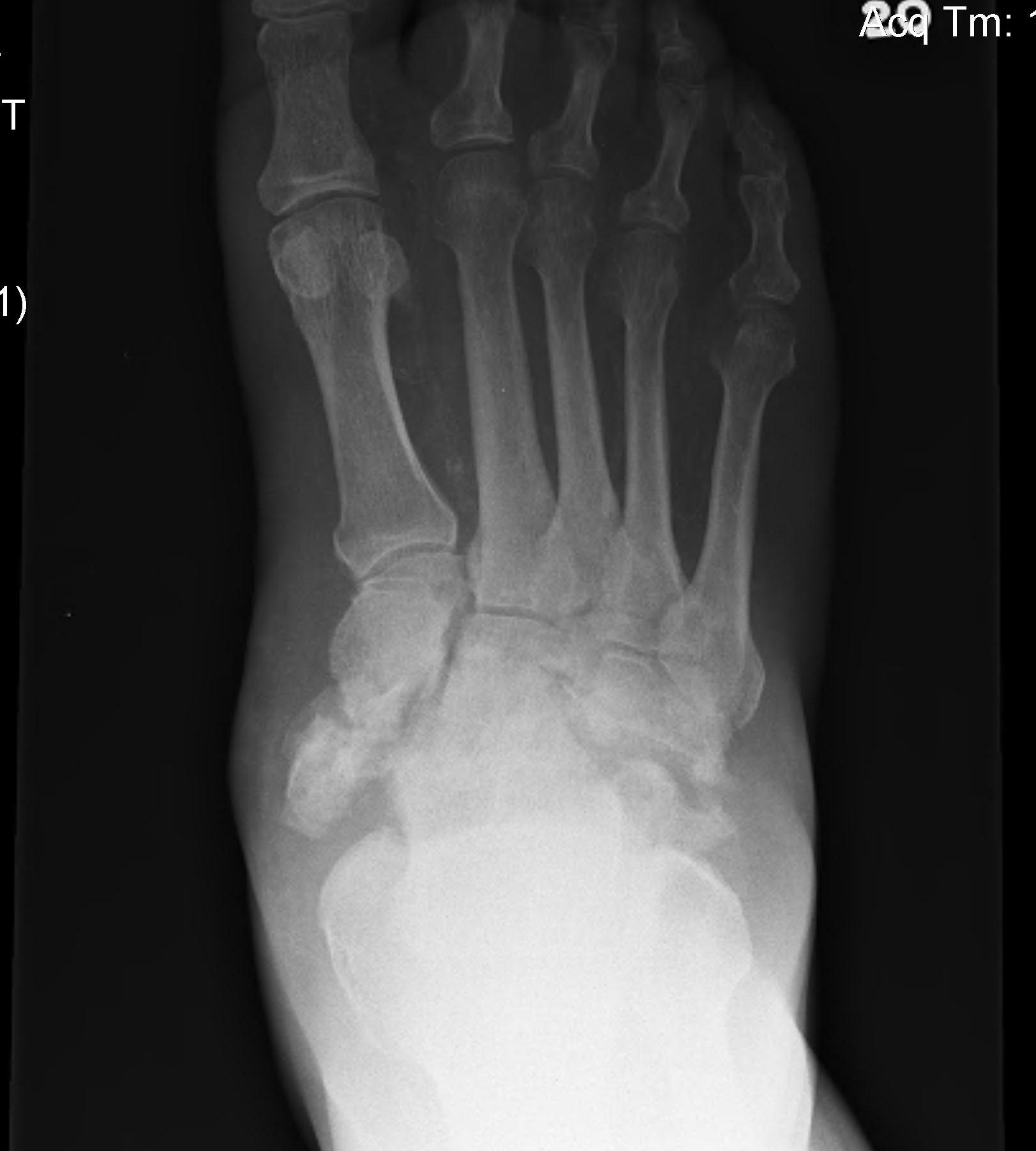
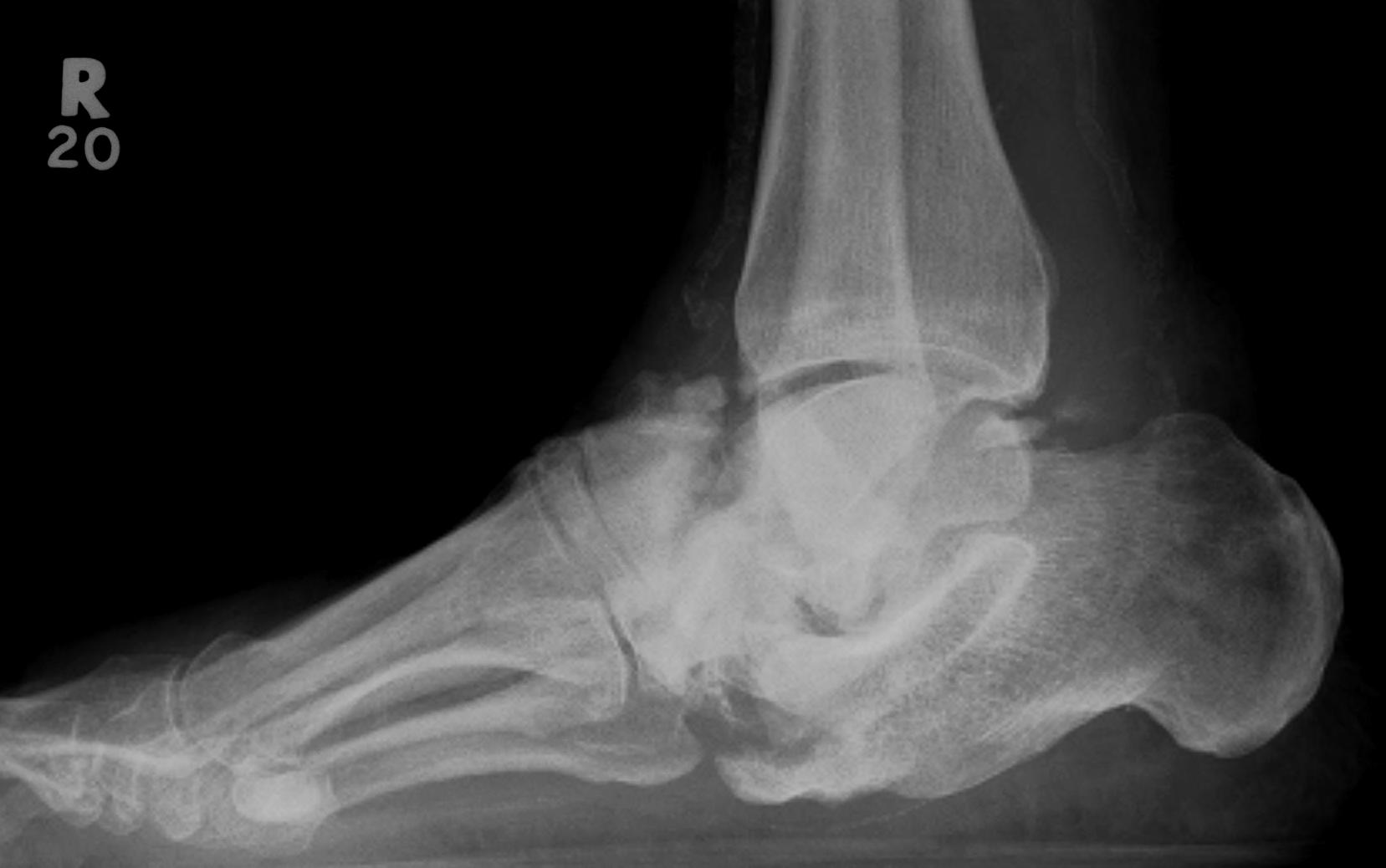
Definition
Neuropathic arthropathy
- progressive destructive arthropathy secondary to neuropathy
- usually minimal to no trauma
Etiology
SAD SLIPS
Spina bifida
Alcohol
Diabetes - most common
Syphilis (tabes dorsalis)
Leprosy
Indifference to pain (congenital)
Peripheral nerve lesions
Syringomyelia
Epidemiology
0.5 - 1% of diabetics
Onset
- 5th decade of life
- average of 15 years from onset of type II diabetes
- average of 30 years from onset type I diabetes
Pathophysiology
1. Neuro-traumatic theory - cumulative trauma in insensate foot
2. Neurovascular theory
- neurally stimulated vascular reflex stimulates bone resorption
