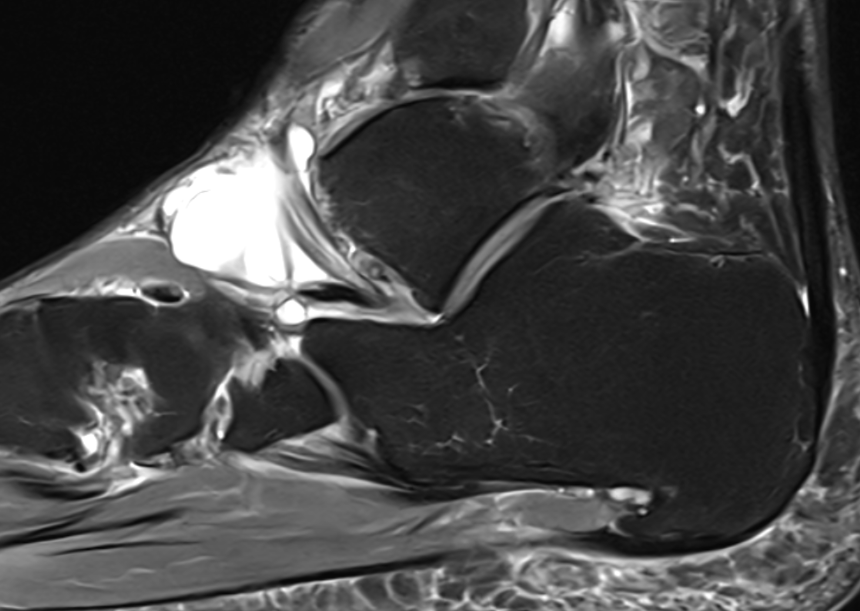
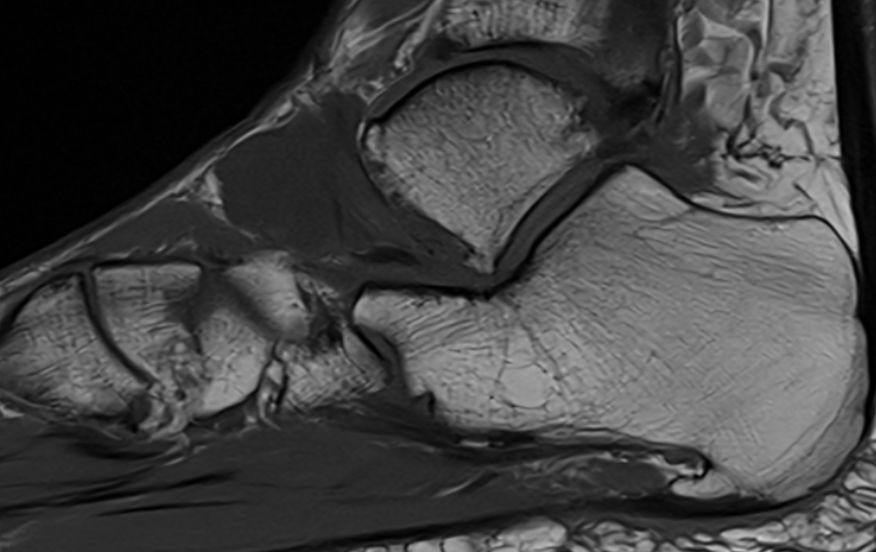
Giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath
Types
Ganglion
Giant cell tumor tendon sheath
Neurofibroma / Schwannoma
Fibroma /Plantar fibromatosis
Lipoma
Glomus tumor
PVNS / Synovial osteochondromatosis
Hemangioma
Ganglion
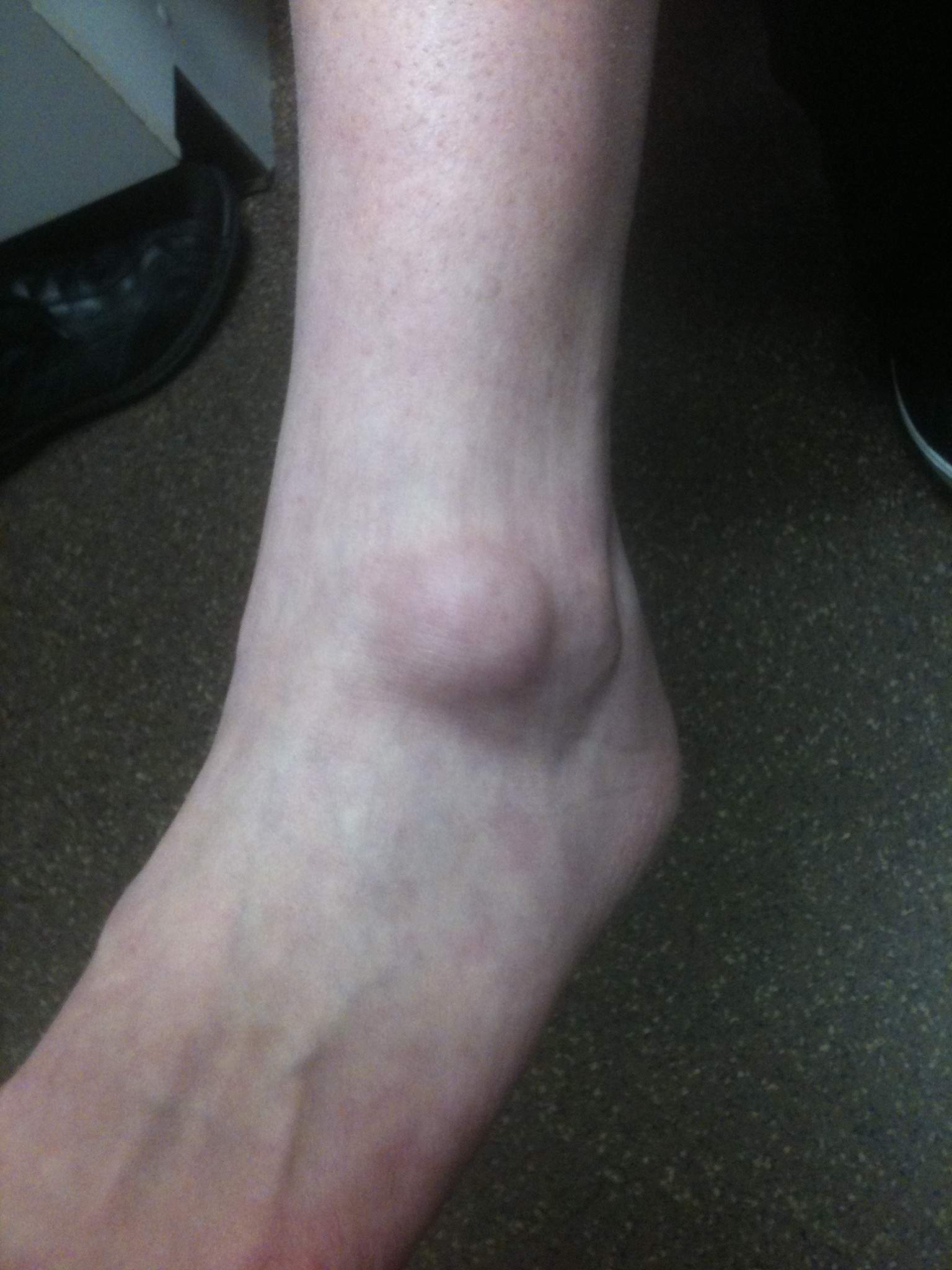
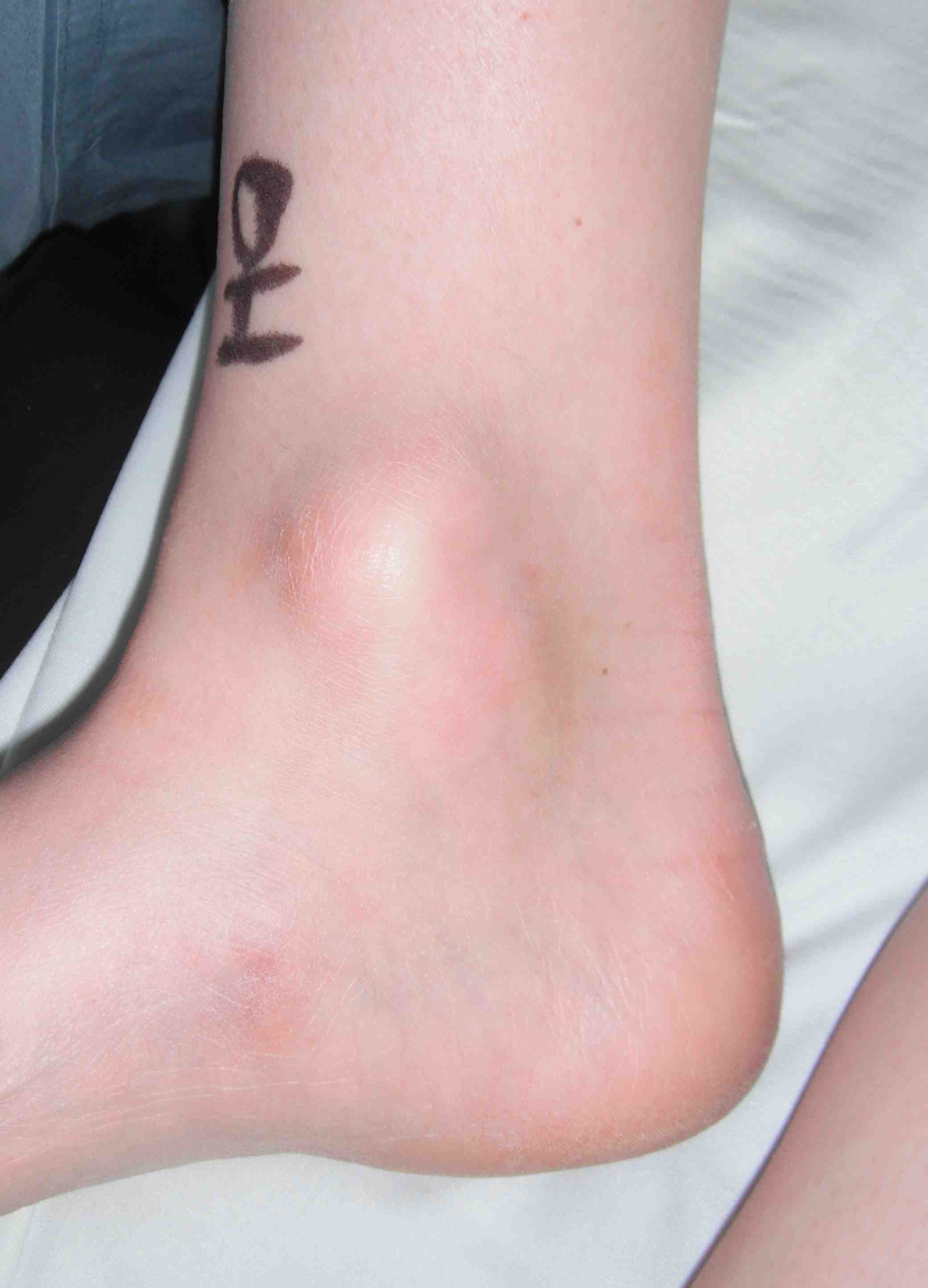
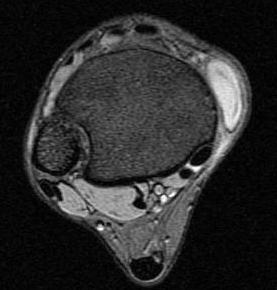
Firm subcutaneous nodule
- fluctuate in size
- arise from joint capsule or tendon sheath
- transilluminate
Treatment options
- observe
- multiple aspirations / cortisone injections
- surgical excision
Surgical excision
- need to find neck
- may arise from ankle joint / subtalar joint / tibialis posterior tendon
