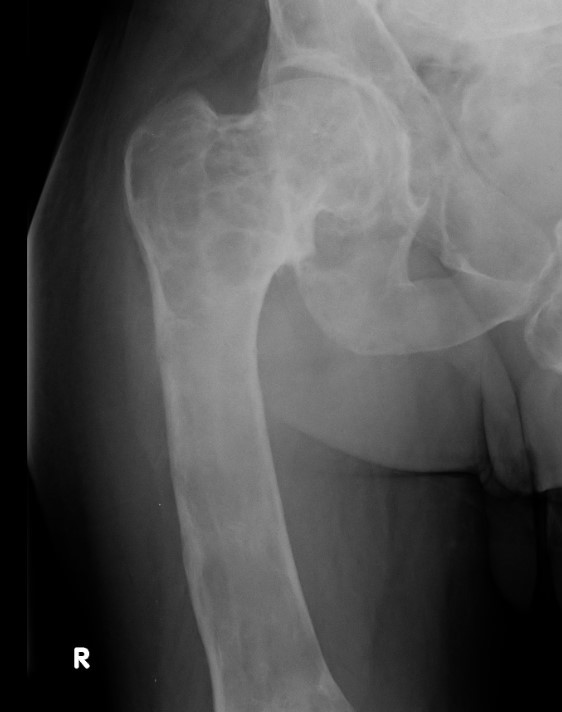
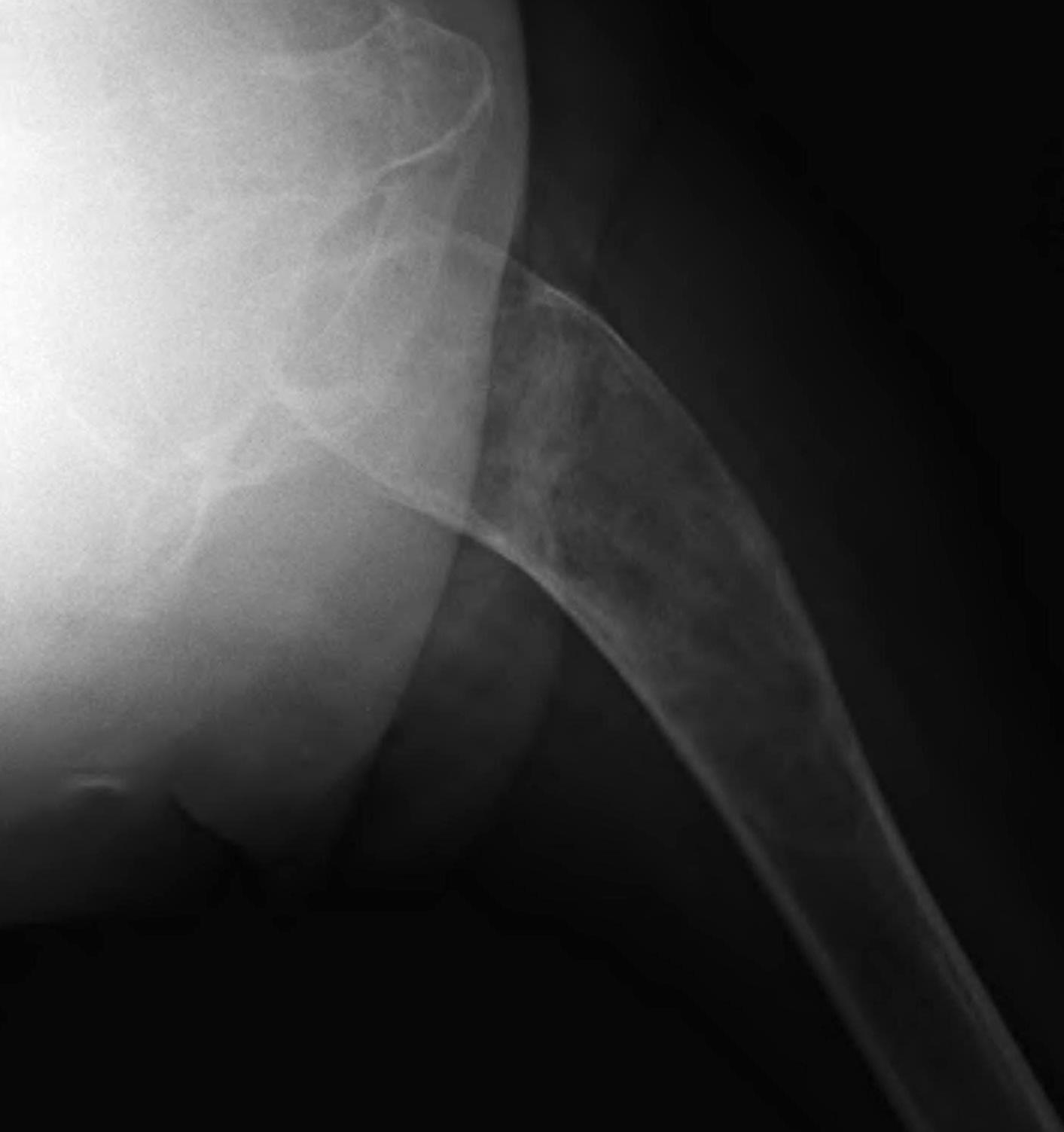
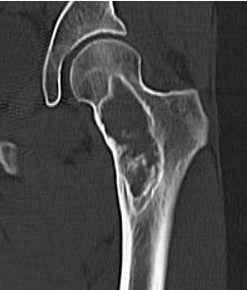
Coxa vara and Shepherd's Crook deformity of proximal femur
- Shepherd's Crook - anterior bowing of femur
- secondary leg length discrepancy
- pain, difficulty walking
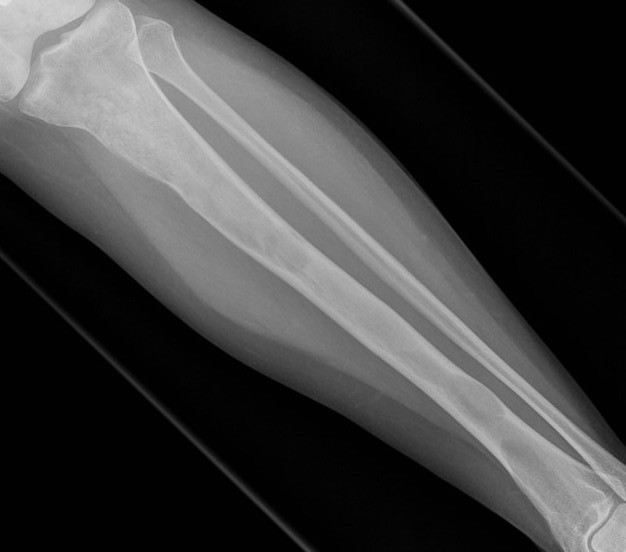
Sabre tibia
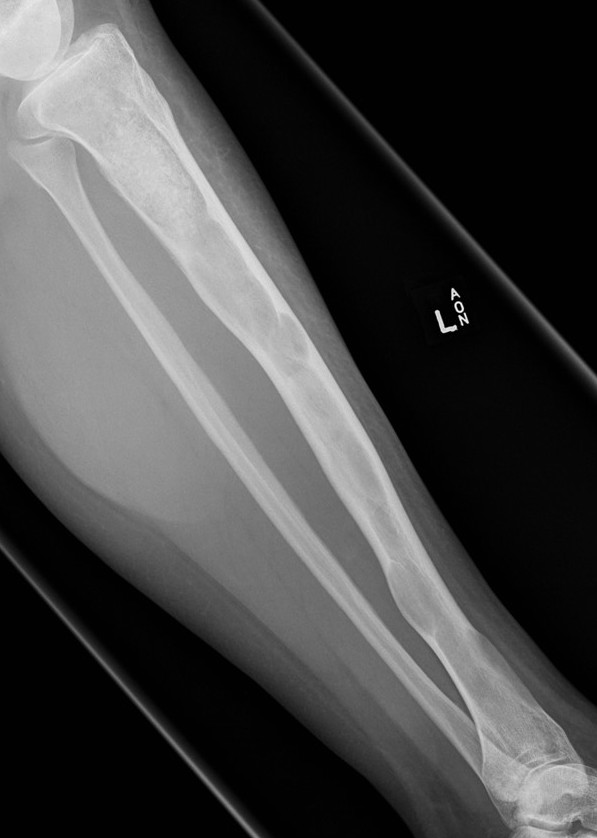