Eichenholtz Classification
| Stage 0 | Stage 1 Dissolution | Stage 2 Coalescence | Stage 3 Reconstruction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Findings |
Acute inflammation - swollen, red, warm - reduces with elevation |
Acute inflammation - swollen, red, warm - reduces with elevation |
Inflammation decreases Reduced swelling Reduced temperature
|
Normal temperature Swelling reduced |
| Xray | Normal |
Demineralisation of regional bone Periarticular fragmentation Joint dislocation |
Absorption of osseous debris Organization and early healing of fracture fragments Periosteal new bone formation |
Smoothing of edges Oosseous or fibrous ankylosis Bone healing Resolution of osteopenia
|
| Management |
NWB May prevent collapse |
Total contact cast until stage 2 FWB |
CROW (Charcot Resistant Orthotic Walker) Bivalved AFO |
Accommodative shoes with custom moulded orthotic
CROW or AFO if ongoing ankle instability |
|
|
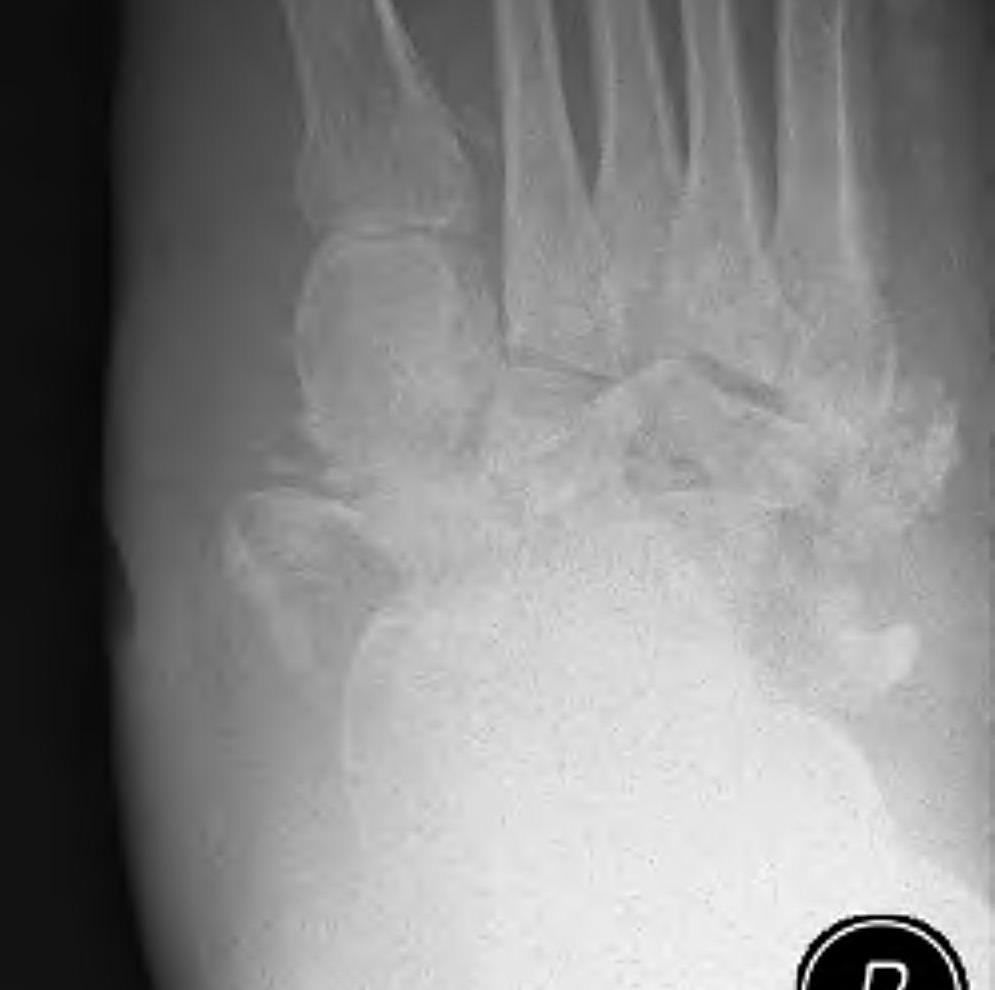
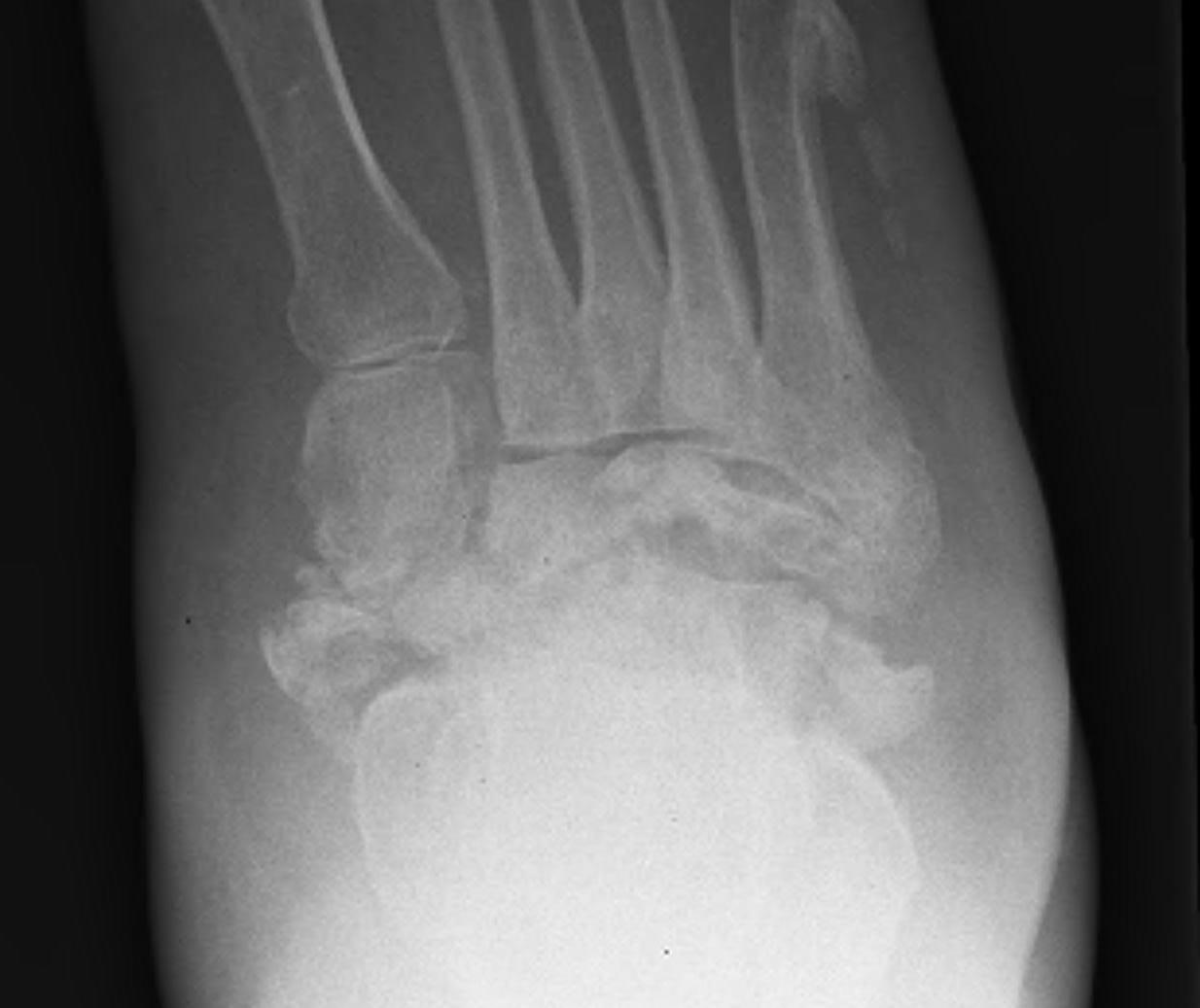
Midfoot dissolution, coalescence and reconstruction
Brodsky Classification
| Type 1 Midfoot (60%) | Type 2 - Hindfoot (30%) | Type 3 (10%) |
|---|---|---|
|
Metatarsocuneiform and naviculocuneiform
Collapse of the medial longitudinal arch with rocker bottom foot |
Subtalar joint, talonavicular, calcaneocuboid
More unstable than type 1 Require longer periods immobilisation |
3a: Tibiotalar joint - most unstable pattern
