Definition
Disorder of immune system characterized by antigen-antibody complexes
Epidemiology
Pharmaceutical treatment decreasing severity
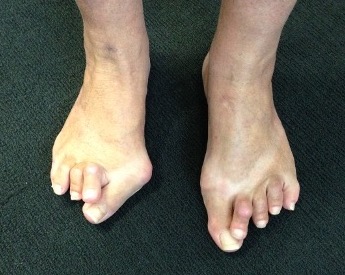
90% will have foot problems, most commonly forefoot
Tominaga et al Mod Rheumatol 2023
- incidence for surgery for RA decreasing over 20 years
- with the exception of foot and ankle surgery
- 5,500 RA patients
- 44% first symptom was foot and ankle
- patients with foot and ankle involvement reported higher disability and lower QOL
Pathology
| Forefoot | Midfoot | Hindfoot |
|---|---|---|
|
Hallux Valgus / Rigidus |
TNJ OA |
Planovalgus |
|
MTPJ synovitis Dorsal subluxation MTPJ |
Achilles tendonitis |
|
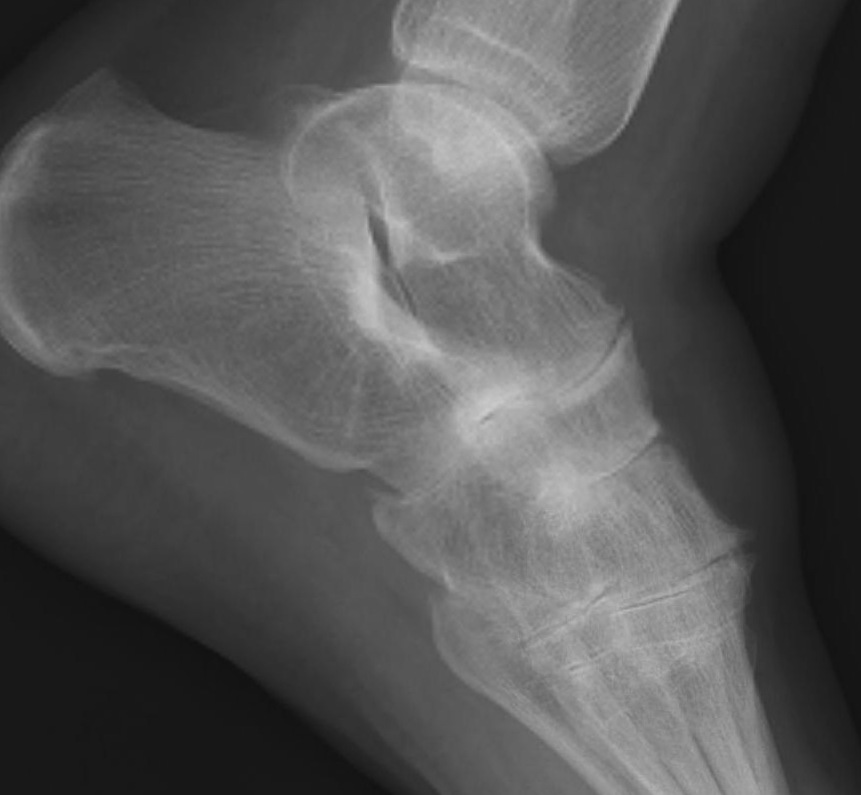
| Clawing of toes | Ankle joint / subtalar joint OA |
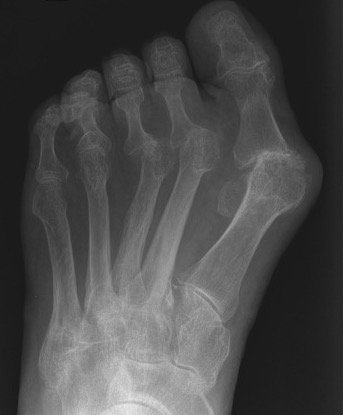
Forefoot
Great toe
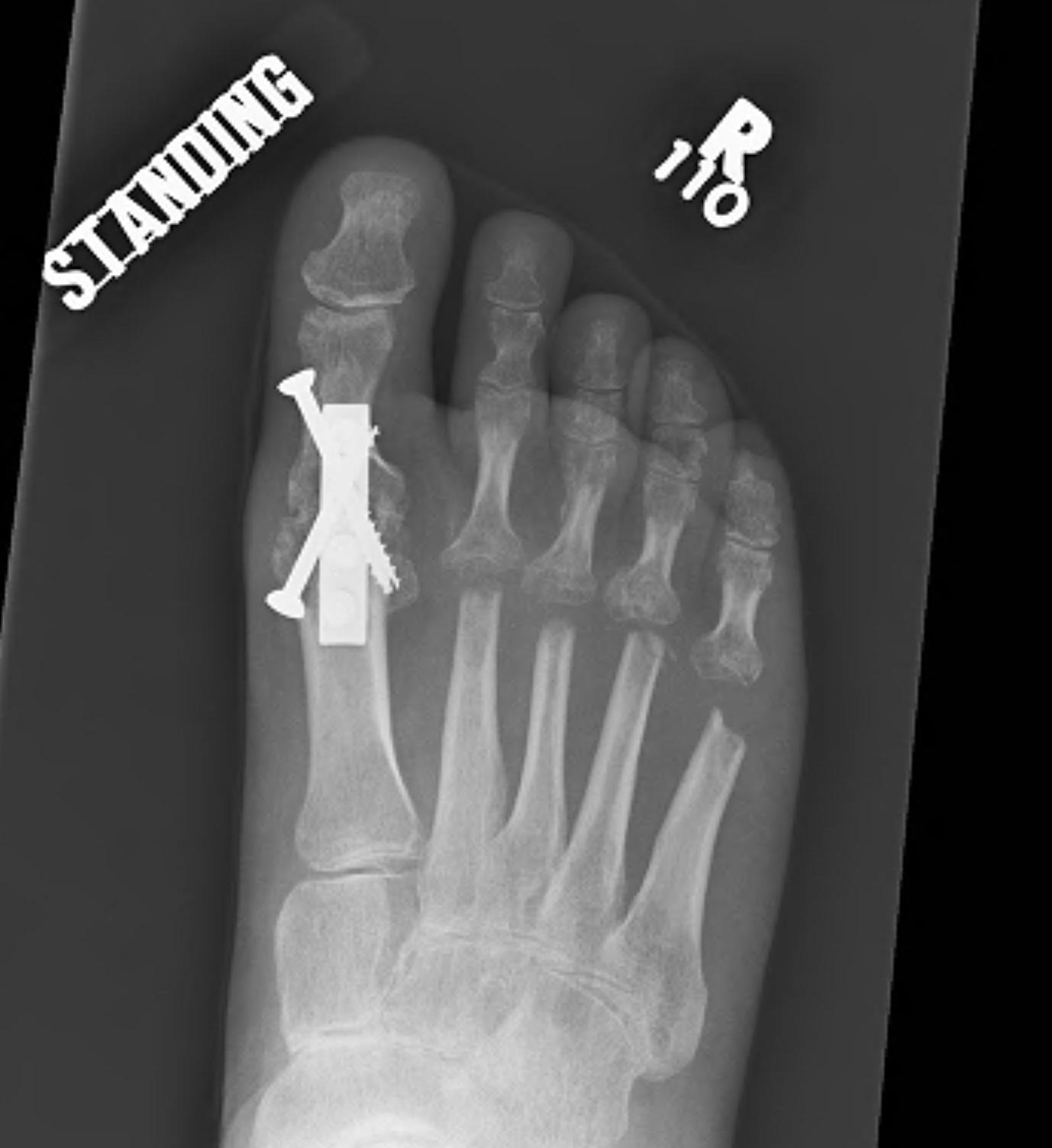
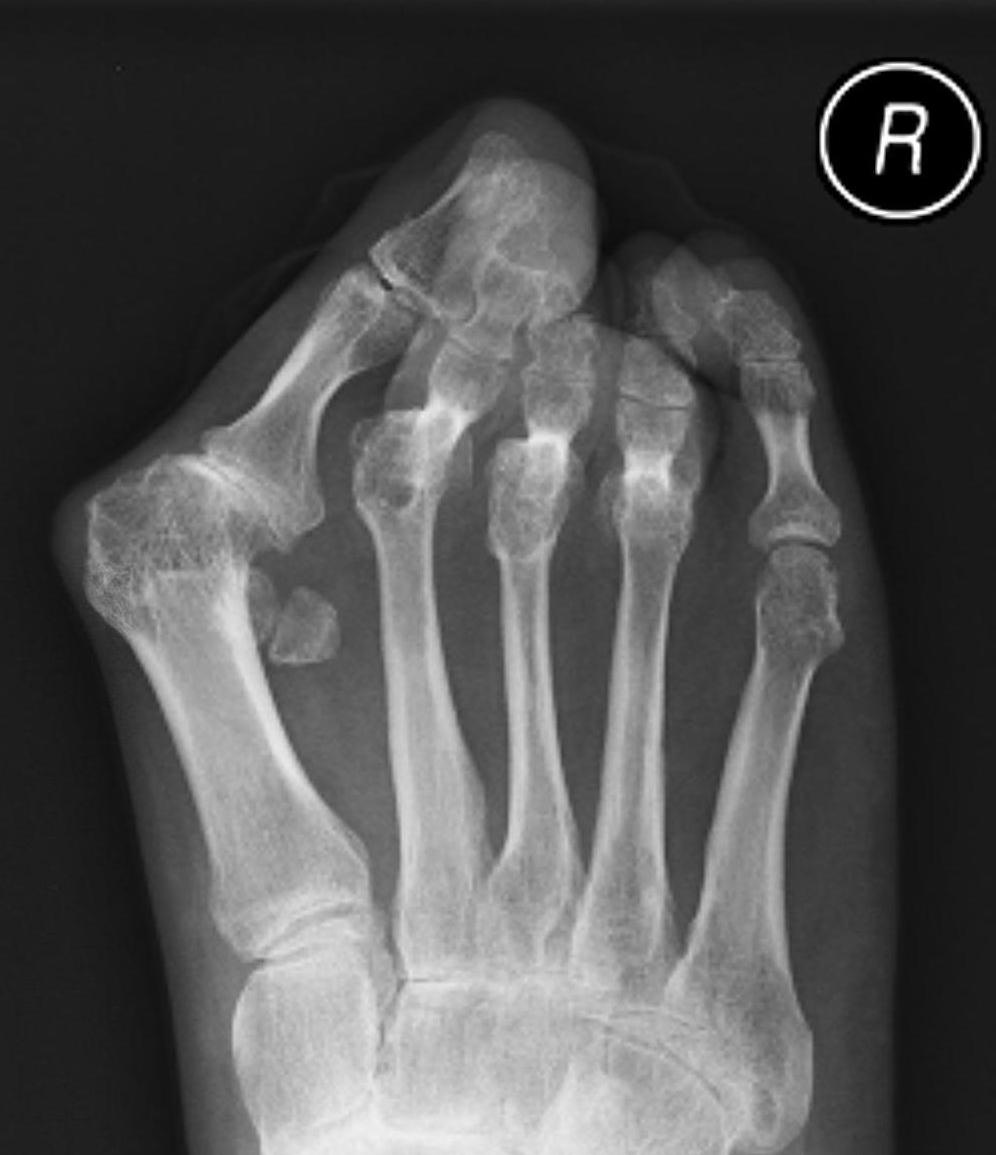
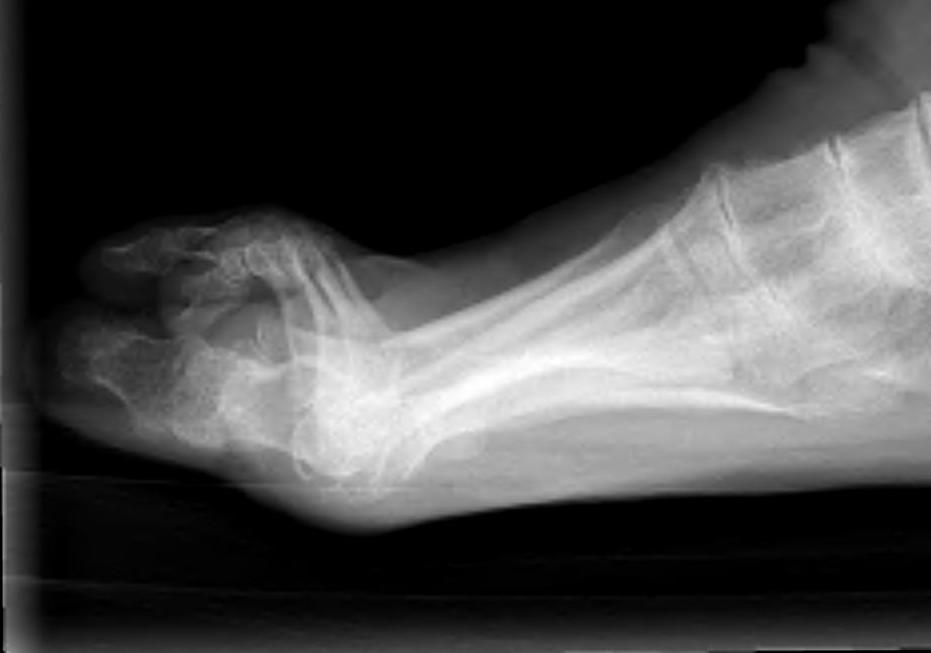
Hallux valgus / rigidus
Operative Options
Osteotomy / Arthrodesis / Arthroplasty / Keller's procedure (excision arthroplasty)
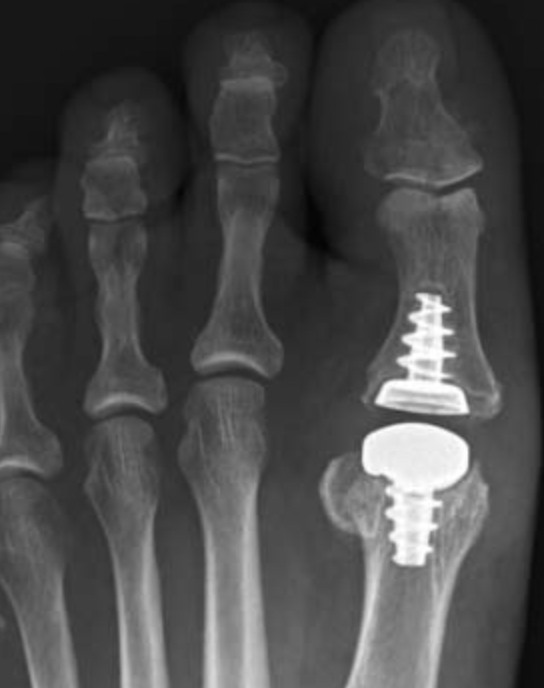
Results