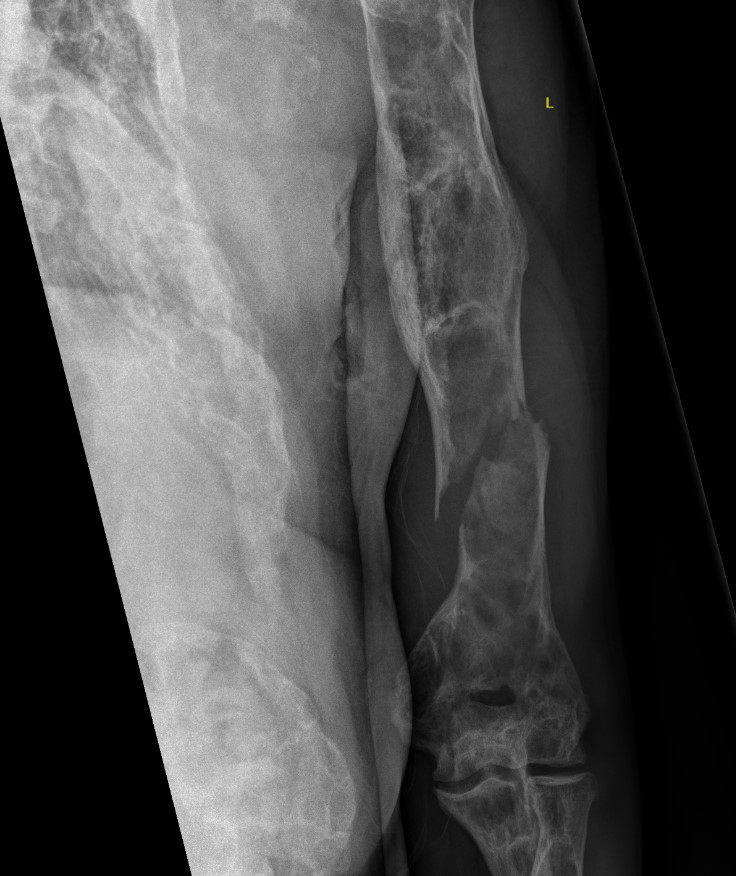
Pathological fracture
Spine involvement / scoliosis
- 62 patients with polyostotic FD
- 40% had scoliosis
Berglund et al J Bone Mineral Res 2018
- 138 patients with fibrous dysplasia / McCune Albright syndrome
- 61% scoliosis
- 35% moderate to severe
- no effect of bisphosphonates in reducing curve progression
CT
Bone Scan
Skeletal survey - determine disease burden / polostotic