3b: Fracture calcaneal tubercle - weak push-off and ulceration |
Examination
Stage 0 / Stage 1
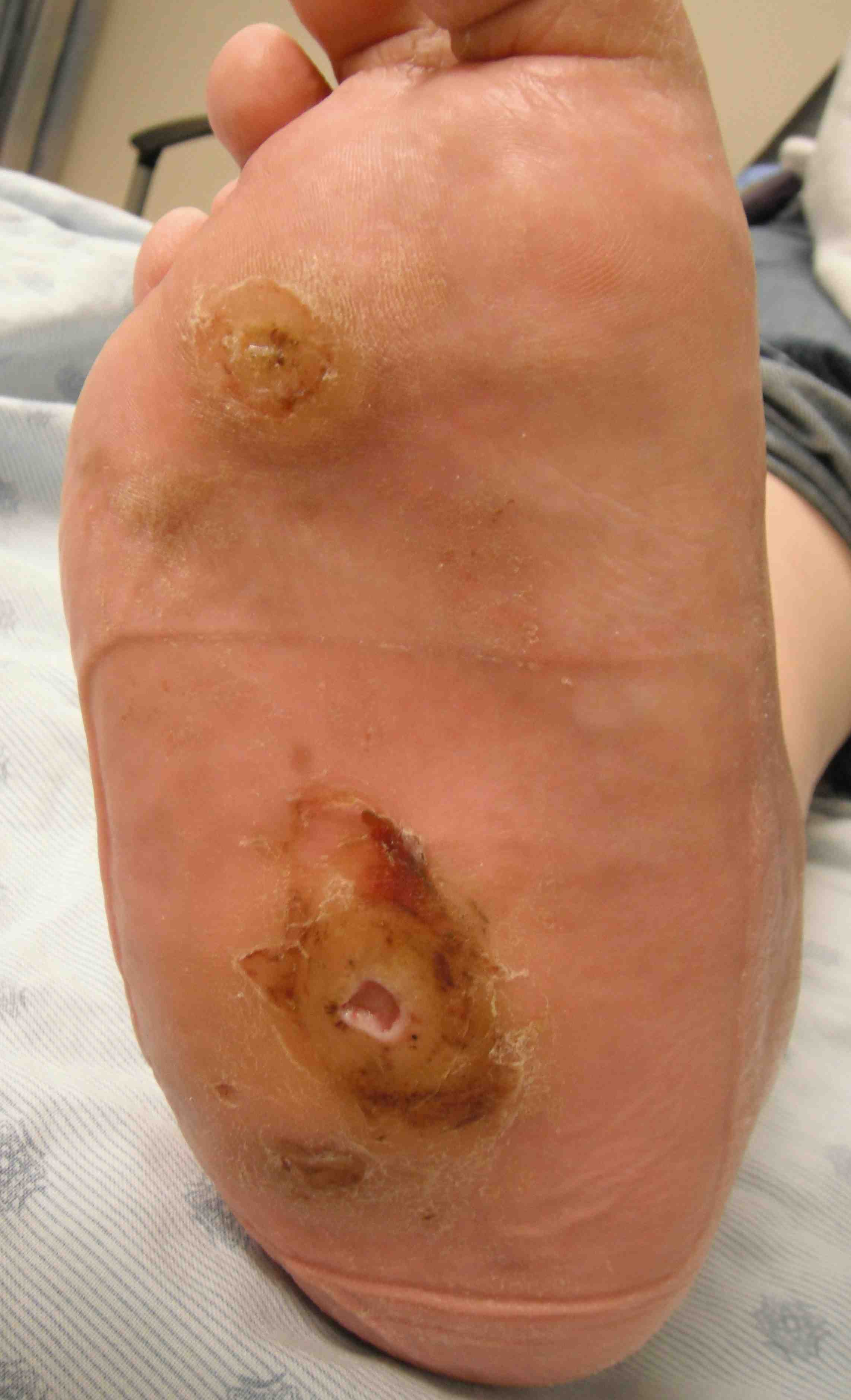
Foot very red
- ? cellulitis
- elevate for 10 minutes and the redness reduces
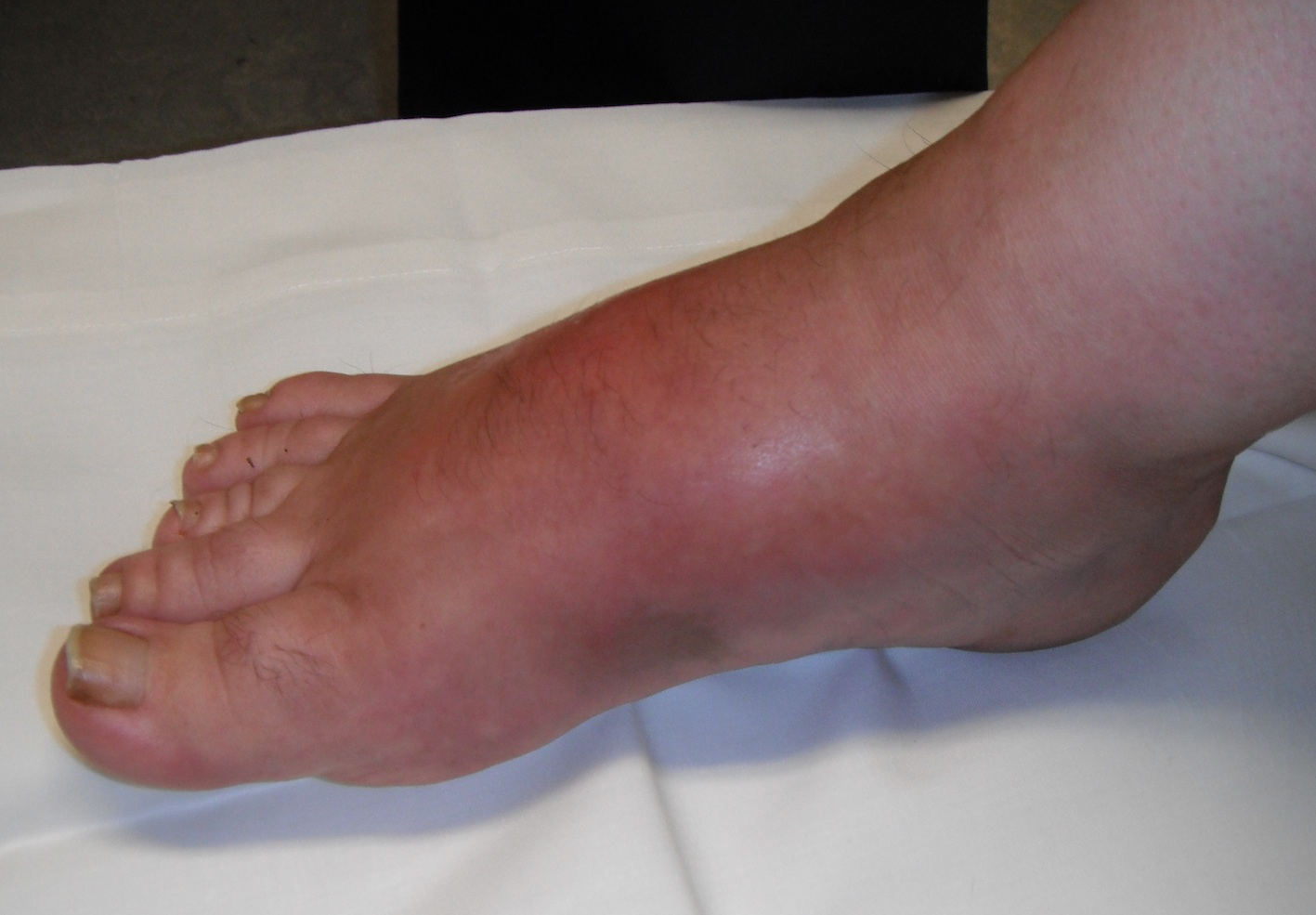
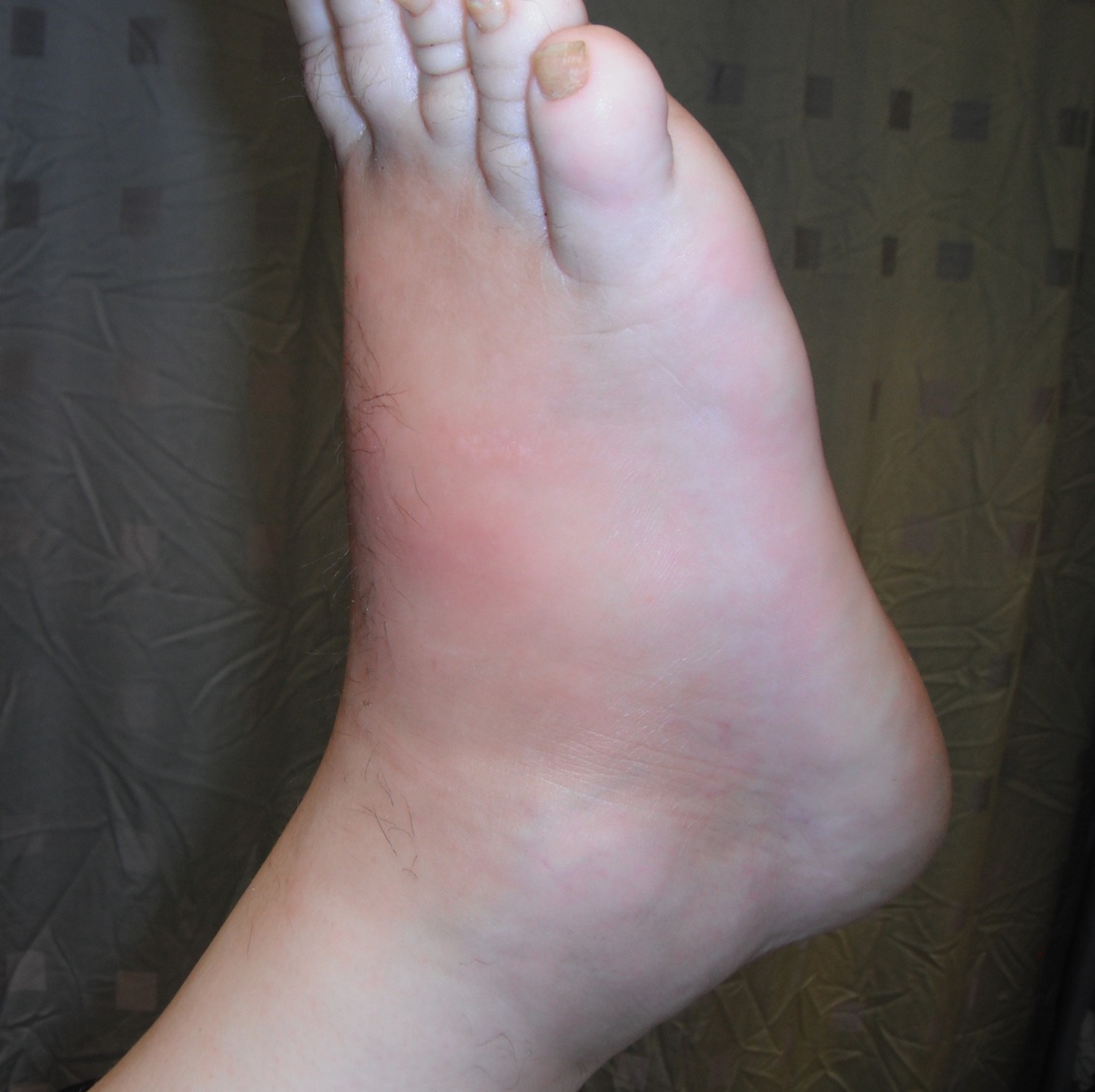
Reduction of redness with elevation
Xray


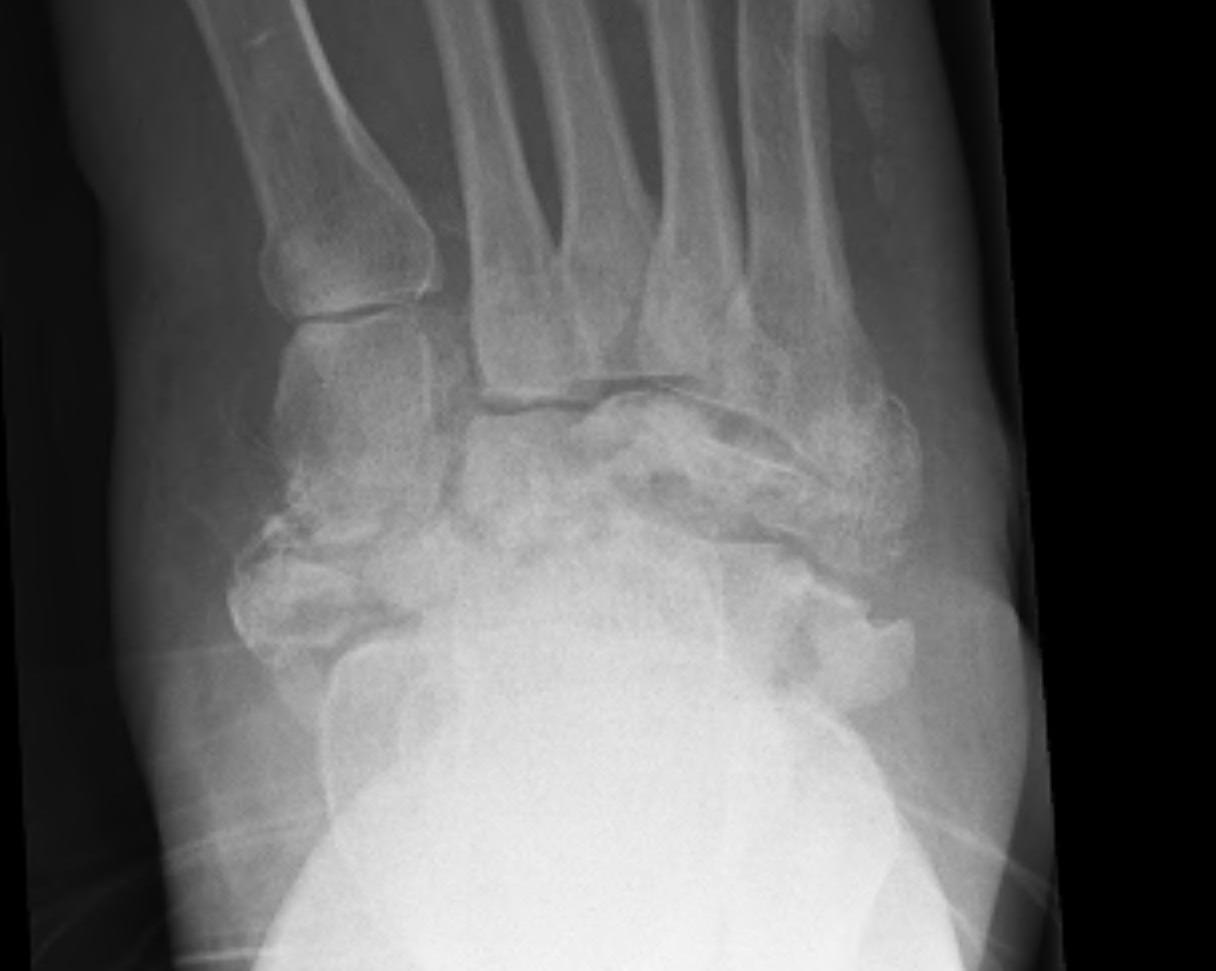
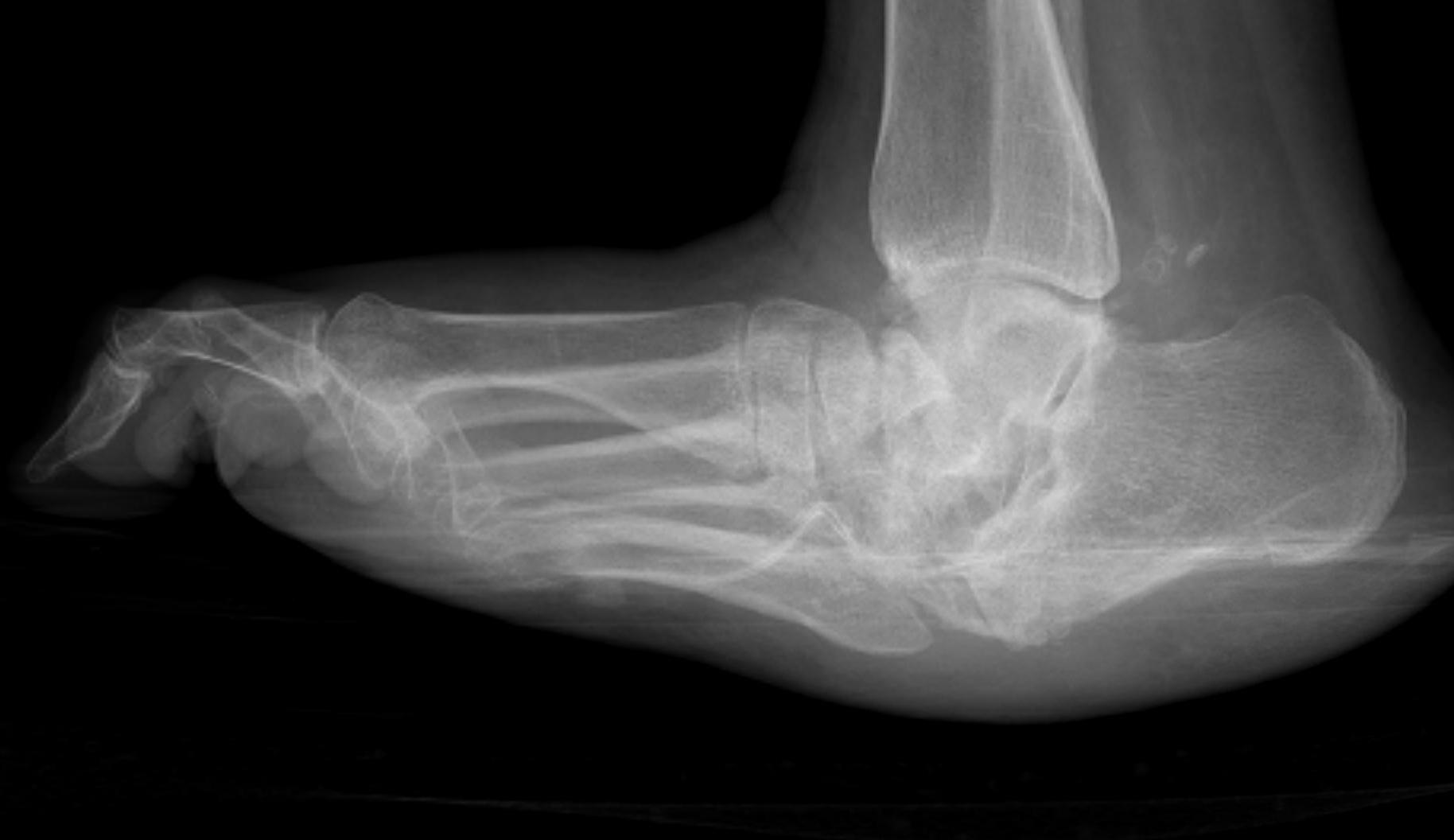
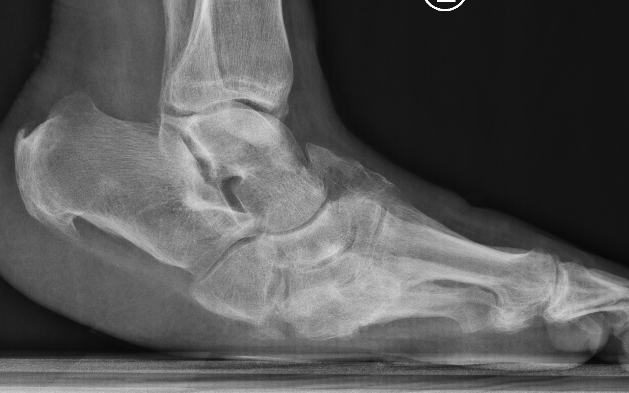
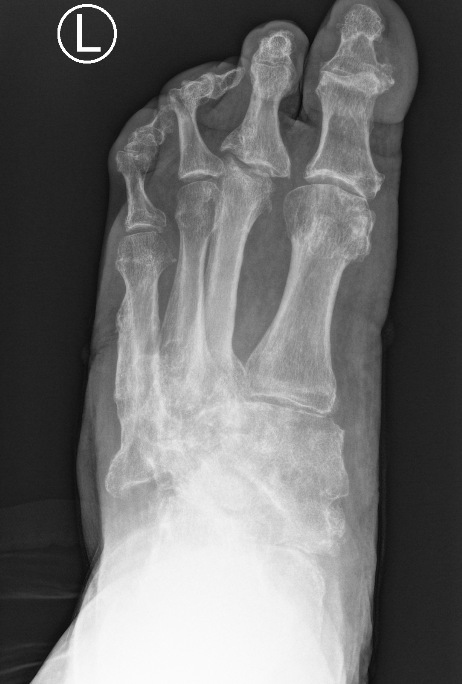
Midfoot collapse
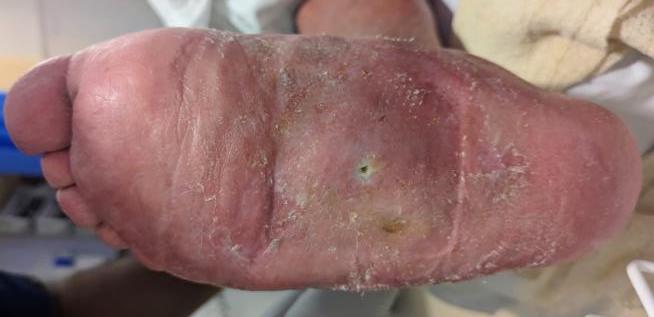
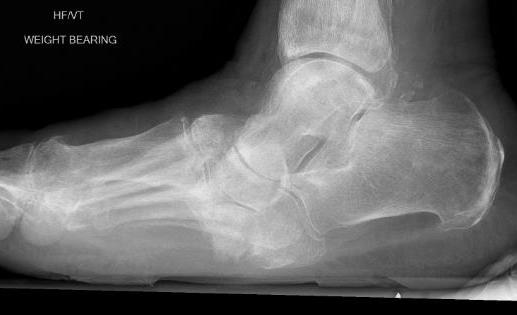
Midfoot collapse and rocker bottom foot with small ulcer
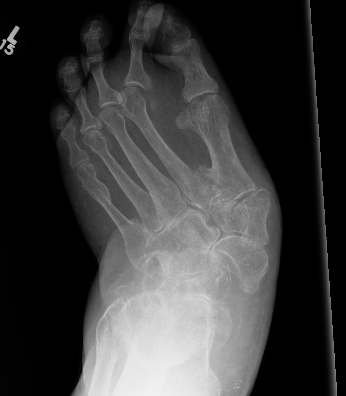
