Definition
Volar Intercalated Segmental Instability (VISI) secondary to injury to the lunate-triquetral ligament
Etiology
FOOSH
Anatomy
Lunate-triquetal ligament C shaped and strongest palmar
- scaphoid imparts a flexion moment on proximal row
- triquetrum imparts an extension moment
- balanced by ligamentous attachments to lunate
Pathology
Tear lunate-triquetral ligament and get palmarflexion of lunate with dorsiflexion of triquetrum
Classification
| CID | CIND VISI |
|---|---|
|
Static Dynamic |
Ligamentous laxity in teenage girls Entire proximal row is flexed Lunate triangular / scaphoid cortical ring sign |
|
Wrist clunking Non operative |
Symptoms
History of injury
Pain on ulnar side of wrist
Weakness
Signs
Swelling and tenderness over triquetro-lunate joint
Pain with ulna deviation / pronation / axial compression
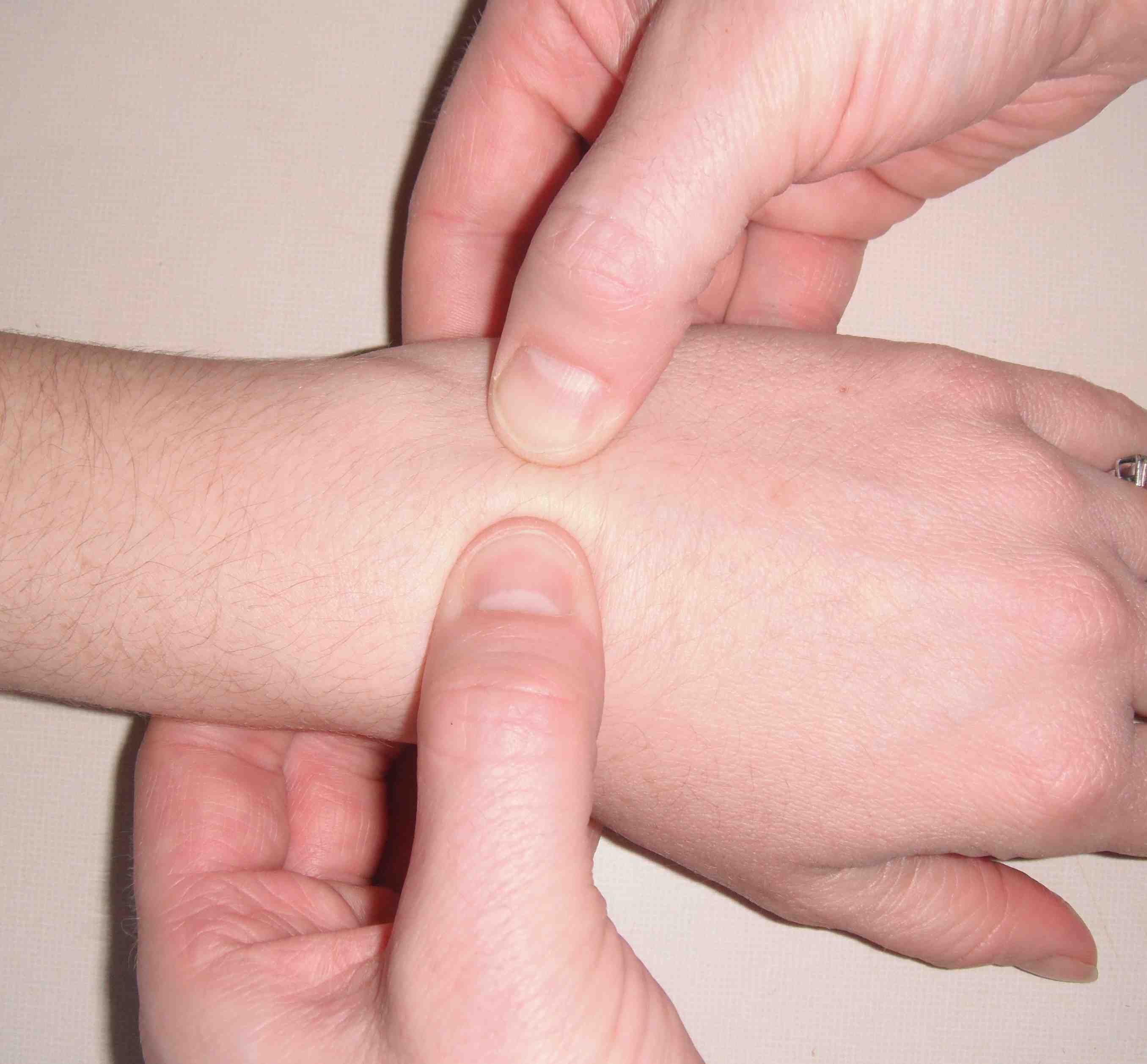
Reagan Ballotment
- Triquetro-lunate ballottement
- pisiform-triquetral with thumb and index finger
- lunate with other hand
Differential diagnosis
DRUJ instability
TFCC tear
Ulna head OA
Pisiform triquetral OA
Hamate fracture
ECU subluxation
Xray
AP xray
- palmarflexion of scaphoid - Scaphoid shortened + cortical ring sign
- palmarflexion of lunate - appears triangular
- broken Shenton's line (of proximal carpal row)
Lateral xray
- decreased scapholunate angle < 30o
- palmarflexion of lunate: capitate - lunate angle > 10o / radio - lunate angle > 10o
Operative management
Options
Repair
Reconstruct with ECU
Lunate - triquetral fusion
Technique
Dorsal approach
- restore LT orientation with K wires
- repair ligament with intra-osseous sutures
- +/- reconstruct with half of ECU through drill holes
Lunate-triquetral fusion
