Etiology
Repetitive high impact exercises
- athletes - runners / gynmasts / dancers / soccer players / basketball
- military
Predisposing factors
- female triad - amenorhea, disordered eating, low bone mineral density
- nutritional deficiencies
- Vitamin D deficiency
Locations
| Posteromedial cortex | Anterior cortex | Tibial plateau |
|---|---|---|
|
Most common
|
4% of tibial stress fractures | |
|
Compression side Better prognosis
|
Tension side More problematic May develop dreaded black line / fracture |
Signs
Pain with activity
Point tenderness on tibia
Differential diagnosis
Shin splints / medial tibial stress syndrome
- medial tibial periosteitis
Exertional compartment syndrome
Xray
Cortical thickening
Look for "dreaded black line" - sign of fracture

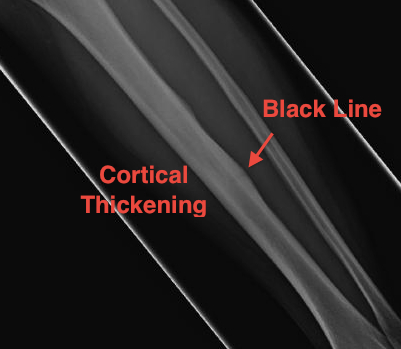
Periosteal thickening with possible "dreaded black line"

Anterior cortical thickening with dreaded black line
Bone scan
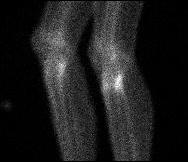
Increased uptake tibial plateau
MRI
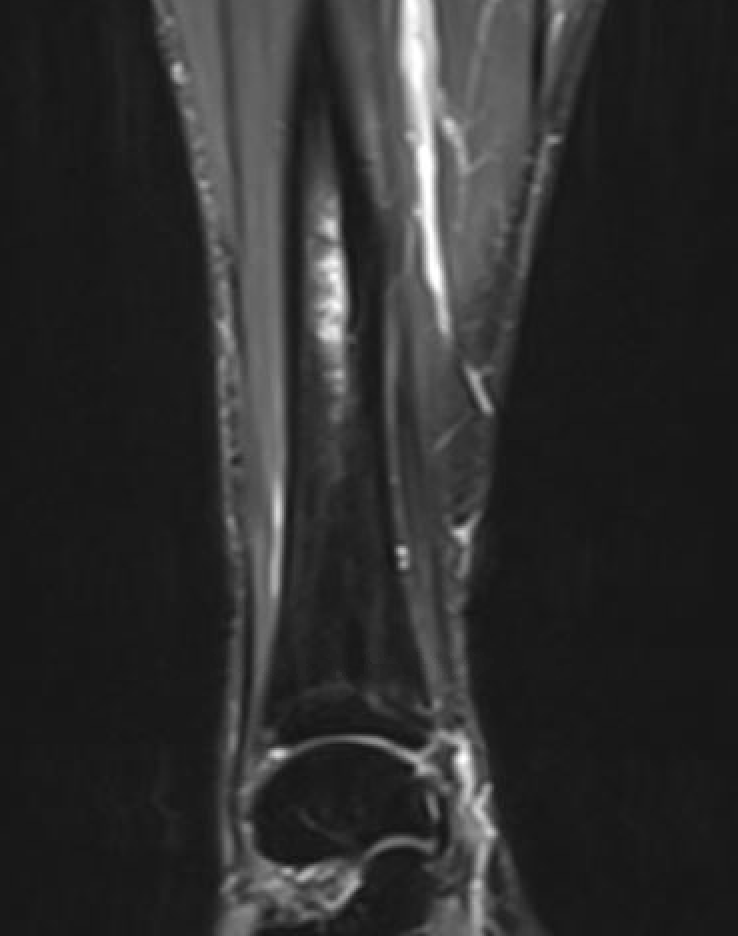
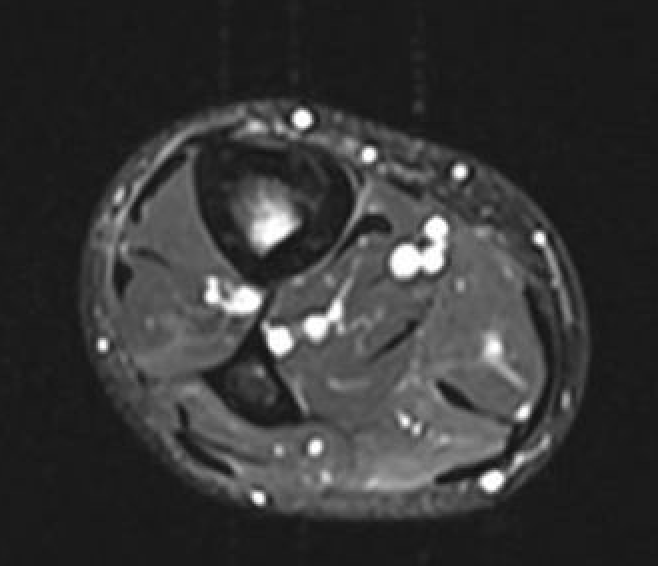
Fredericson Classification of Medial Tibial Stress Fractures on MRI
Grade 1: Periosteal edema
Grade 2: Bone marrow edema on T2
Grade 3: Bone marrow edema on T1 and T2
Grade 4a: Intra-cortical stress changes
Grade 4b: Frank tibial stress fracture
CT
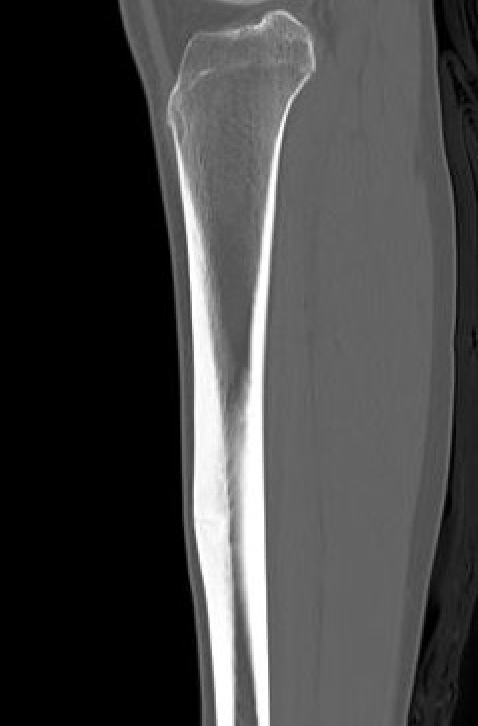
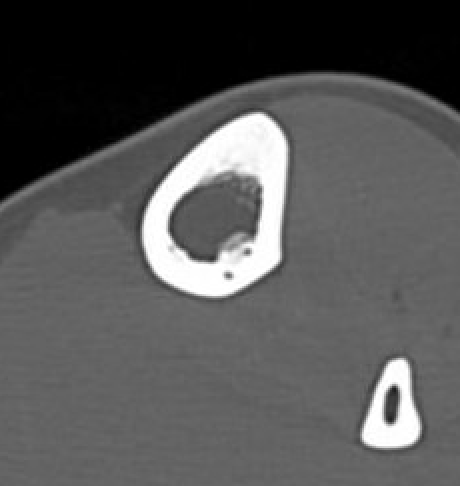
Nonoperative management
Options
Rest
Air cast brace
Extra-corporeal shock wave
Low intensity pulsed ultrasound / Exogen /bone stimulator
Air cast brace
- RCT of 31 patients with tibial stress fracture air cast v no air cast
- no difference in outcomes
Low intensity pulsed ultrasound
Results
Ditmars et al Pediatr Radiol 2020
- 42 tibial stress fractures < 19
- mean return to play with no pain 55 days