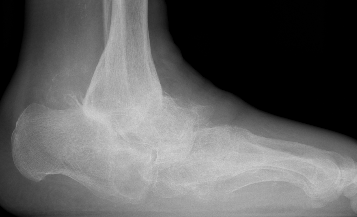
Midfoot collapse with subluxation of midtarsal joints
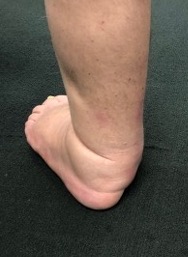
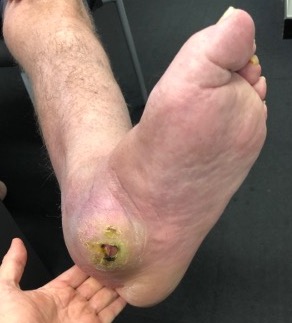

Hindfoot collapse with ulcer
Nonoperative Management
Goal
Stable plantigrade foot that is shoe-able or braceable
Avoid ulcers
Indications
Eichenholtz Grade 0 / 1 - Total contact cast (TCC)
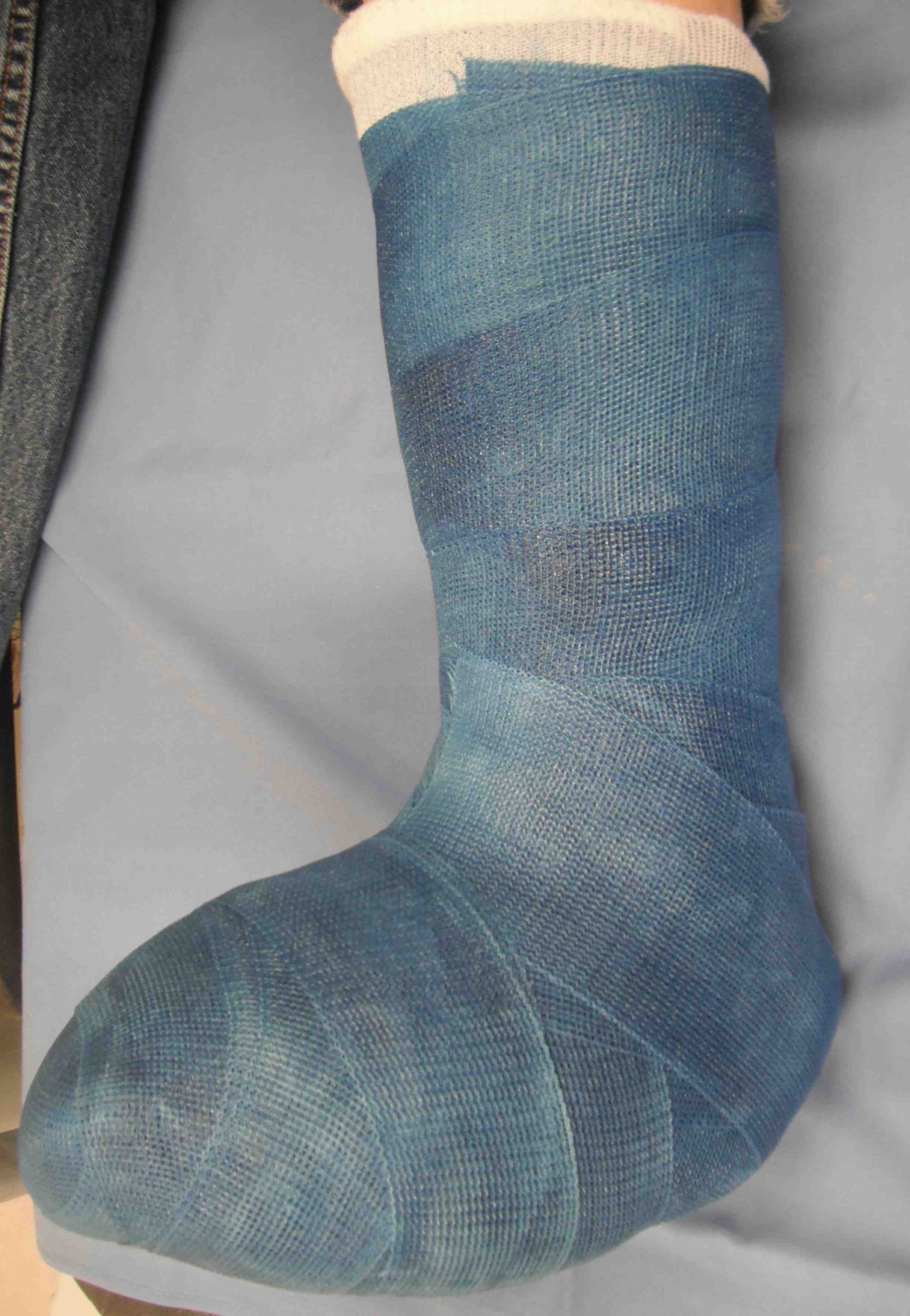

Total contact cast
Eichenholtz Grade 2 / 3 - CROW (Charcot Resistant Orthotic Walker)
Operative Management
Indications
1. Severe deformity unable to brace or wear shoes
2. Skin at risk
3. Ulcers with midfoot collapse
4. Marked instability - type II / hindfoot
Goals
Allow brace and / or shoe wear
Protect skin