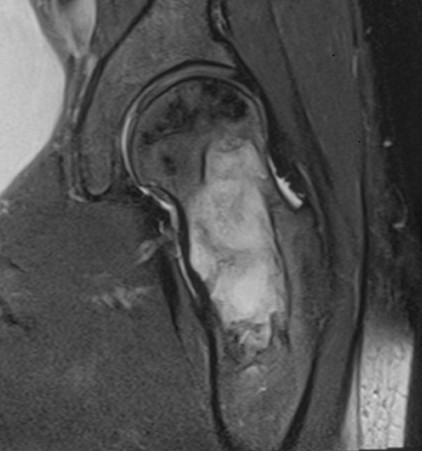
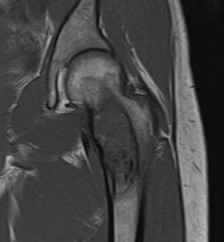
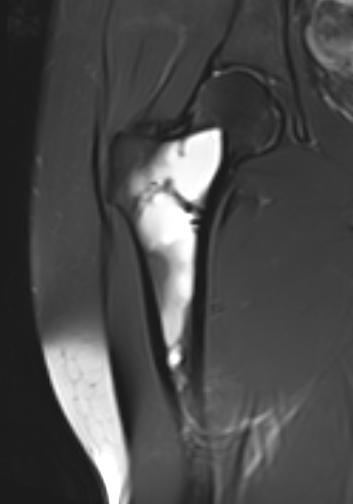
MRI
Low signal intensity T1 / High signal intensity T2


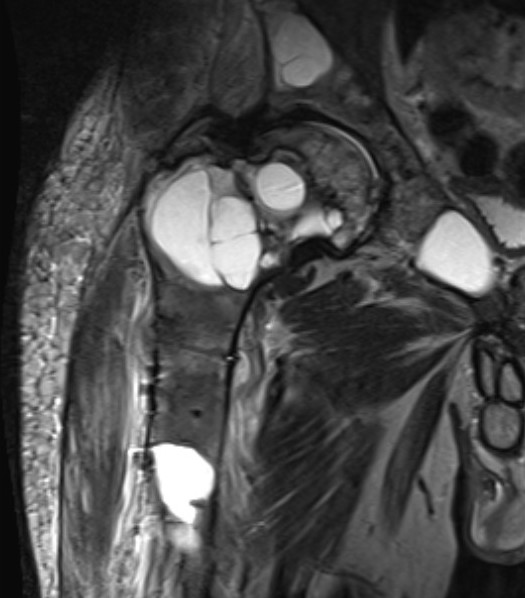
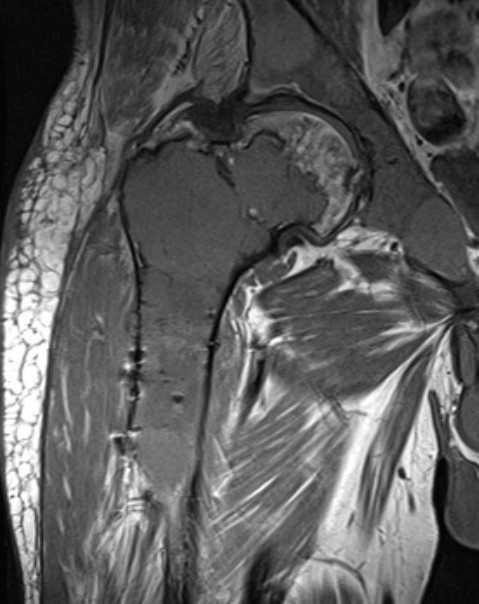
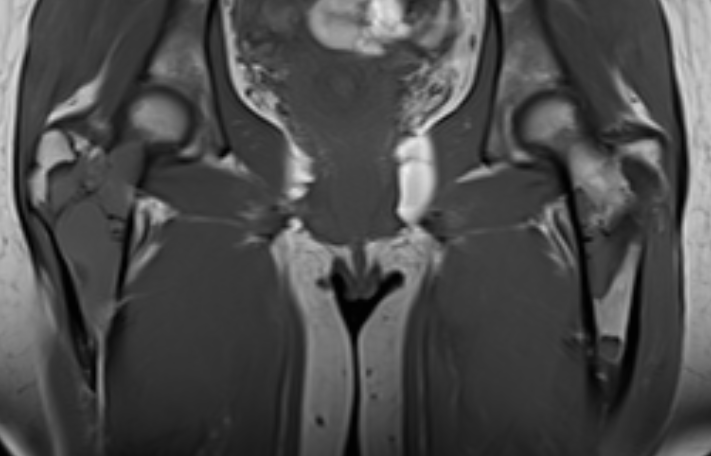
Histology
Fibrous tissue with irregular, randomly oriented bony trabeculae
Management
