Definition
Dislocation of the talo-calcaneal and talonavicular joint
No talar neck fracture
Epidemiology
Rare
1% of all dislocations
Male:Female 6:1
Types
Based upon direction of calcaneal dislocation
Lugani et al Musculoskeletal Surg 2022
- systematic review of 387 subtalar dislocations
- 68% medial
- 28% lateral
- 2% posterior / 1% anterior
- 28% open dislocations
1. Medial
- calcaneum dislocated medially
- more common
- forced inversion in plantar flexed position
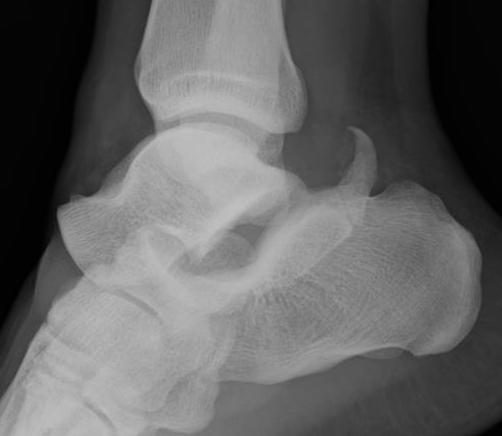
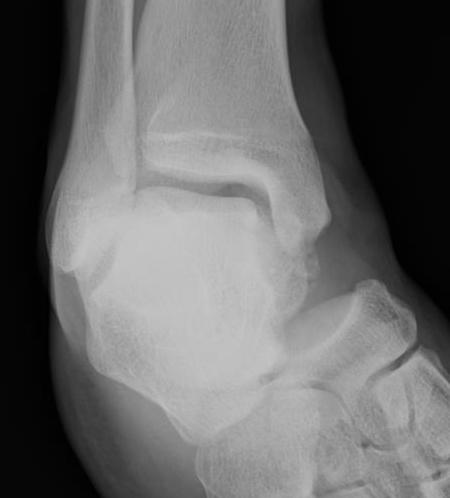
Medial subtalar dislocation
2. Lateral
- calcaneum dislocated laterally
- high energy trauma
- often associated with fractures
- can be difficult to reduce due to incarceration of tibialis posterior and FDL
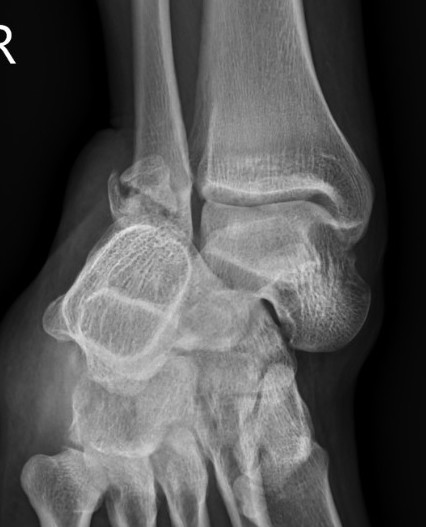
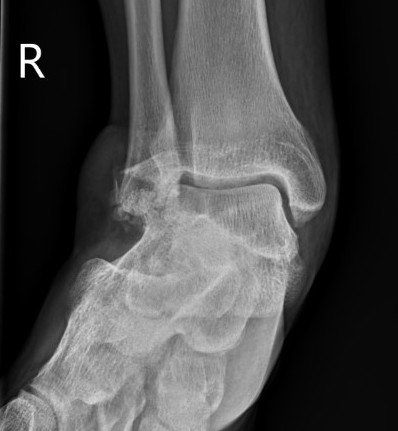
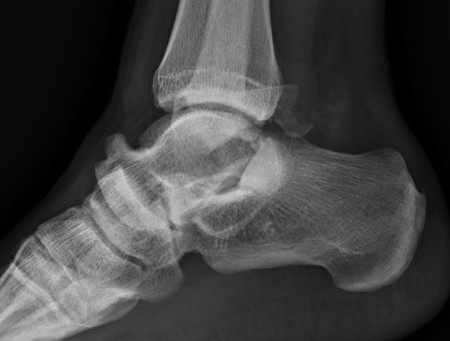
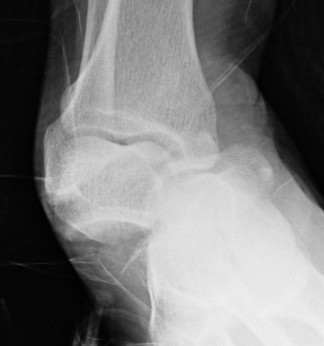
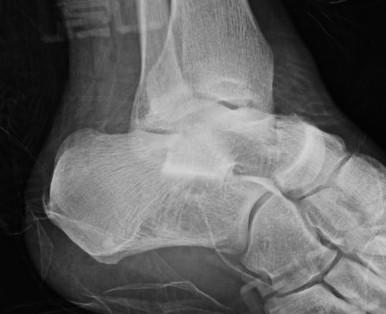
Lateral subtalar dislocation with fracture of the lateral malleolus
3. Anterior / posterior (rare)
Pathology
Tearing of strong interosseous ligament
Dislocation of talonavicular joint / talo-calcaneal
Reduction
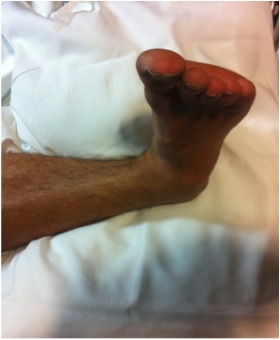
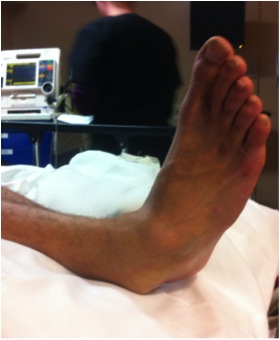