Prevent amputation
Contra-Indications
Uncontrolled diabetes
Peripheral vascular disease
Medically unwell
Stage 1 disease
Timing
Stage III - resolution / consolidation
Midfoot surgery
Background
Midfoot most common site for neuropathic destruction
- mid foot collapse
- rocker bottom foot
- recurrent ulceration
Options
Exostectomy
Osteotomy and Fusion
Midfoot Exostectomy
Remove bony prominence causing ulcer
- avoid areas of ulceration
- medial or lateral incision
- full thickness soft tissue dissection to expose exostosis
- remove with osteotome / saw and smooth edges with rasp
- postoperative TCC for 6 weeks
Catanzariti et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2000
- 27 exostectomy in 20 patients with ulcers
- 74% healing rate
- lateral column surgery failed in 6/7 cases
Midfoot Osteotomy and Arthrodesis
Options
Plates
Intramedullary screws
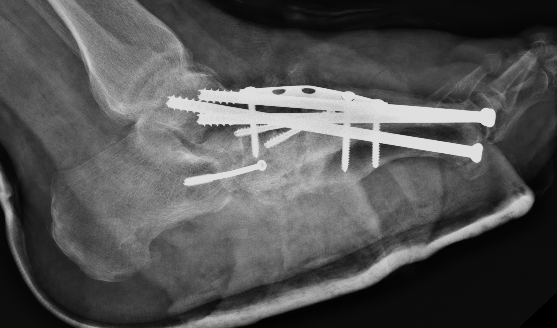
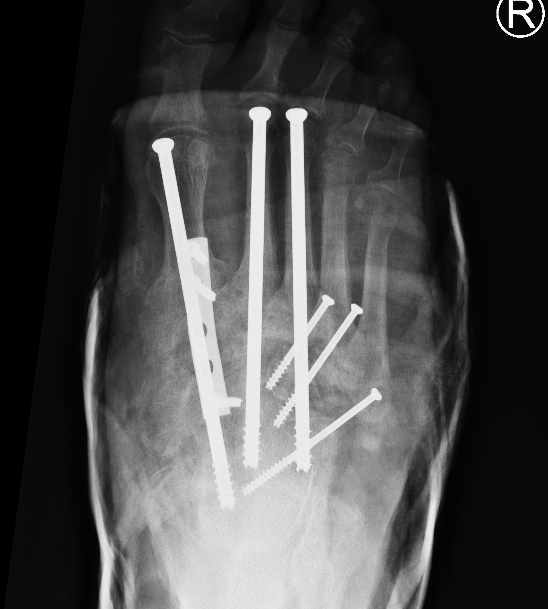
Technique
Sammarco et al Inst Course Lecture 2024
Superconstructs (4 concepts)
1. Fusion is extended beyond the zone of injury to bridge the area of bony dissolution
2. Aggressive bone resection - allows reduction of deformity with reduced soft tissue tension
3. Stronger implants - medial / central and lateral column fixation
4. Load sharing devices
- intramedullary beams
- axial screw fixation from 1st MTPJ through metatarsal into talus
- also IM screw through 2nd and 3rd metatarsal into talus