- tie off neck or excise segment of capsule to prevent recurrence
- systematic review of recurrence rates after treatment of foot and ankle ganglion
- aspiration 78%
- aspiration and steroid injection 62%
- steroid injection 38%
- surgical excision 18%
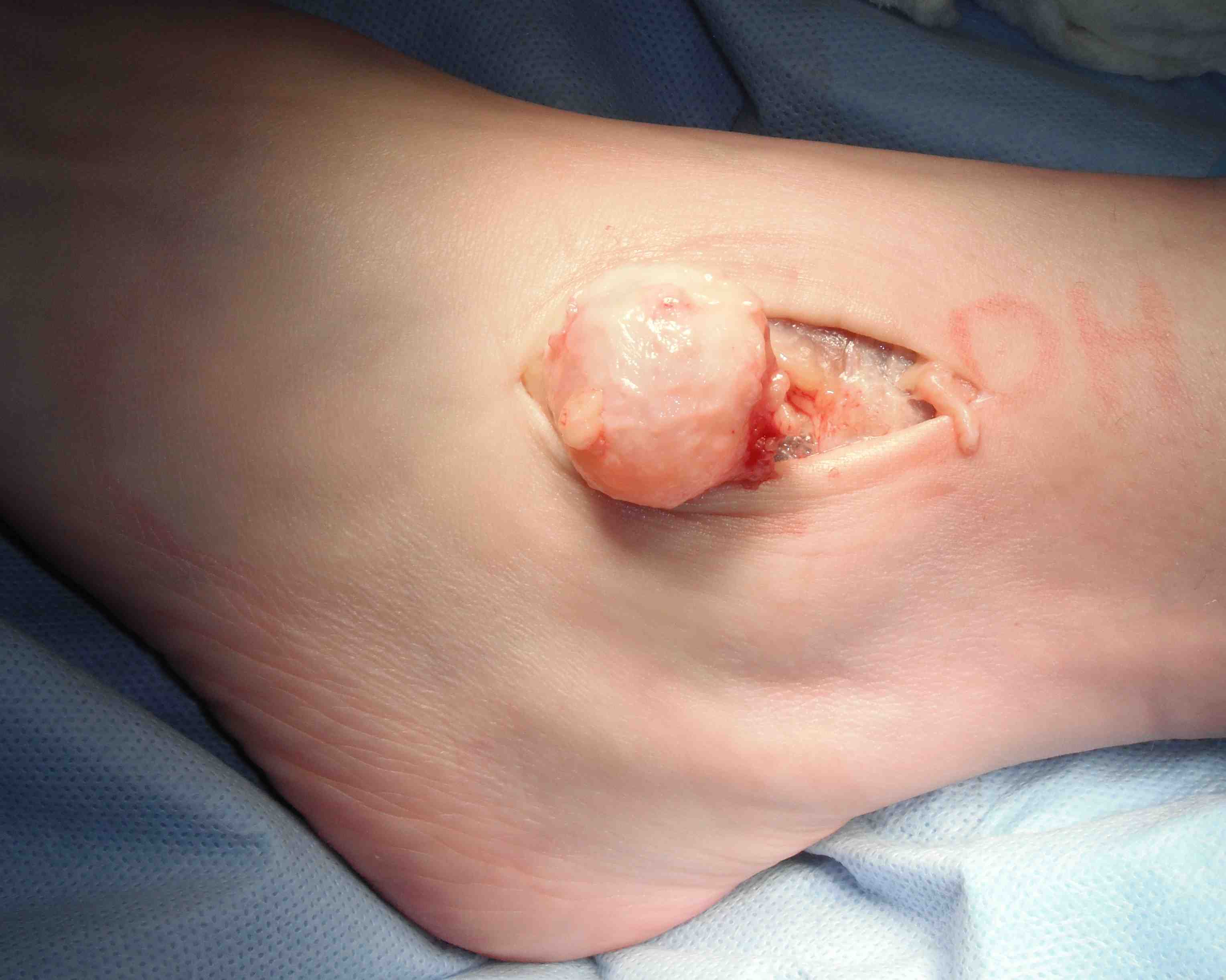
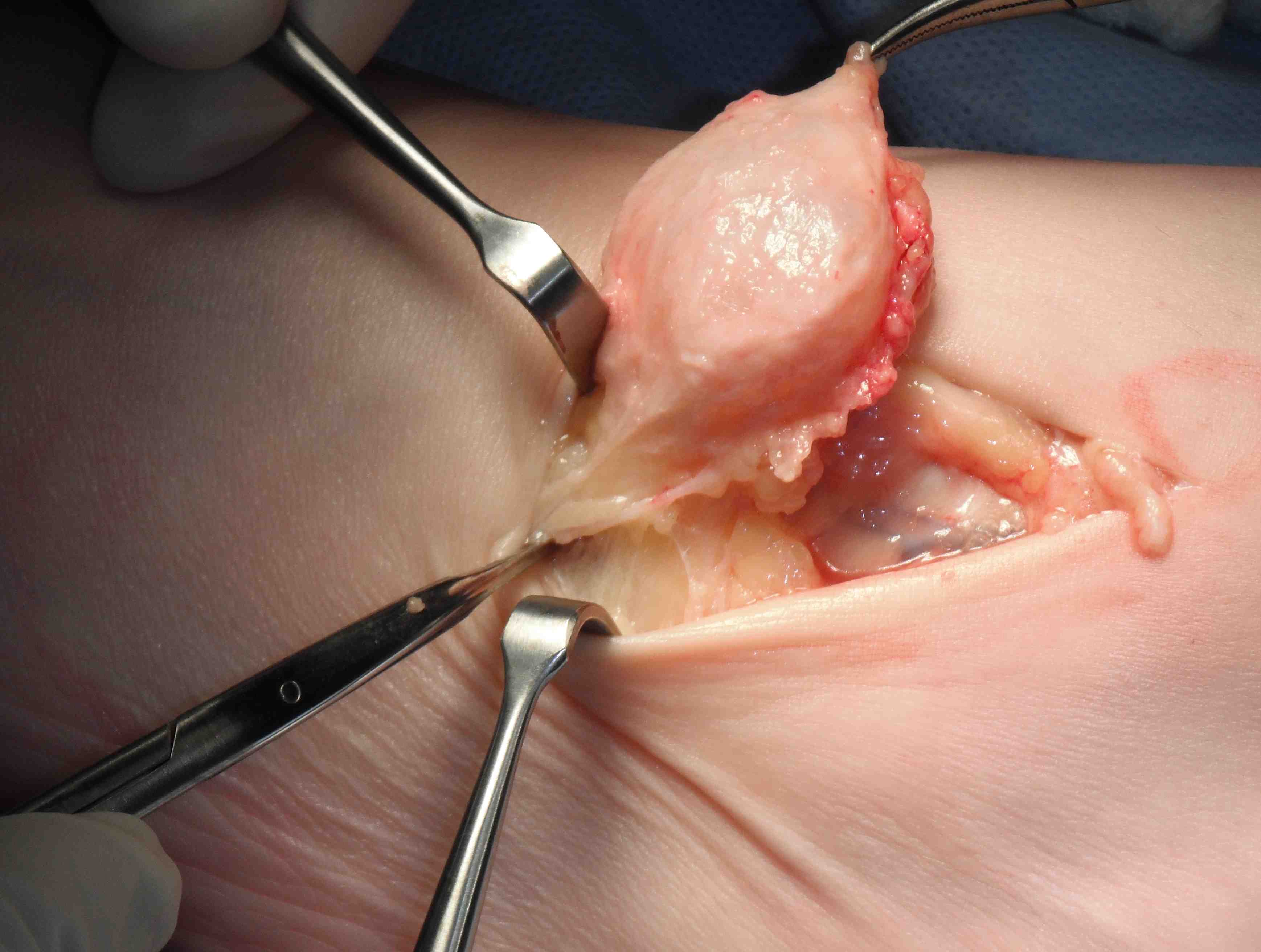
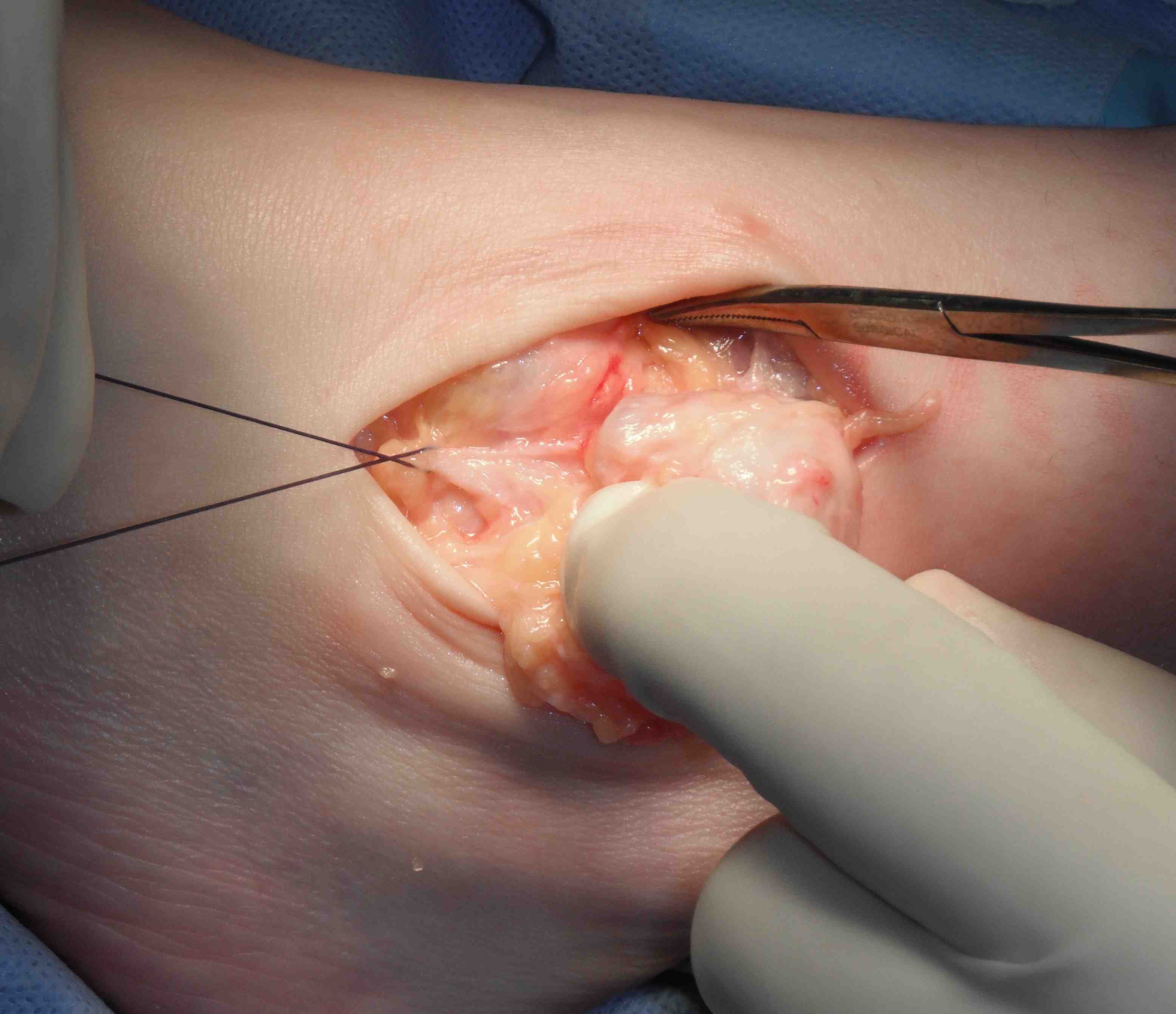
Closing neck of ganglion arising from tear in capsule
Giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath
Slow growing benign tumor arising from tendon sheath
- most common 3 - 5th decade
- more common in hand & wrist than in foot & ankle
Diagnosis
- heterogenous mass on MRI
- biopsy - abundant giant cells