Multidisciplinary team
Orthopedics / Endocrinology / Dentistry
Bisphosphonates
Bertin et al Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2023
- systematic review and meta-analysis of bisphosphonates
- increased bone density and reduces bone pain
Surgical intervention
Indications
- deformity correction
- fracture prevention (>75% of cortical diameter)
- prevention deformity
- pathological fracture
Bone grafting
Bone grafting is of limited value with fibrous dysplasia
- curettage and bone grafting of lesions
- 100% resorption of bone graft with recurrence of lesion
- osteotomy and fixation with reconstruction nail mainstay of treatment
Majoor et al CORR 2017
- cortical strut allograft for 30 patients with impending or fractures proximal femur
- 50% radiological resorption of graft
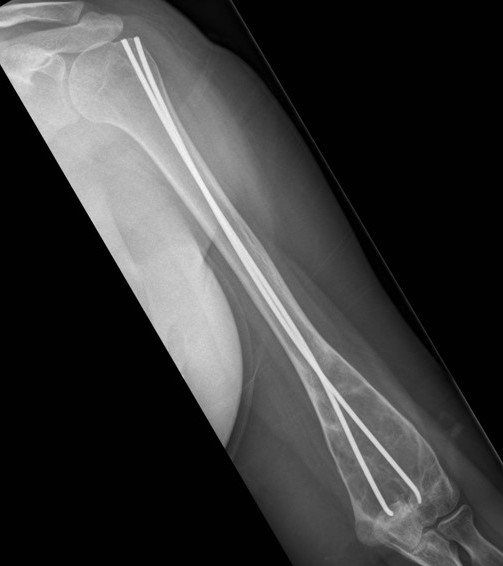
Corrective osteotomy / Intra-medullary nailing
Mainstay of treatment
Ippolito et al J Orthop Traumatol 2023
- 24 patients with 34 femurs and 14 tibias requiring intra-medullary nailing
- mean age 32
- osteotomy and deformity correction often required
- nonunion / delayed union / implant failure in 5 cases
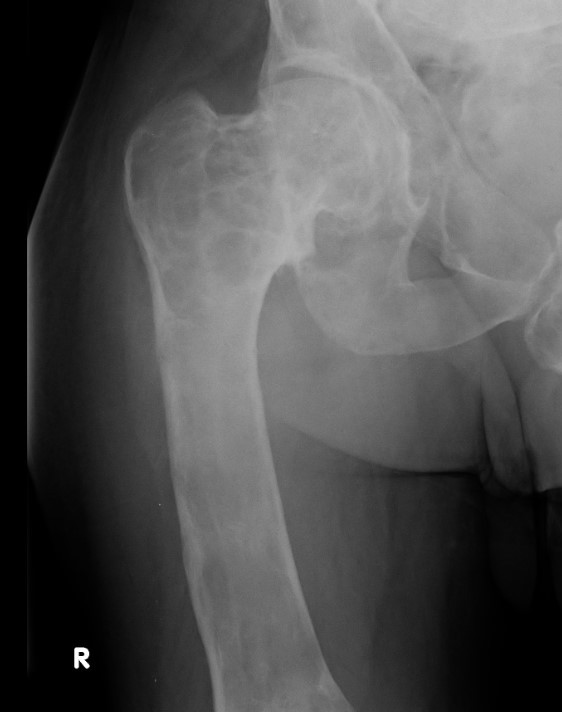
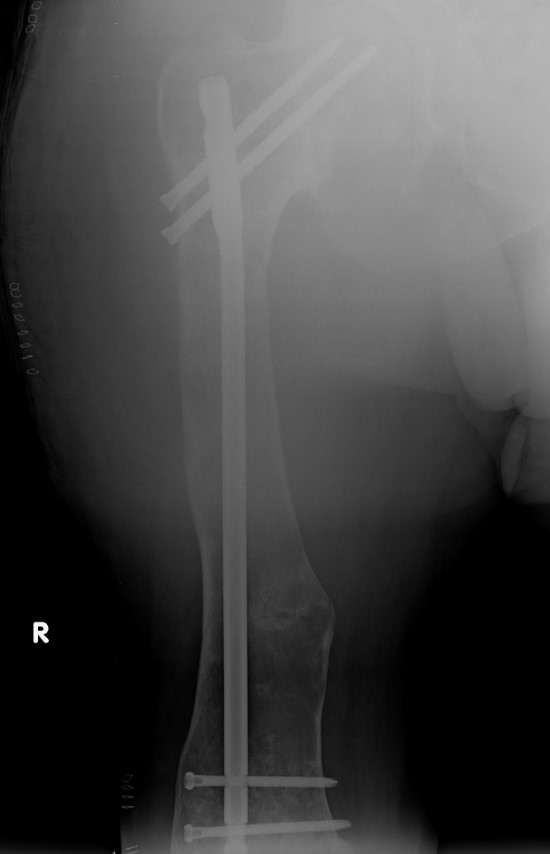