- no correlation to Fredericson grading
Schundler et al Arthrosc Sports Med 2023
- systematic review of operative v nonoperative management tibial stress fractures
- 22 studies and 340 patients
- failure rate nonoperative: 0 - 25%
- failure rate operative: 0 - 6%
Operative Management
Indication
High risk - anterior stress fractures
Options
Intra-medullary nail
Anterior tension band plating
Liimatainen et al Scand J Surg 2009
- drilling of stress fracture in 20 patients
- union rate 50%
- fixation union rate 93%
- isolated drilling not recommended
Anterior tension band plating
Technique
Fluoroscopy to identify fracture
- debride fracture +/- bone graft
- anterolateral 3.5 mm dynamic compression plate
Results
Intramedullary nail
- five cases of chronic tibial stress fractures in military treated with IM reamed nail
- minimum 1 year nonoperative treatment
- 2 excellent results (unlimited pain free running)
- 3 good results (occasional pain with vigorous exercise)
Varner et al AJSM 2005
- 7 athletes with chronic tibial stress fracture treated with IM reamed nail
- symptoms 1 year, nonoperative treatment 4 months
- return to sport by 4 months
- one patient developed bursitis at nail insertion site which settled with HCLA
- one patient developed a distal tibial traumatic fracture which healed non operatively
Anterior tension band plating
- 13 athletes undergoing anterior plating for chronic tibial stress fractures
- return to training 11 weeks
- 92% return to competition
- 38% required plate removal
IM nail v anterior plate
Randall et al Arch Orthop Trauma 2025
- systematic review of IMN v plate
- 8 studies and 37 athletes
- nail: return to sport 100%, mean time 20 weeks, 14% chronic anterior knee pain
- plate: return to sport 95% (19/20, mean time 11 weeks, 30% hardware removal