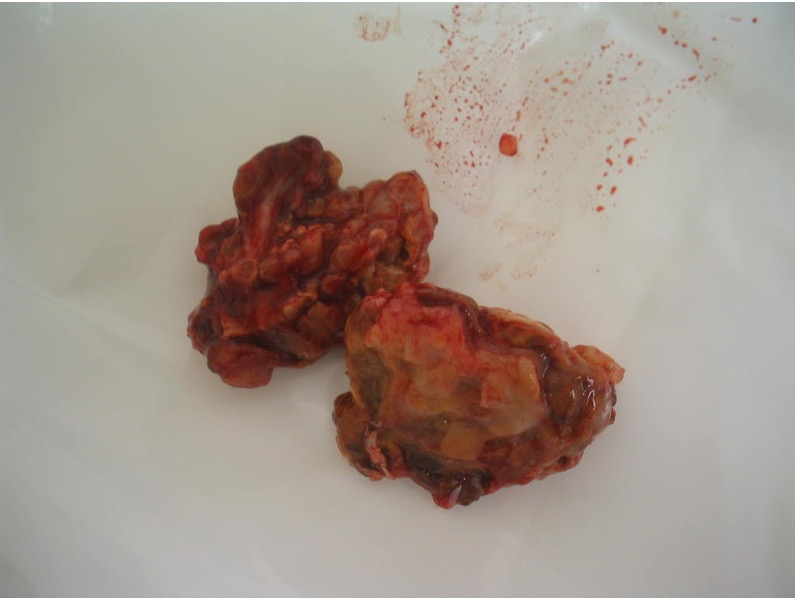
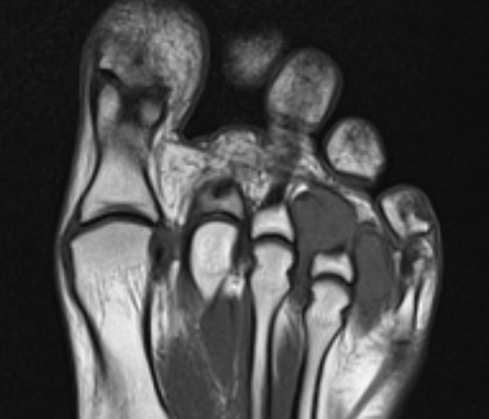
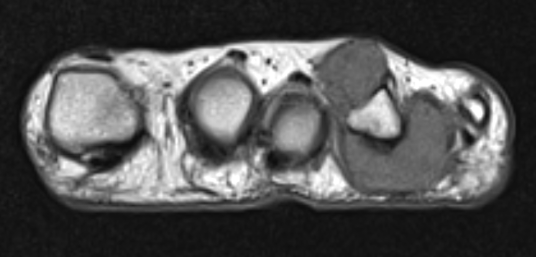
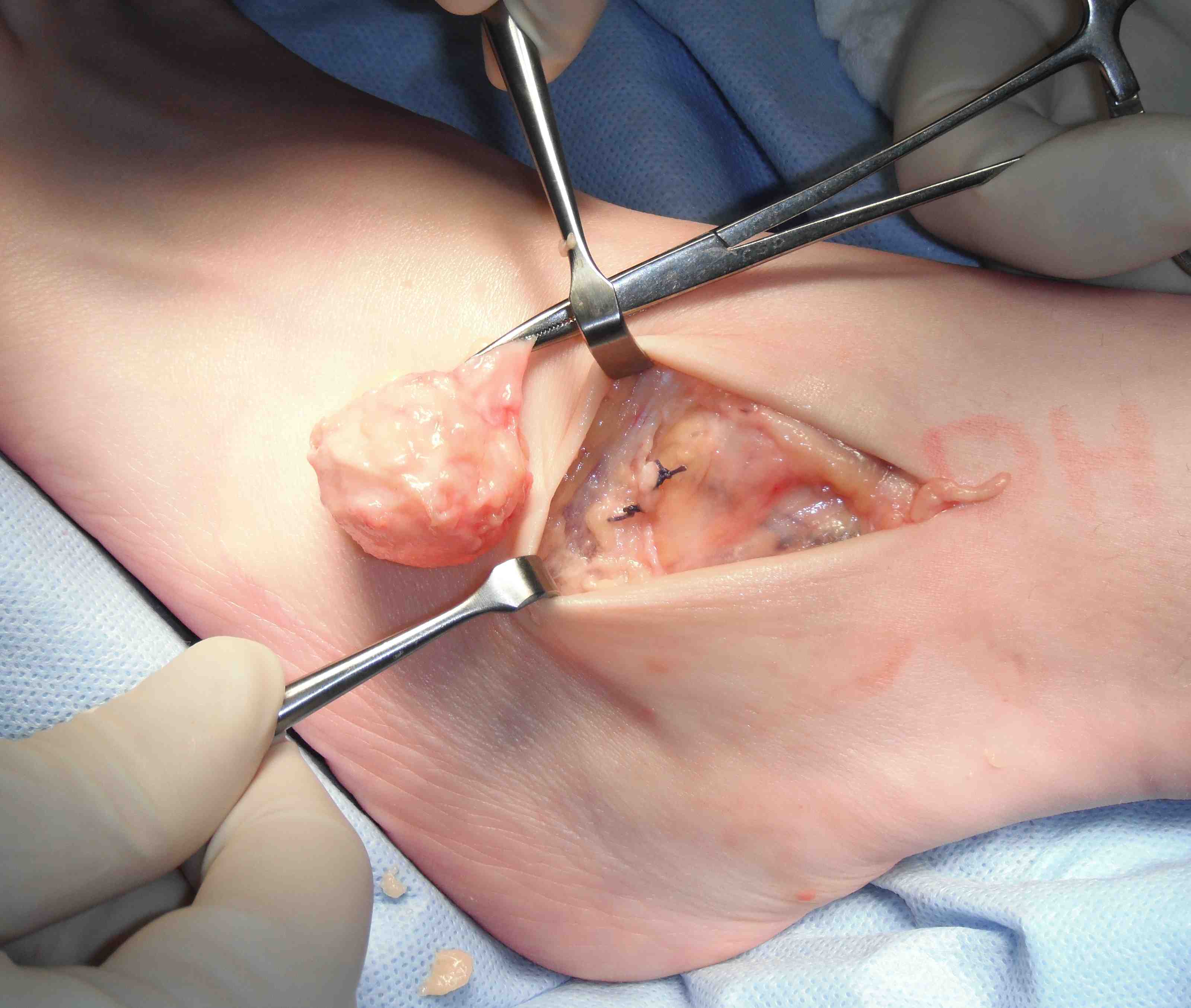
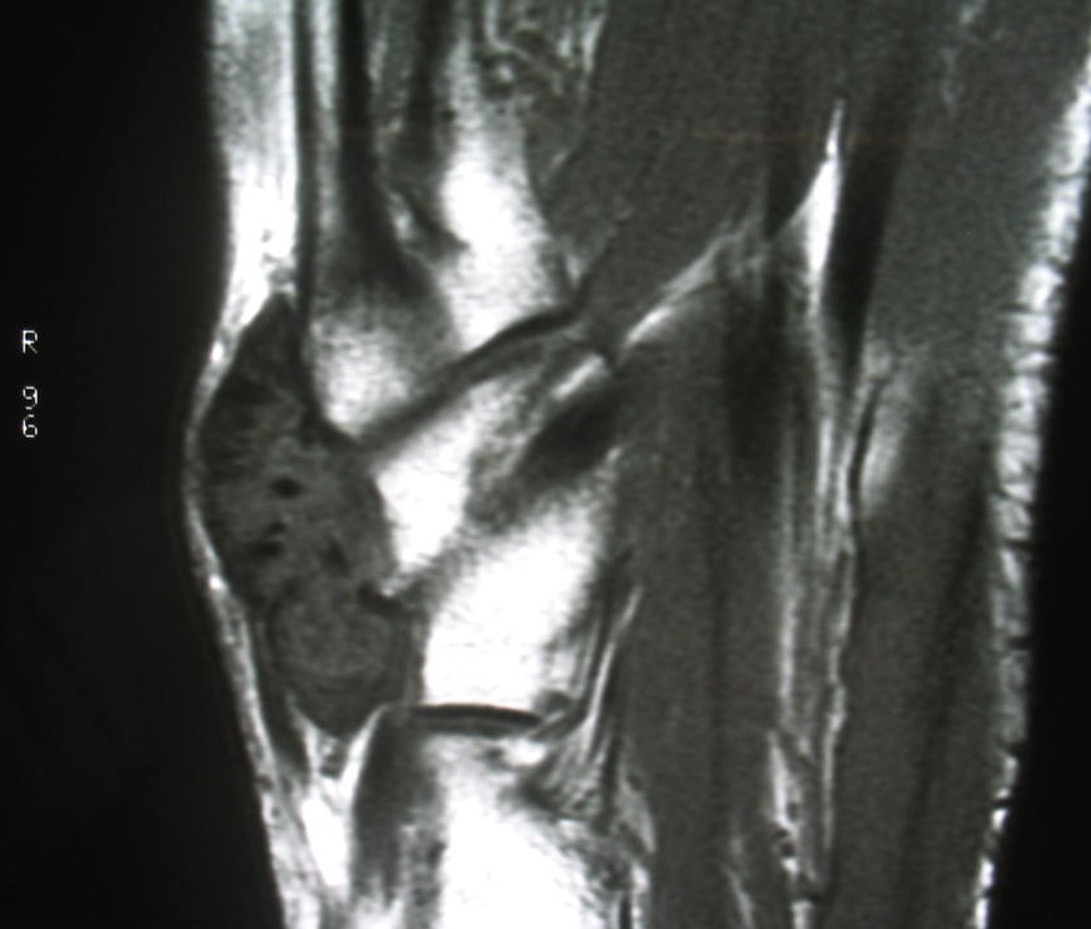
GCT flexor tendon sheath

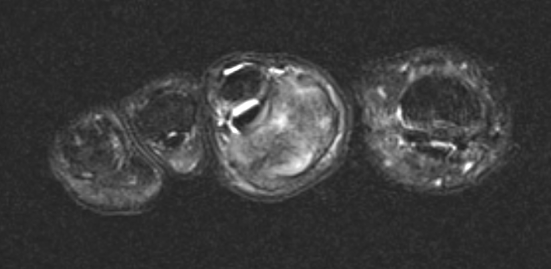
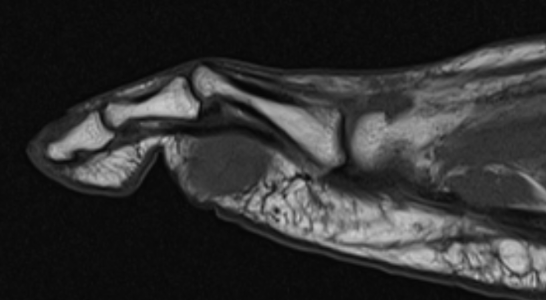
GCT flexor tendon sheath
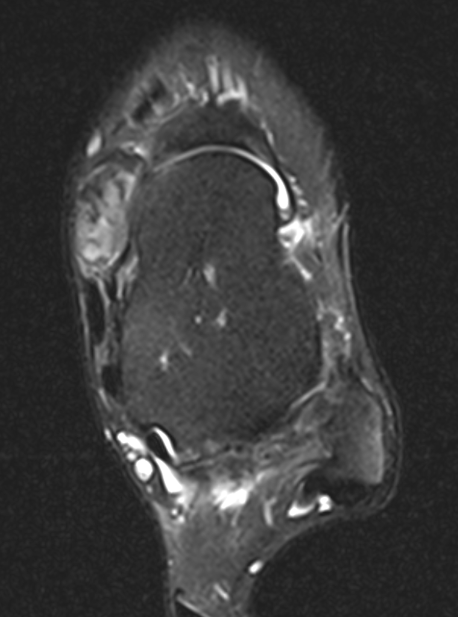
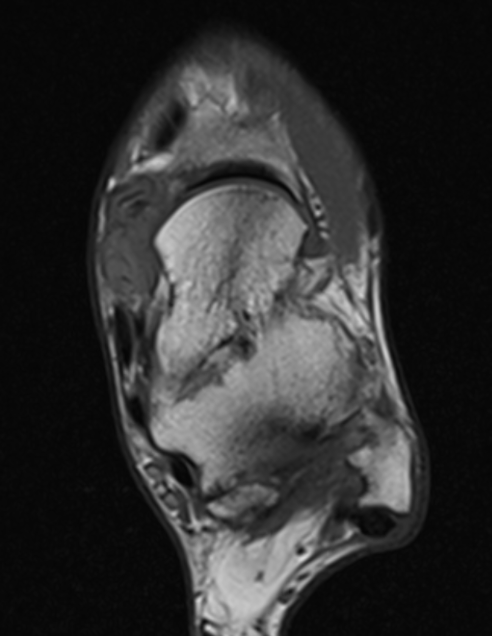
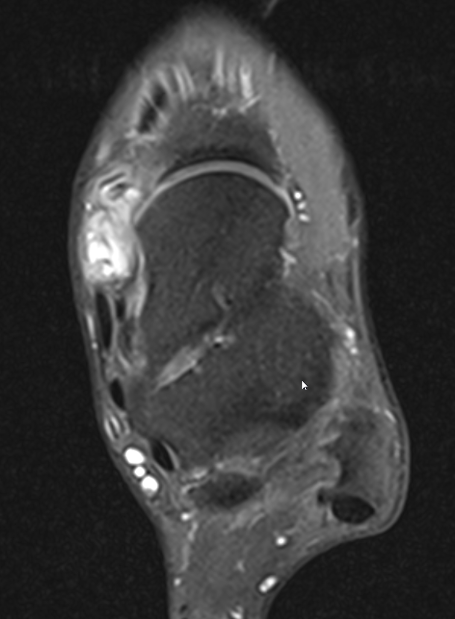
GCT of tibialis posterior tendon sheath
Treatment
- observe
- local excision
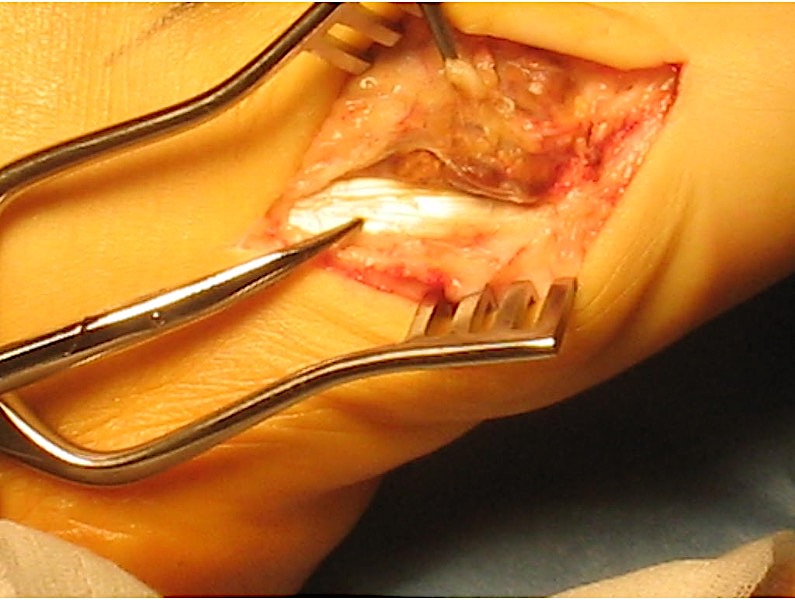
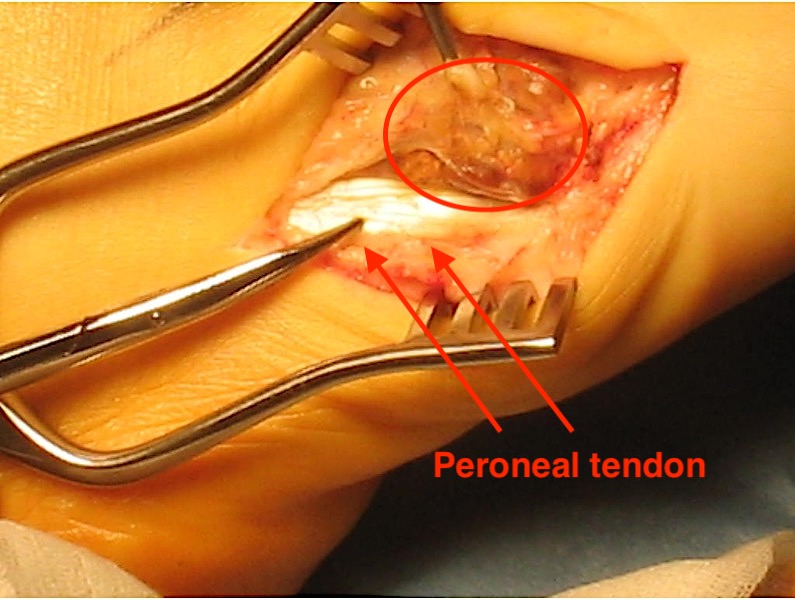
Zhang et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2013
- surgical excision of 20 giant cell tumour tendon sheath foot & ankle