Dai et al Zhongguo Gu Shang 2012
- 1st MTPJ fusion in 129 feet with RA
- 3% nonunion
He et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2021
- systematic review of 1st MTPJ arthrodesis v arthroplasty in RA
- no difference in pain score, outcome, or reoperation rates
- complications of Keller procedure
- hallux valgus, cock up, flail toe
- reserve for salvage only
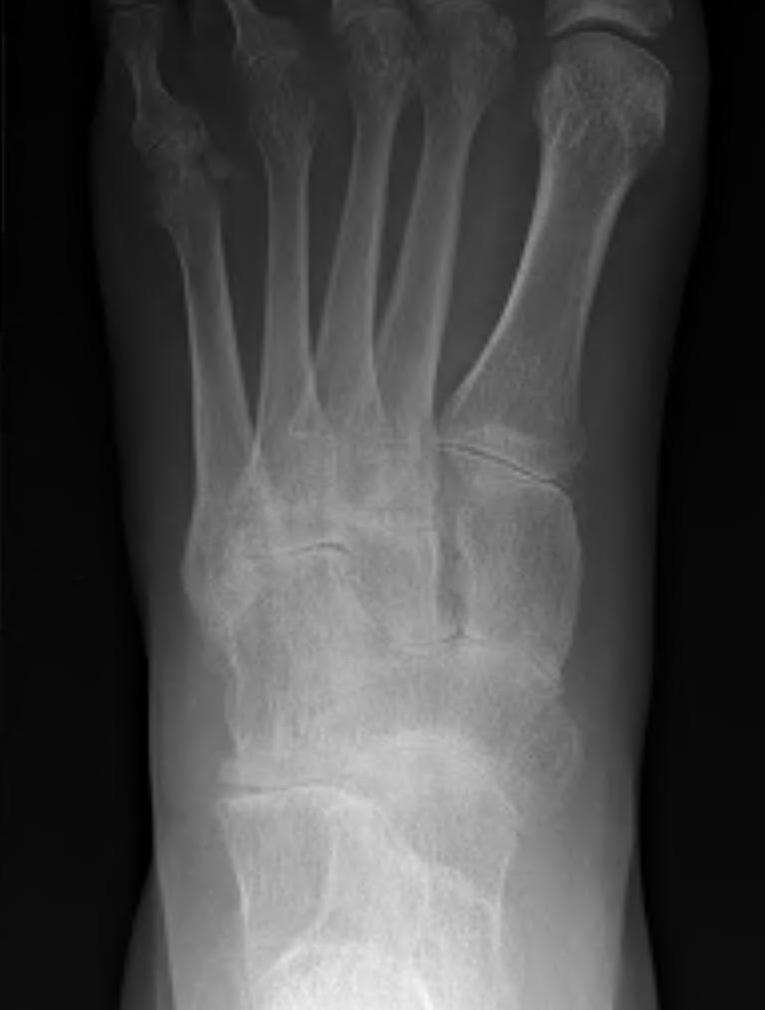
Metatarsalgia
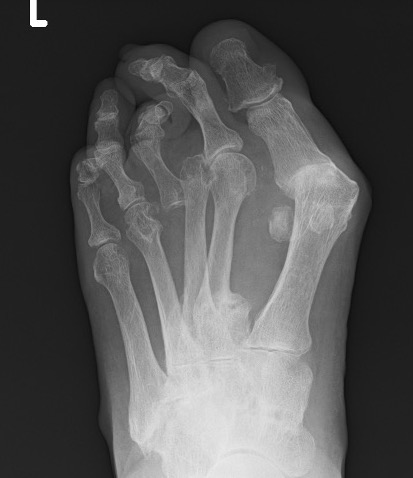
Pathology
Synovitis of MTPJ with capsular destruction
- dorsal subluxation MTPJ
- claw toes develop (MTPJ hyperextended, PIPJ flexed)
