techniques
Deltoid ligament injury
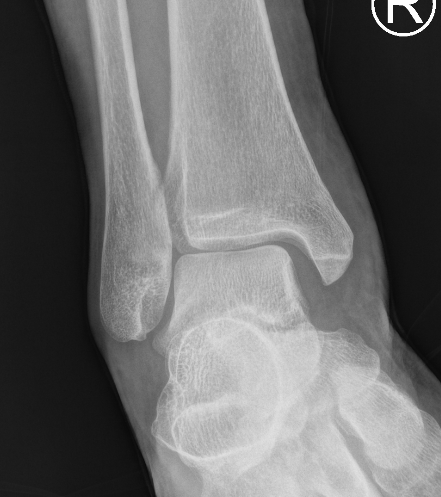
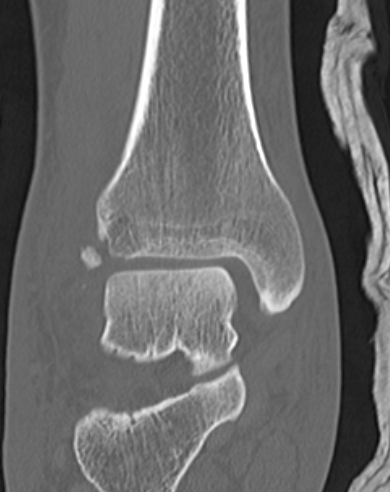
Etiology
Ankle sprain
- eversion / external rotation
Ankle fractures
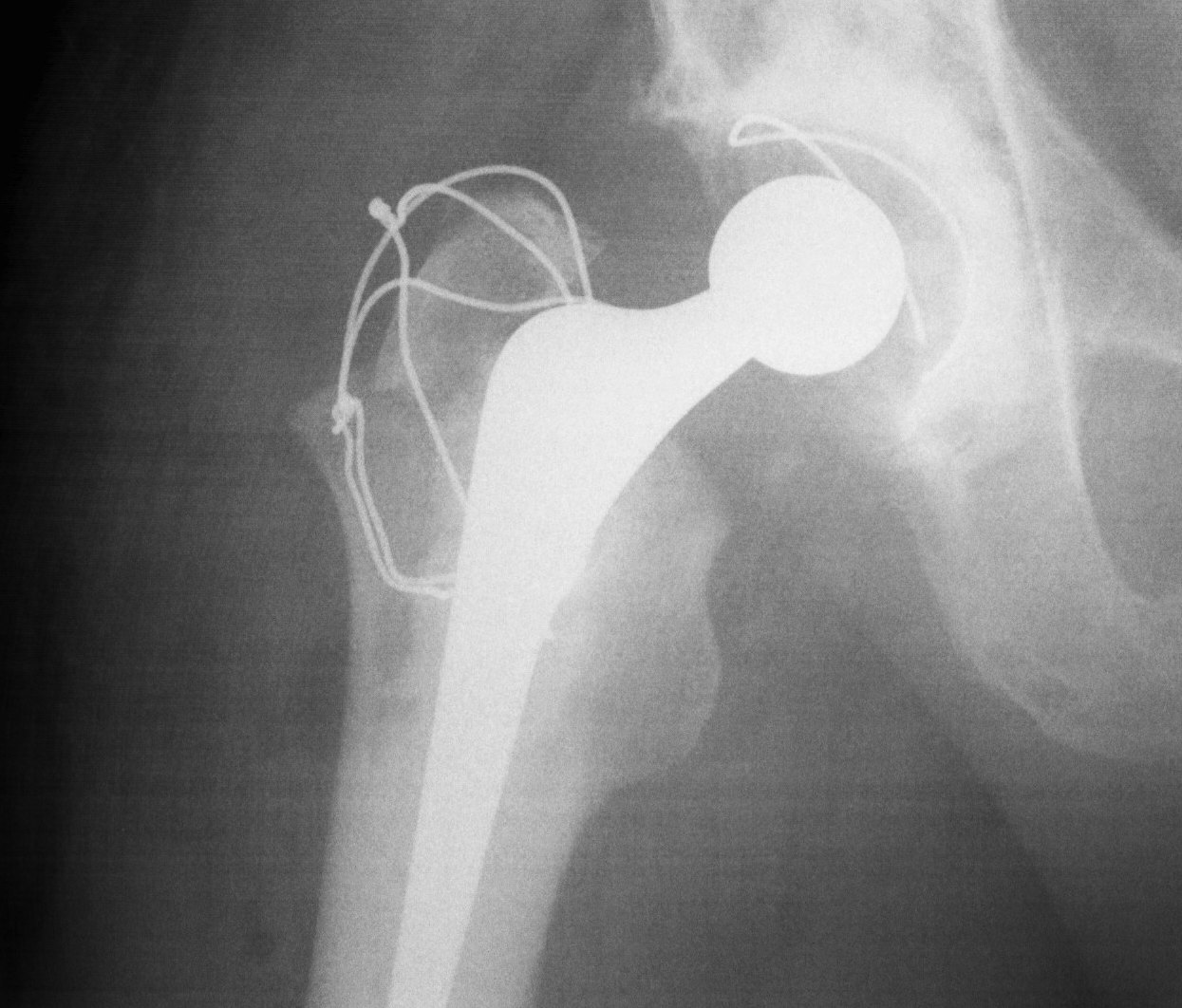
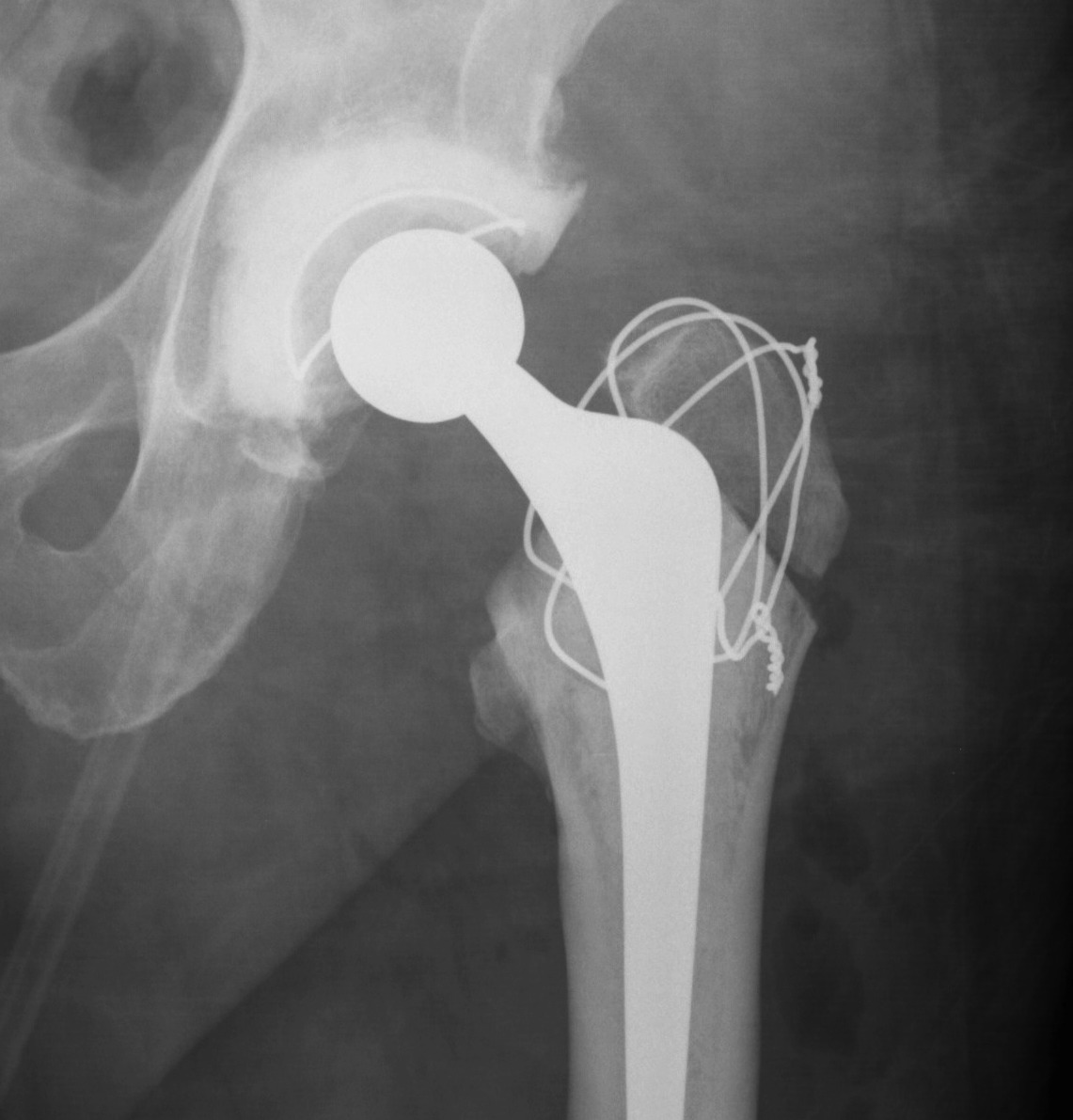
Trochanteric Osteotomy
Types
1. Standard trochanteric osteotomy
2. Sliding trochanteric osteotomy
3. Extended trochanteric osteotomy
Standard Trochanteric osteotomy
Tibial tubercle fractures
Epidemiology
Adolescent boys
Ossification
Proximal tibia / primary ossification centre
Tibial tuberosity / secondary ossification centre
- eventually merges with primary ossification centre
Ogden Classification
Type I - Tibial tuberosity ossification only
TFCC tears
Definition
Present with pain but not instability
Types
Traumatic
Degenerative
Different treatment algorithms for each
History
Ulna side wrist pain
- may be worse with rotation
- opening doors and jars
History of trauma
Examination
Local tenderness DRUJ
Stems
Advantage
1. Reduce implant loosening
- offset load sharing to diaphysis
- 30% if > 70 mm
2. Restore optimal alignment
Indications
1. Using augments or bone grafting
2. Increased constraint
- VVS / hinge
Full thickness tears
Surgical Options
1. Open antero-lateral approach
Large / Massive Cuff Tear
2. Deltopectoral approach
Large Subscapularis tear
3. Arthroscopic Assisted Mini-open
Indication
- Small / Moderate Cuff Tear < 3cm
- no retraction
Technique
- arthroscopic SAD
De Quervain syndrome
Definition
Stenosing tenosynovitis of the first dorsal compartment of wrist
Epidemiology
Most are middle aged women
Aetiology
Repetitive thumb movements
- abduction & extension
- combined with RD & UD movements
Any mechanical irritation
- foreign body
- prominent bony surface
- restricted fascial compartment
Subscapularis tears
Anatomy
Largest and most powerful rotator cuff
- arises coastal border of scapula
- superior 2/3 tendon inserts into LT
- inferior 1/3 inserts into proximal humerus
Action
- IR (with T major, P major, Lat Dorsi)
- part of force couplet depressing humeral head
Incidence