- recurrence rate 20%
Neurilemmoma / Schwannoma
Well encapsulated solitary tumor originates from nerve sheath
- slow growing
- nerve fibres spread over its surface
MRI - hyperintense on T2
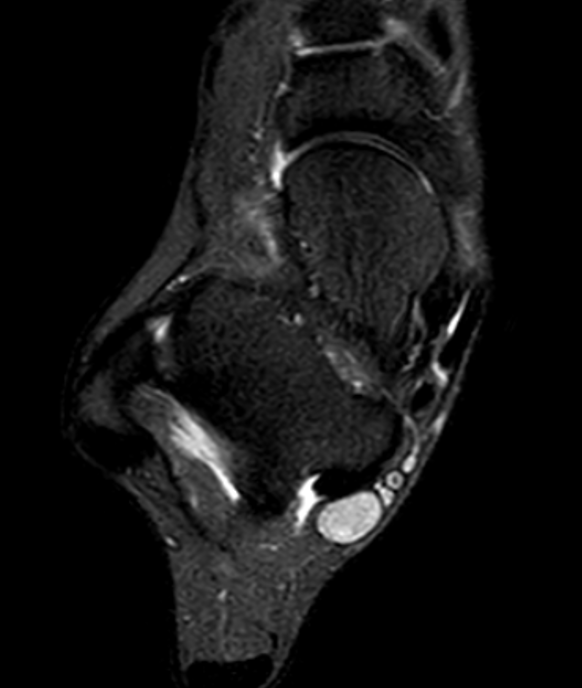
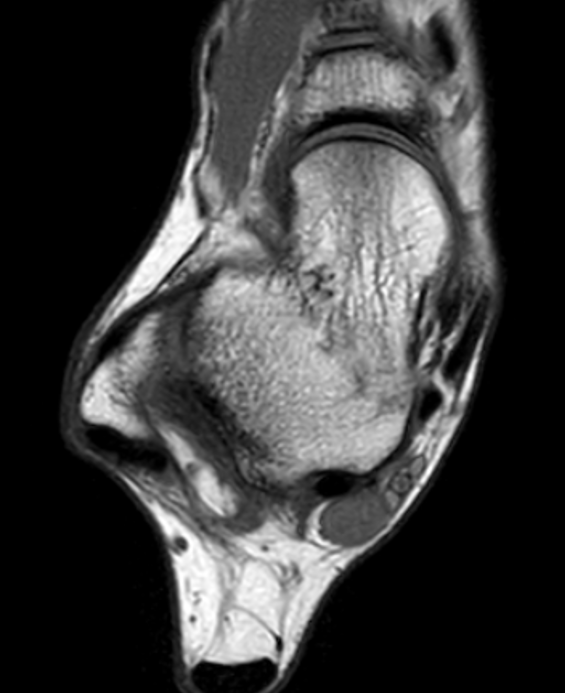
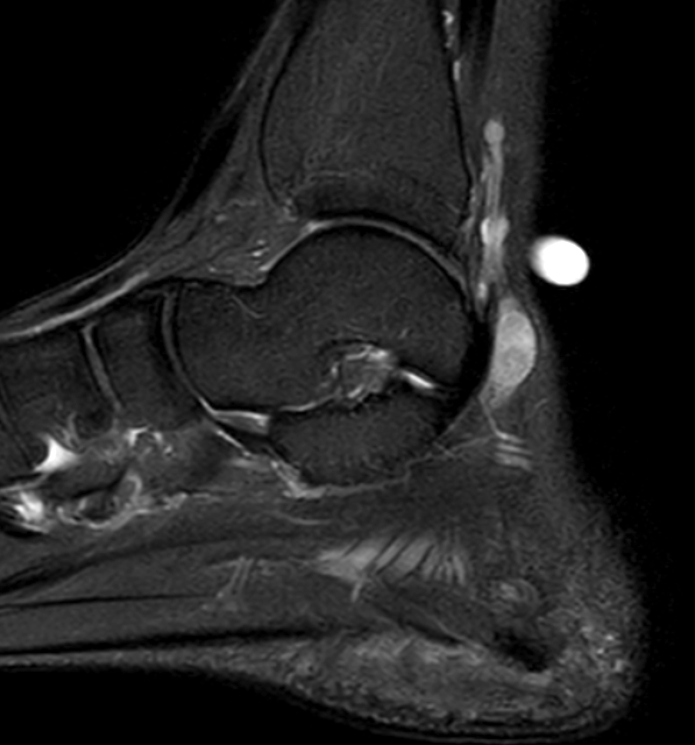
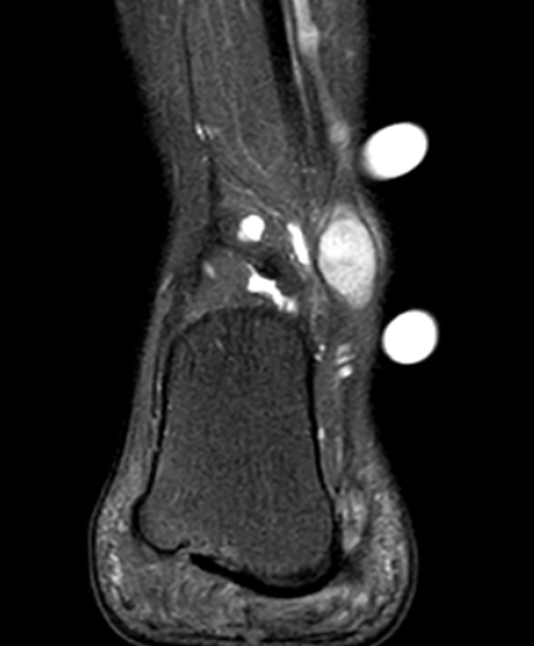
Schwannoma on tibialis posterior nerve
Management
- marginal excision
- excise neurilemmoma and attempt to preserve normal nerve fibres
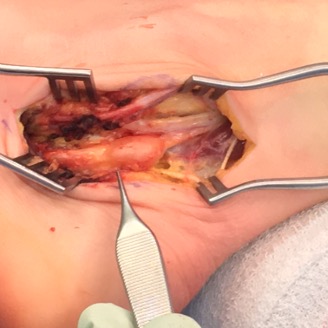
Schwannoma on posterior tibial nerve
Neurofibroma
www.boneschool.com/neurofibroma
Singular or multiple lesions extending along course of the nerve