- plantar fat pad displaced distally and metatarsal heads exposed to plantar skin
Operative Options
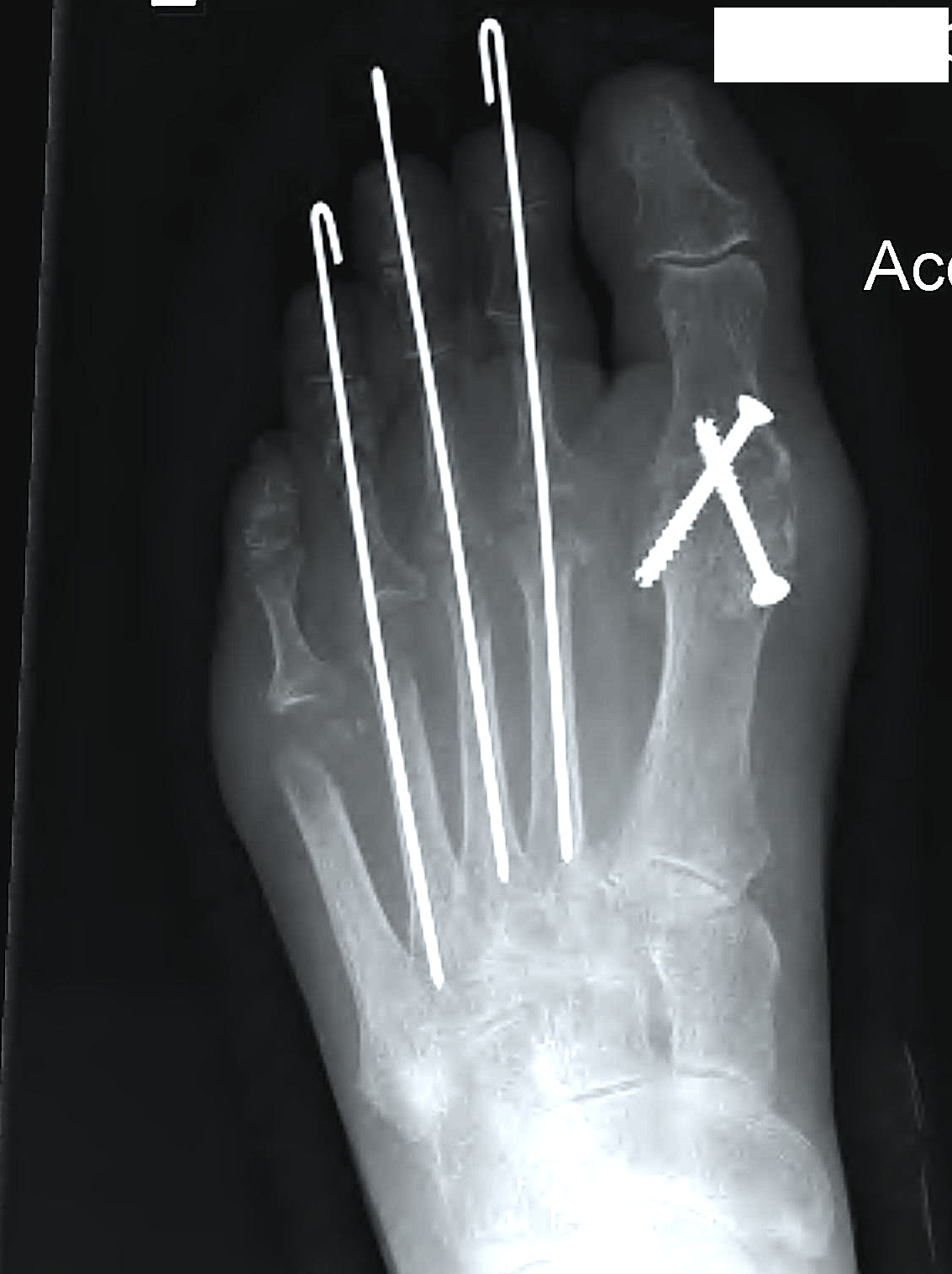
Synovectomy / Weil's osteotomy / Fowler's procedure (excision arthroplasty)
www.boneschool.com/metatarsalgia
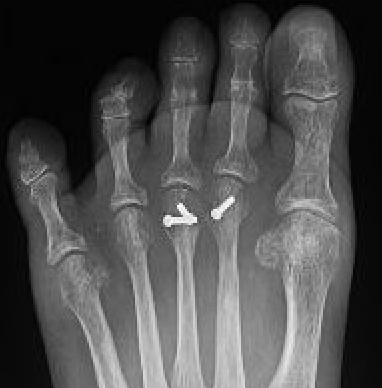
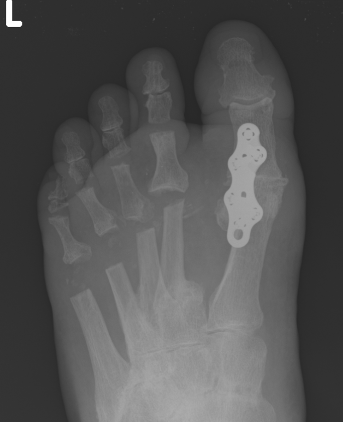
Results
- Weil osteotomy in 72 RA feet
- 88% good or excellent results
- recurrent / persistent subluxation in 14%
Horita et al Foot Ankle Int 2018
- 16 resection arthroplasty v 18 Weil osteotomy in RA
- resection: outcome score 84, recurrence 3 feet