Technique
Conscious sedation
- flex knee to relax gastrocnemius
- increase deformity
- reduce calcaneum whilst holding talus
Usually stable after reduction
- 4 weeks in a cast
Failed reduction
Lugani et al Musculoskeletal Surg 2022
- systematic review of 387 subtalar dislocations
- overall failure closed reduction in 32%
- medial: 25% required open reduction
- lateral: 48% required open reduction
Blocks to reduction
- medially - talar head buttonholes through capsule / FHL / EDB / fracture fragments
- laterally - tibialis posterior (most common) / FDL / FHL / fracture fragments
CT post reduction
Ensure
- congruent reduction
- look for fractures of talus / calcaneum
- look for intra-articular fragments
Lugani et al Musculoskeletal Surg 2022
- systematic review of 387 subtalar dislocations
- fractures see in 13% of cases on CT scan
- head of talus / body of talus / lateral process
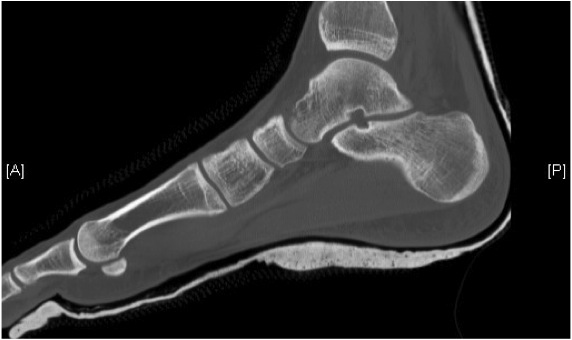
Congruent reduction

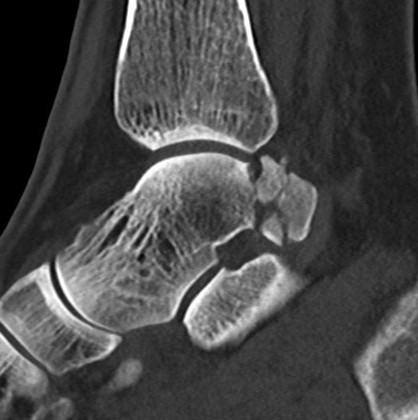
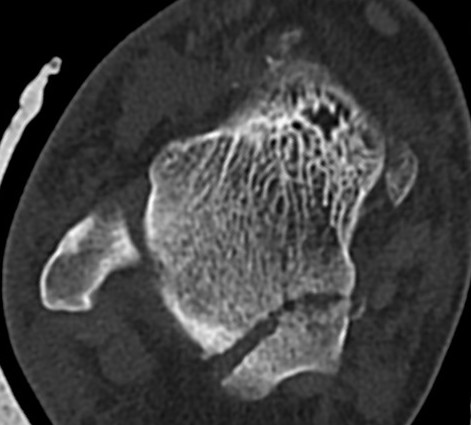
Posterior process fracture talus after medial subtalar dislocation
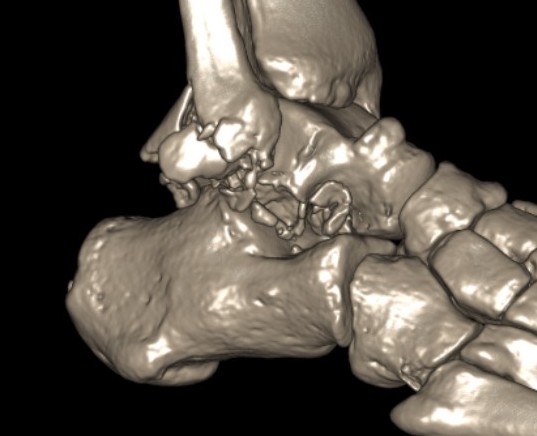
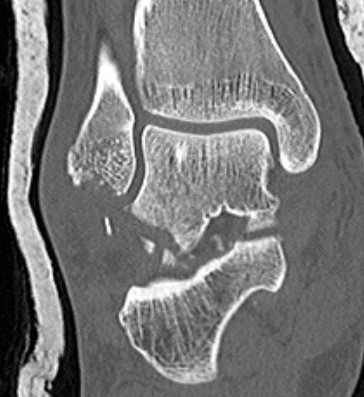
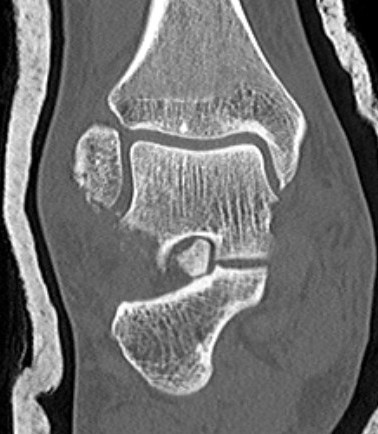
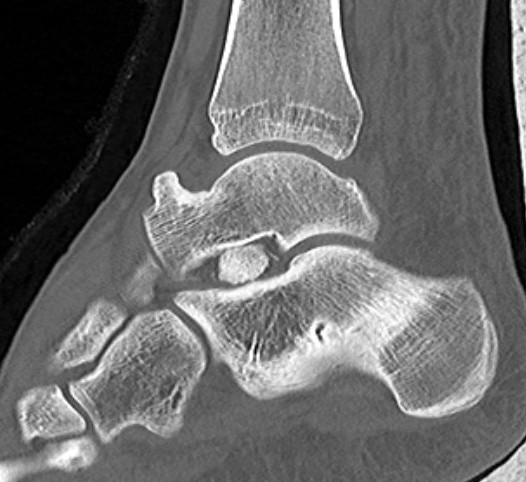
Fibular fracture and subtalar loose bodies after lateral subtalar dislocation
Results
Generally
- stiff subtalar joint
- reduced functional outcome
- subtalar OA associated with associated fractures
Isolated subtalar dislocation (no fracture)
De Palma et al Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2008
- 30 patients with isolated subtalar joint dislocations, AOFAS score at 5-12y follow up
- 7 medial dislocations AOFAS 100
- 14 (11 medial, 3 lateral) AOFAS 85
- 6 patients (3 medial / 3 lateral) AOFAS 65
- 3 patients (all lateral subtalar dislocation) AOFAS 23 (all underwent subtalar fusion)
Ruhlmann et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2017
- 13 isolated subtalar dislocations with 6 year follow up
- all treated with closed reduction
- good result in 69%
- poor result in 31%
- 62% had reduced subtalar ROM
- subtalar OA in 46%
- talonavicular OA in 23%
Subtalar dislocations with associated fractures
Bibbo et al Foot Ankle Int 2003
- 25 subtalar dislocations with 5 year follow up
- 88% had associated injuries to foot and ankle
- subtalar OA seen in 89%, mostly in patients with subtalar fractures
- 4 patients required subtalar fusion
Complications
Stiff subtalar joint
Subtalar OA
Talonavicular OA