- 50% not associated with NF
- often local pain especially with compression
- may affect distal nerve function
- malignant change rare in solitary lesion (occurs with NF)
MRI - target sign, which can be seen with neurilemmoma
Treatment
- tumor arises from within the nerve
- excision usually cause further loss of function
Fibroma / plantar fibromatosis
Discrete nodule on sole or dorsum of foot
www.boneschool.com/plantar-fibromatosis
Lipoma
Most common on dorsum of foot
- subcutaneous
- soft feeling / mobile / grape like
Treatment
- marginal excision
Glomus tumour
Presents as painful toe, sensitive to cold
- usually subungual
- usually benign
- arise from glomus bodies which control blood pressure and temperature
X-ray - may scallop adjacent bone on x-ray
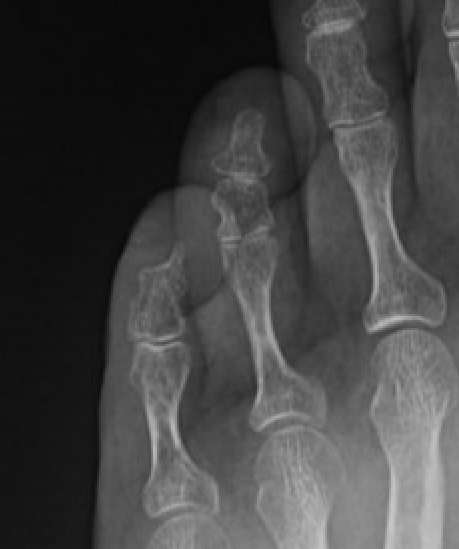
Subungal glomus tumor distal phalanx 5th toe
MRI
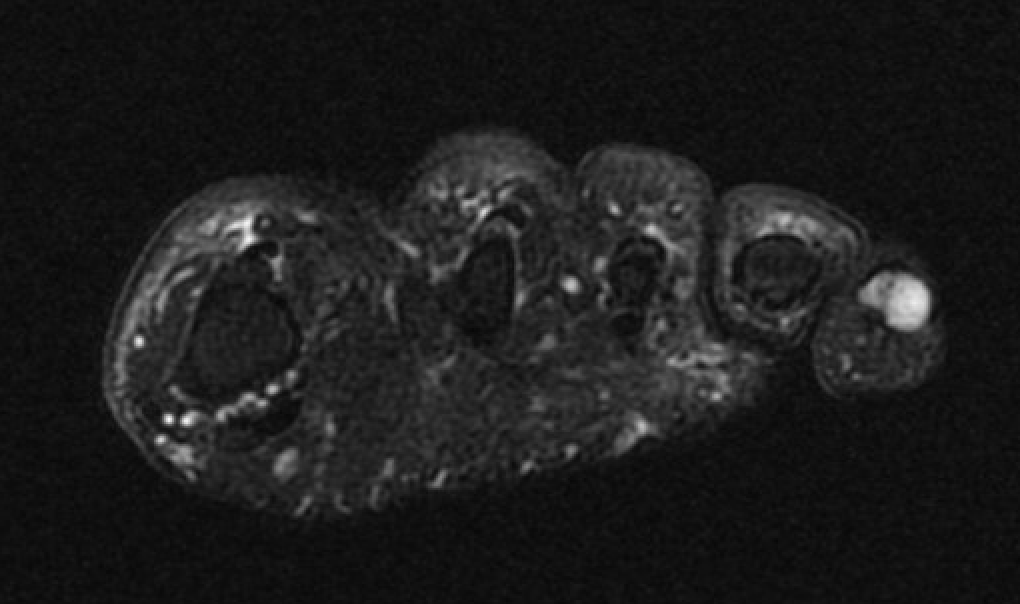
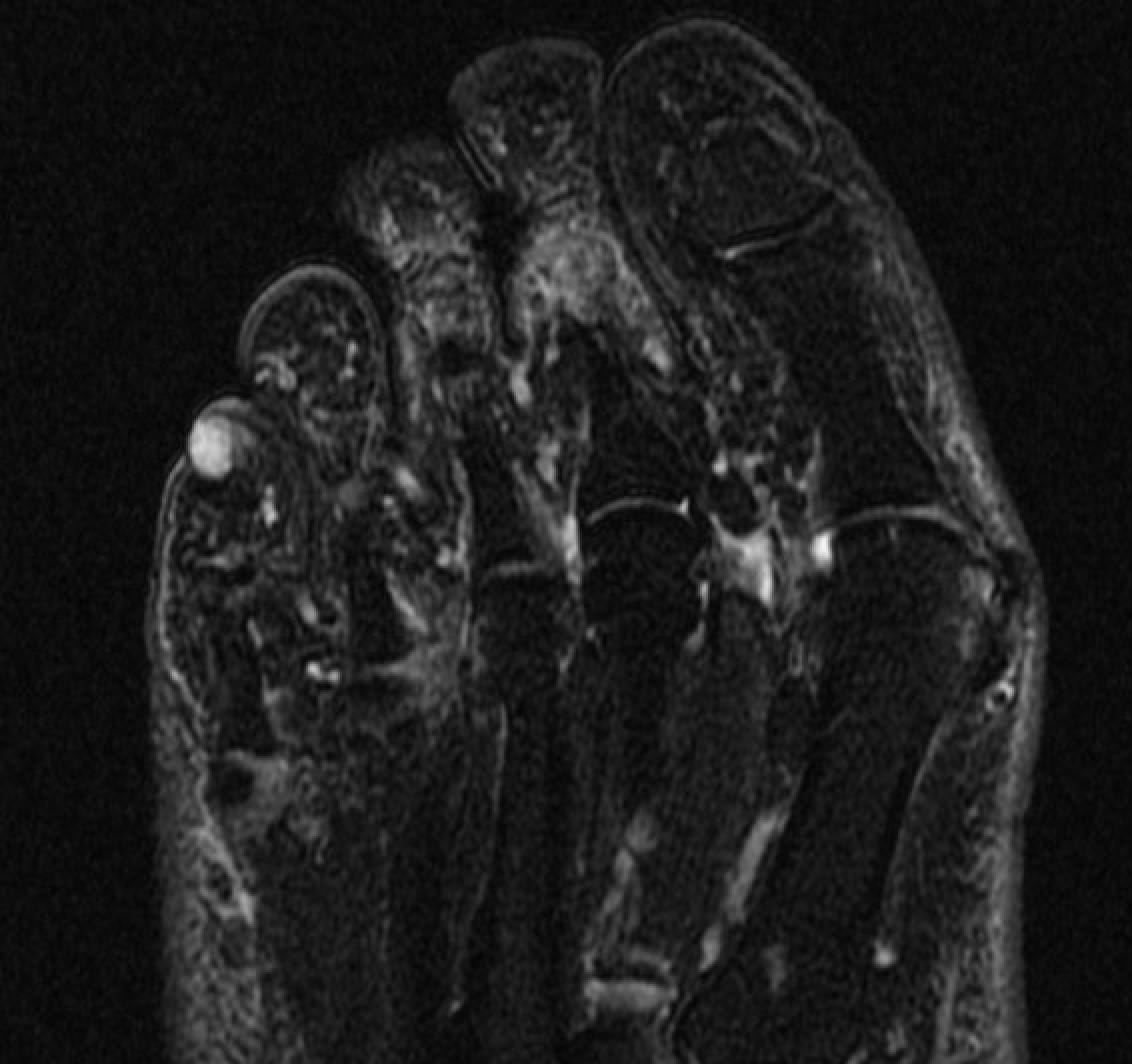
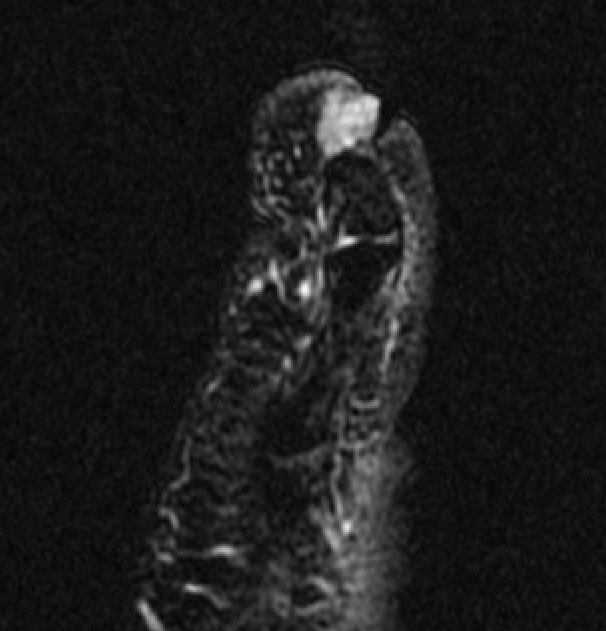
Subungal glomus tumor 5th toe
Treatment - marginal excision for pain
PVNS
Reclassified as same entity as soft tissue giant cell tumour
PVNS characteristically referred to an intra-articular lesion
Common around the ankle or midfoot
- may involve multiple bones
- usually in young adults
Xray - may show bony erosions
MRI - low signal on T1 and T2
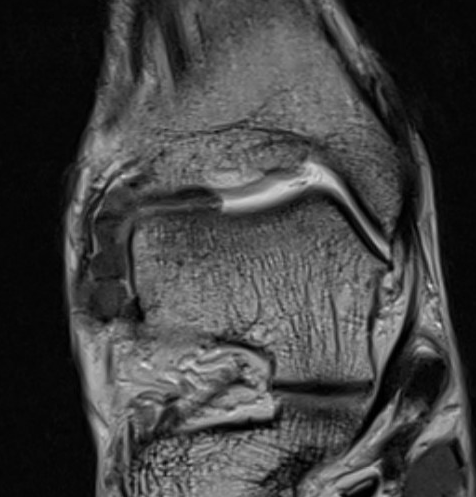
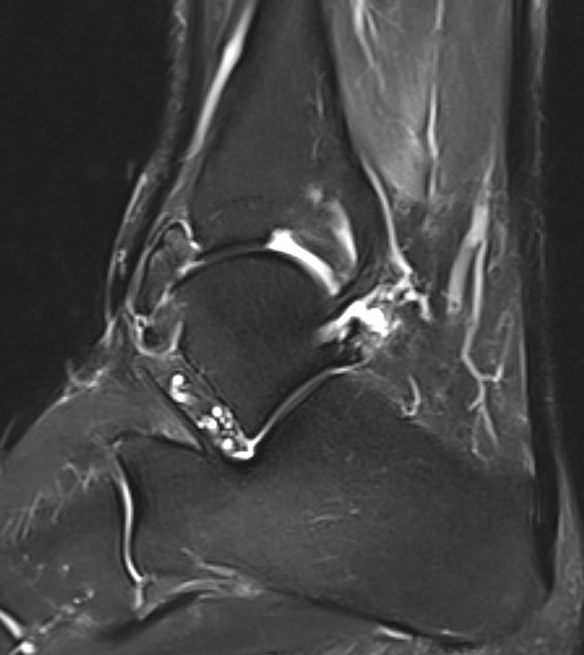
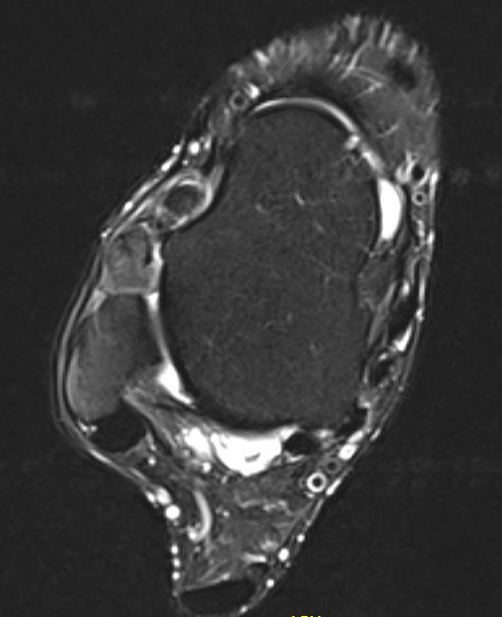