- osteotomy: outcome score 90, recurrence 1 foot
Fowler's Procedure - metatarsal head excision

Dorsal transverse skin excision just proximal to toe webs
- can be performed via transverse plantar ellipse
- with severe dislocation may be easier to approach through plantar aspect
Extensor tenotomy
Cascading excision of II - V metatarsal heads
- dorsal distal to plantar proximal
- contoured on plantar surface to give rounded surface
Claw toes
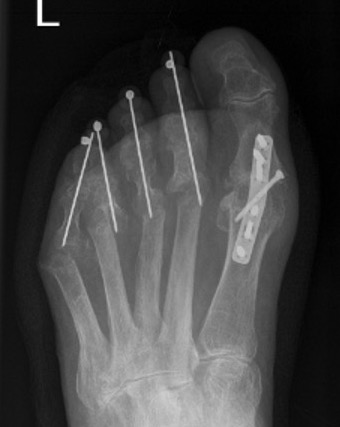
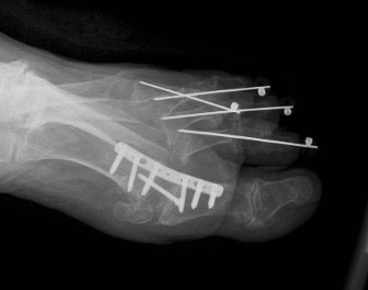
Options
Extensor tenotomy / PIPJ fusion