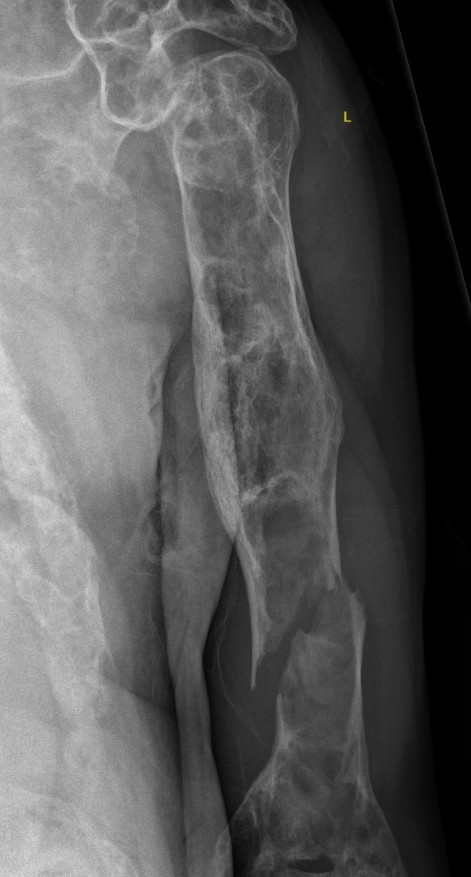
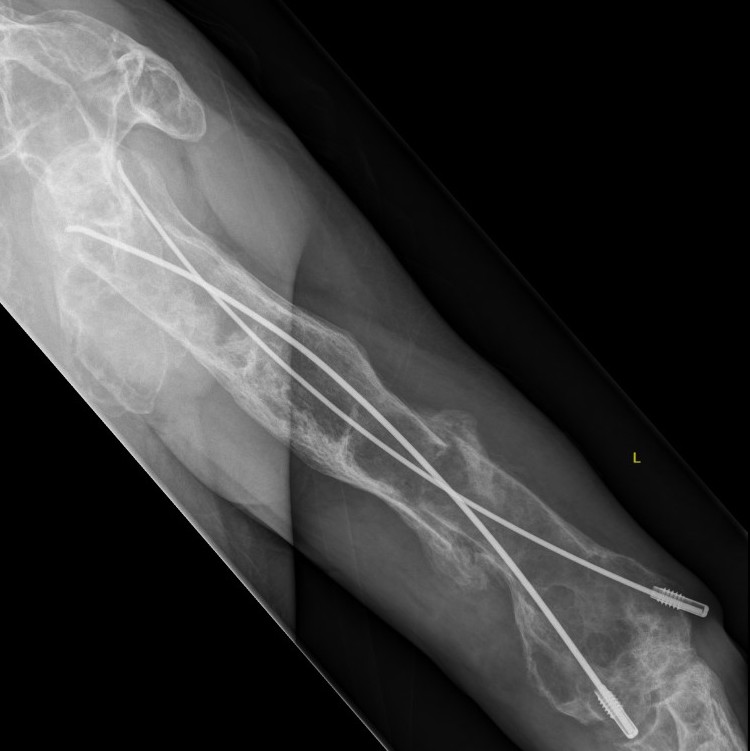
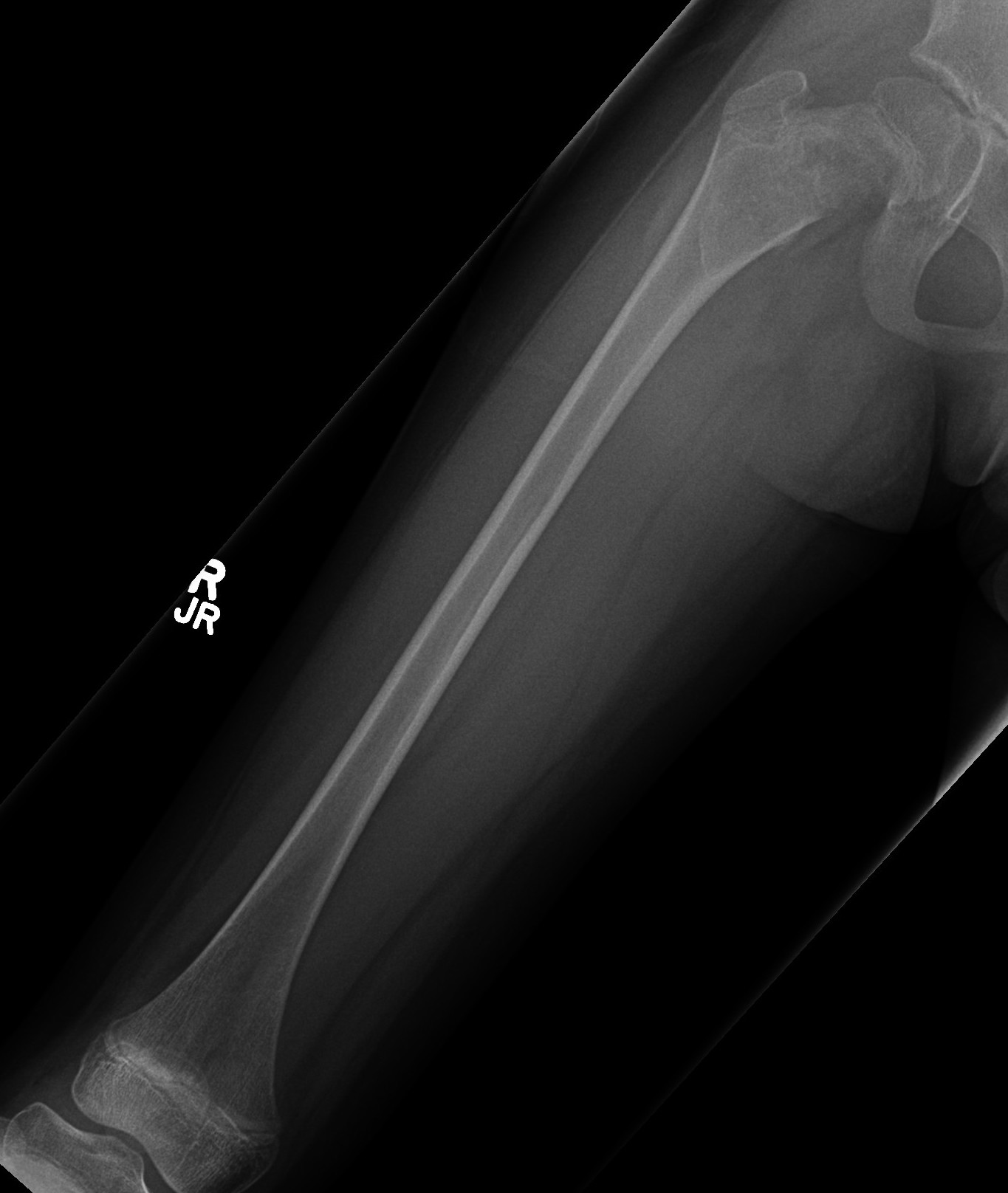
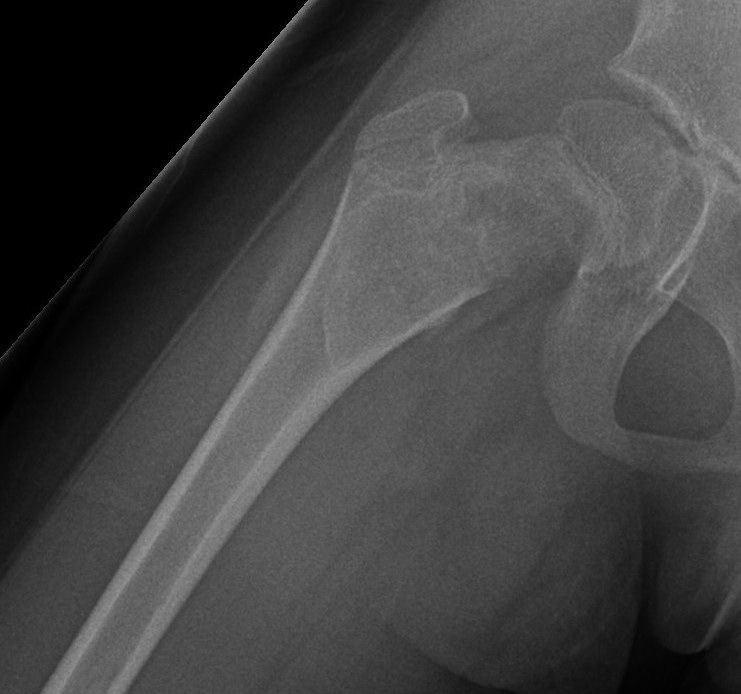
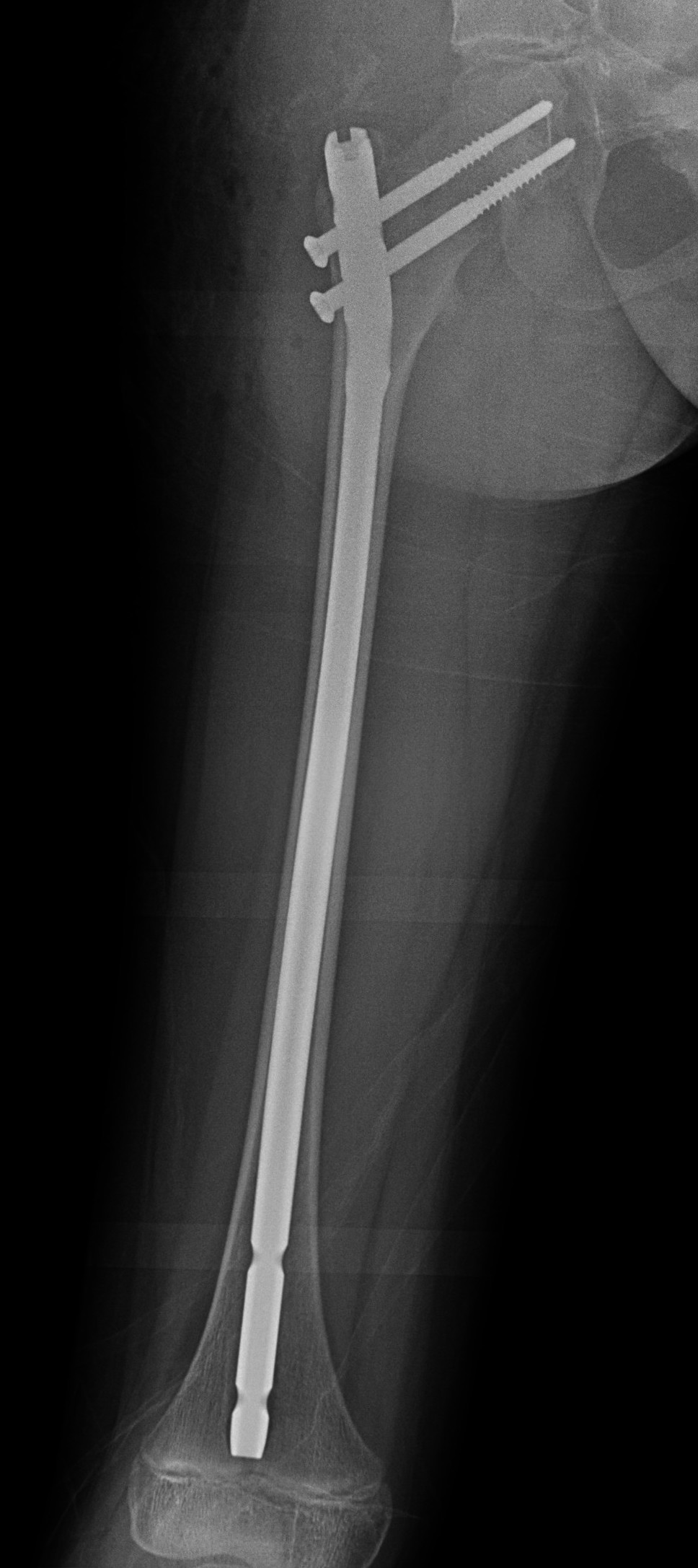
Proximal femur coxa vara and shepherds crook deformity
- 11 cases
- initial osteotomy correction of coxa vara and fixation with hip plate
- later osteotomy and correction of shepherds crook / femoral bowing and insertion reconstruction nail
- improved pain and gait
- significant blood loss at both stages
- 209 patients with FD of the proximal femur
- 12% developed osteoarthritis
- 10 hips in 9 patients with 6 year follow up
- osteotomy to correct coxa vara
- proximal femoral allograft used +/- strut allograft
- one revision due to poor bone stock and femoral implant subsidence