PVNS anterolateral gutter ankle
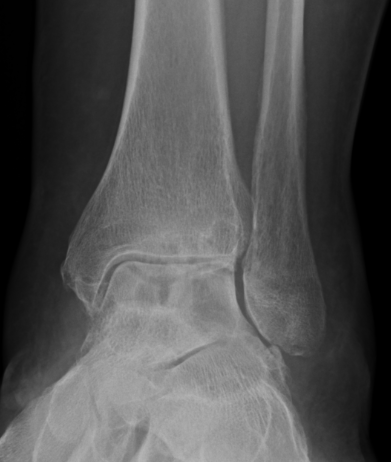
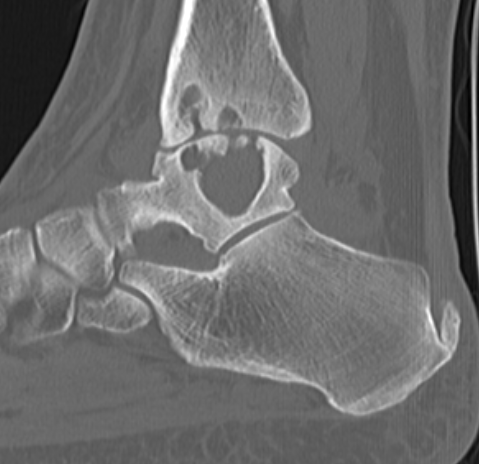
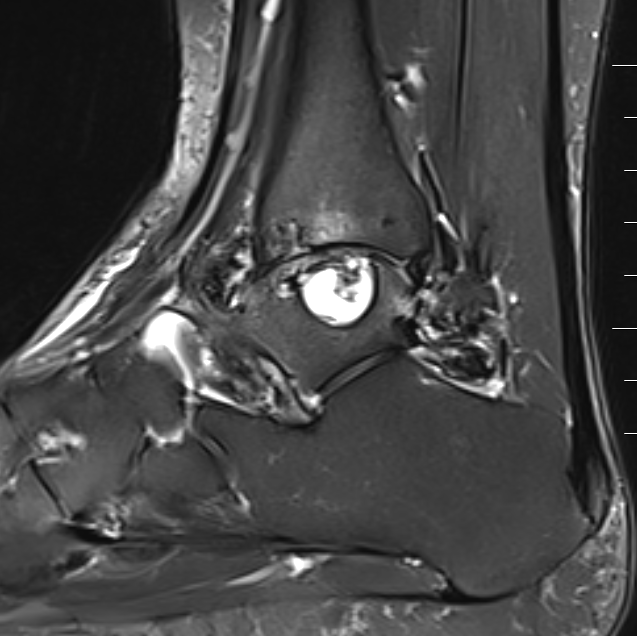
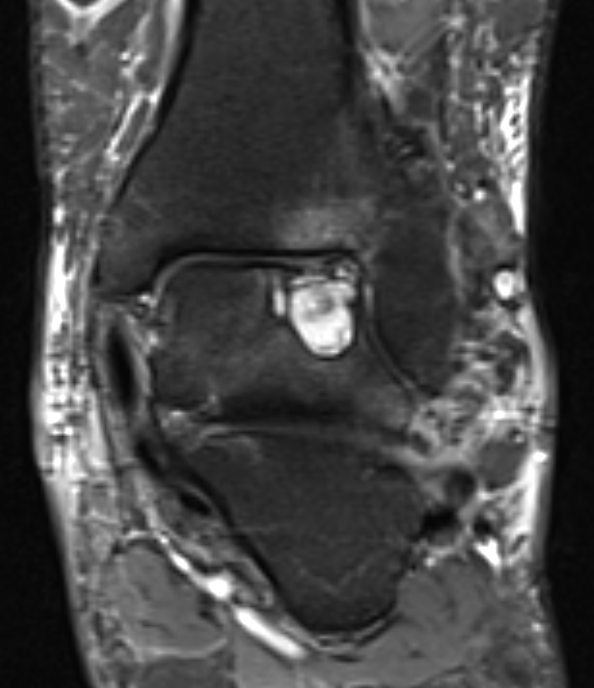
PVNS with ankle joint / talus erosion
Treatment
Surgical technique ankle arthroscopy for PVNS
Complete synovectomy
- recurrences common with diffuse disease but not all symptomatic
Results
- systematic review of 25 studies and 382 patients with PVNS foot and ankle
- diffuse: recurrence rate 21%
- localized: recurrence rate 7%
Barnet et al Foot Ankle Int 2023
- 123 cases ankle PVNS
- recurrence rate 37% with diffuse PVNS
- patients with pain and pre-operative erosive change - 57% had postoperative pain
Synovial osteochondromatosis