www.boneschool.com/lesser-toes
Midfoot
TNJ osteoarthritis
Commonly affected in RA
Talonavicular arthrodesis
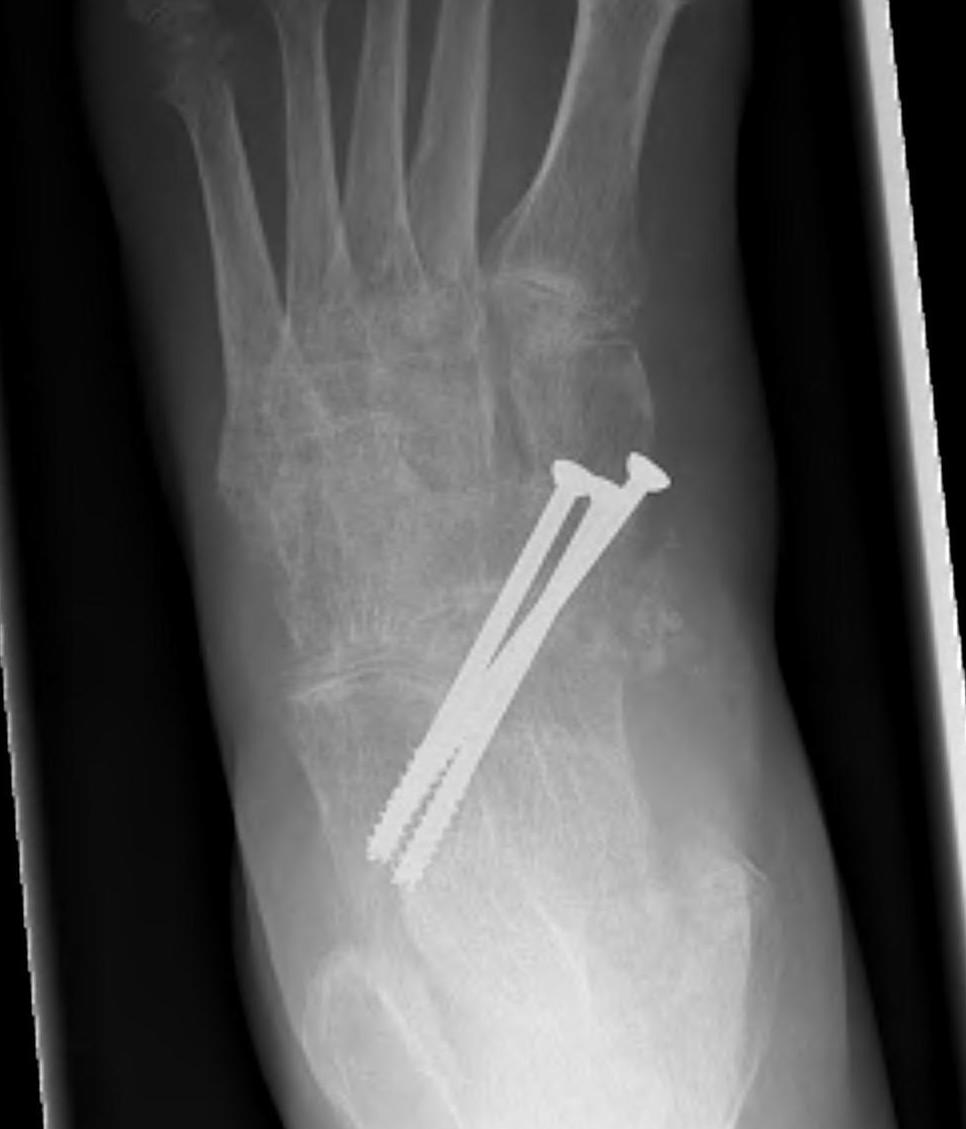
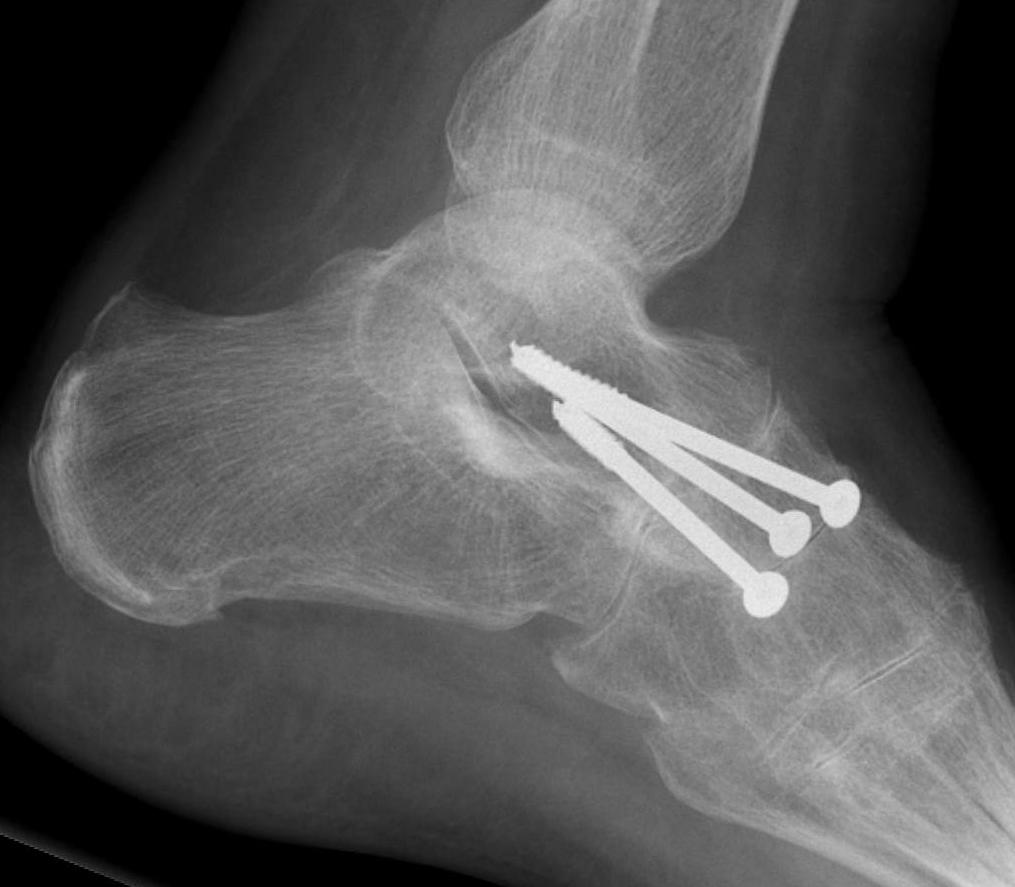
Arthroscopic technique isolated TN arthrodesis
Goh et al Foot Ankle Surg 2022
- 40 cases of isolated TN arthrodesis
- higher fusion rates with plate + screws versus screws alone
Hindfoot
Insertional Achilles Tendonitis
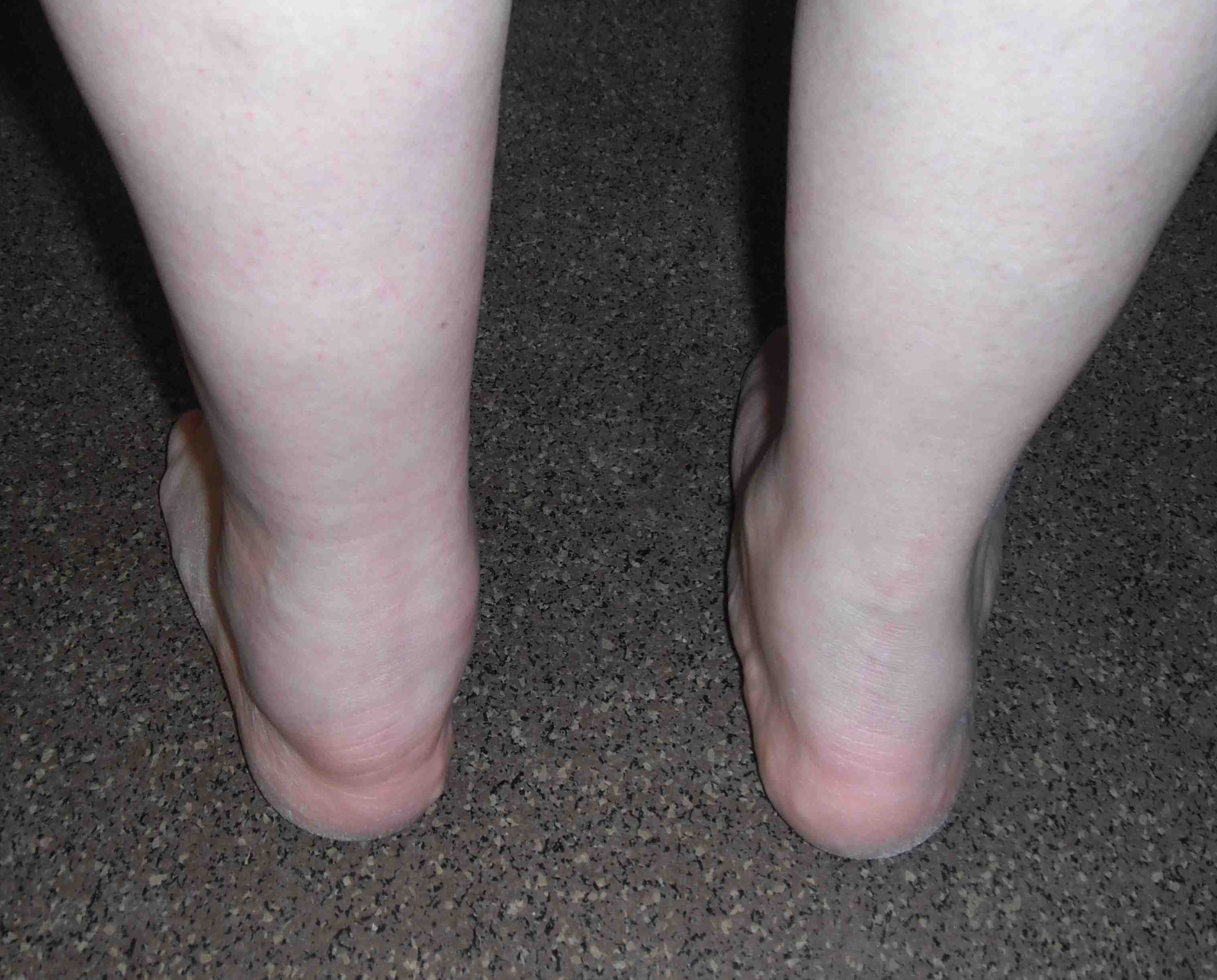
Rheumatoid involvement of bursa at Tendo Achilles insertion
- nodules may develop within the tendon