www.boneschool.com/synovial-osteochondromatosis
Chondroid metaplasia of synovium (synovial chondromatosis)
- form nodules of hyaline cartilage
- break free into joint
- lesions can mineralize or ossify (Synovial osteochondromatosis)
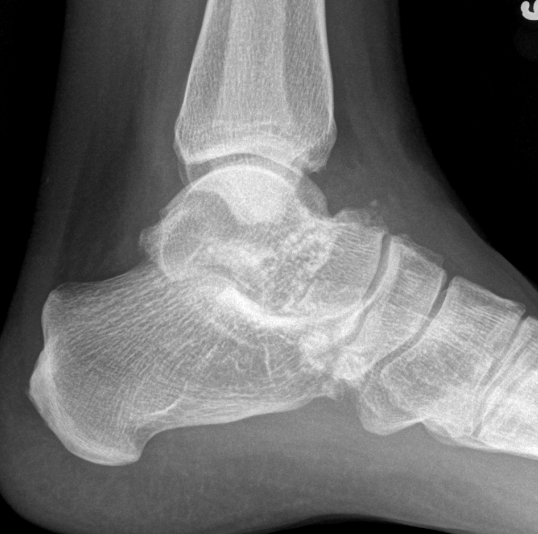
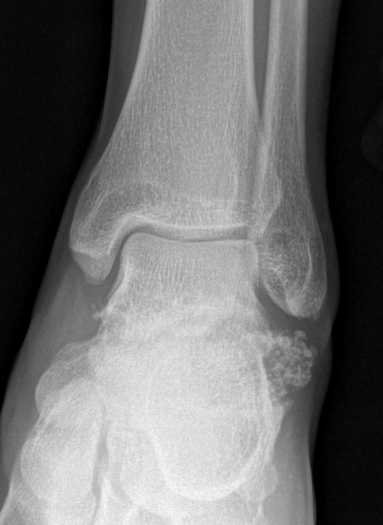
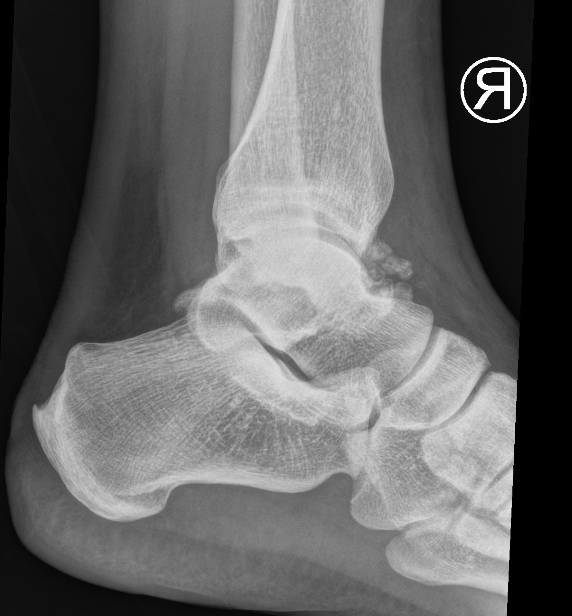

Ankle
Bojanic et al Foot Ankle Int 2021
- 17 patients
- 14/17 had anterior and posterior compartment involvement
- 2/17 dissatisfied
- no recurrence
Solitary Hemangioma
Present with episodes of dependent swelling
Diffuse edges / can be difficult to palpate
Diagnose on MRI - hyper-intense on T2
Treatment
- only needs excision if limits function
- often incomplete - recur