- can weaken attachment & precipitate rupture
Treatment
- excision of nodules
- may need tendon augmentation / reconstruction
www.boneschool.com/insertional-achilles-tendinopathy
Planovalgus
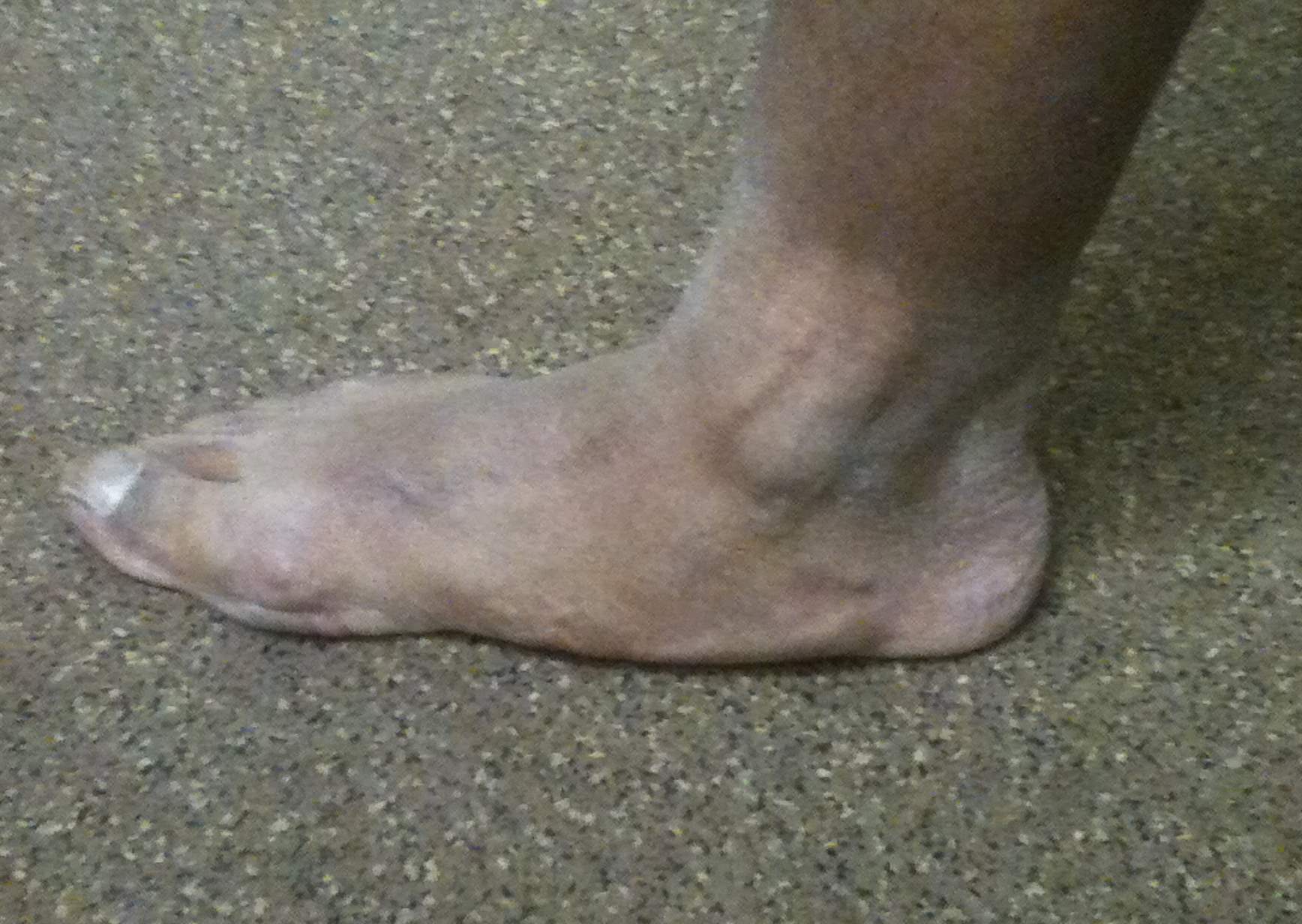
Causes
- STJ OA / TNJ OA
- tibialis posterior rupture
- synovitis and rupture of the talocalcaneal interosseous ligament
www.boneschool.com/tibialis-posterior-dysfunction
www.boneschool.com/triple-arthrodesis
Ankle joint arthritis
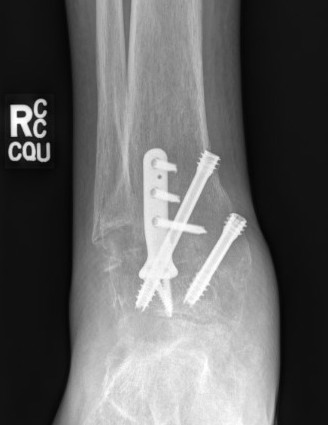
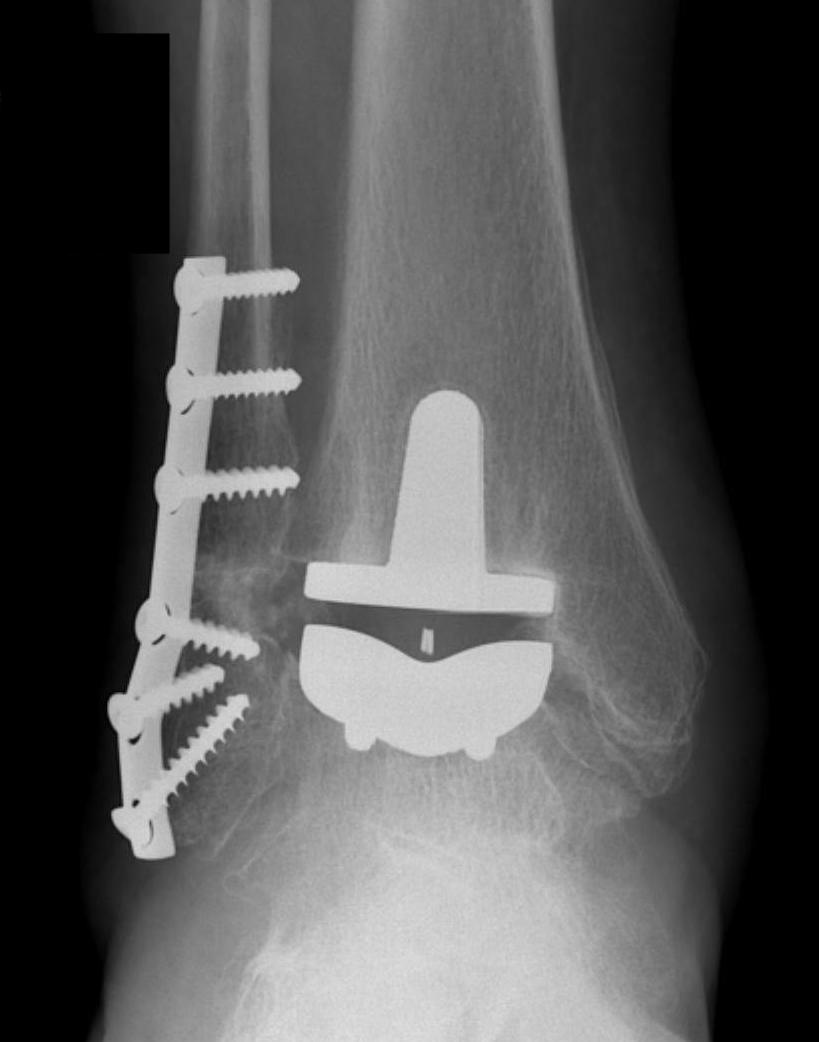
Ankle synovectomy
- arthroscopic synovectomy of the ankle in 18 patients with RA
- 78% clinical success
- improvements plateau at 12 months then decline
Total ankle arthrodesis / ankle arthrodesis
van Heiningen et al BMC Musculoskeletal Disorder 2013
- systematic review of ankle arthroplasty v arthrodesis in RA
- 17 studies and 800 patients
- similar outcomes
- reoperation rates 11 - 12%
Mousavian et al Foot Ankle Spec 2023
- systematic review of ankle replacement in inflammatory v non inflammatory arthritis
- no difference in outcomes or complication rate
- isolated ankle arthrodesis in 20 RA patients
- 90% union rate