Synthes Midfoot Fusion Bolt surgical technique PDF
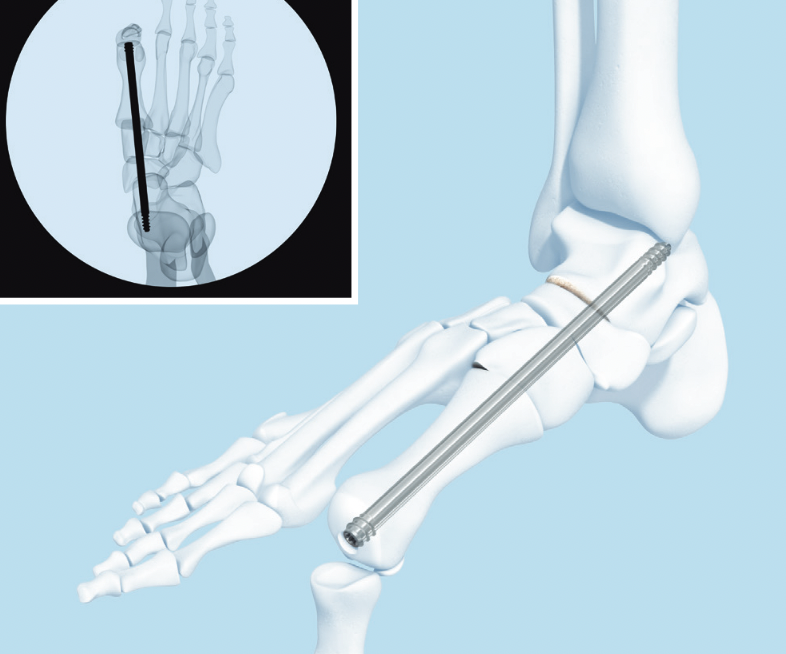
Results
Manchanda et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2020
- 30 midfoot fusions for Charcot
- reduced complications with increased number of medial screws
- reduced complications with inclusion of subtalar fusion
Wukich et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2022
- systematic review of midfoot fusion using intramedullary fixation in Charcot
- compared Charcot specific implants (Midfoot Fusion Bolt) with standard implants
- overall limb salvage 92%
- increased complications with Charcot specific implants
Hindfoot and Ankle surgery


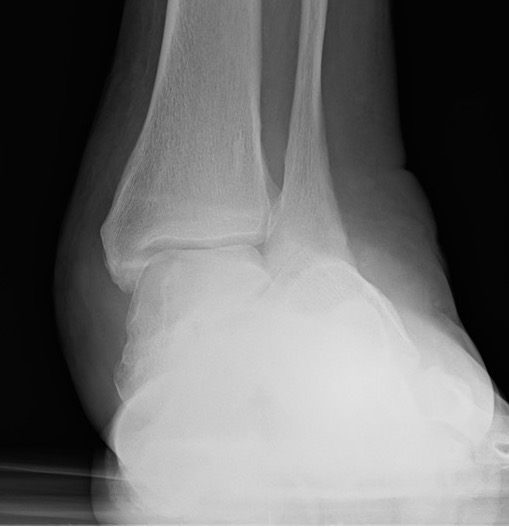
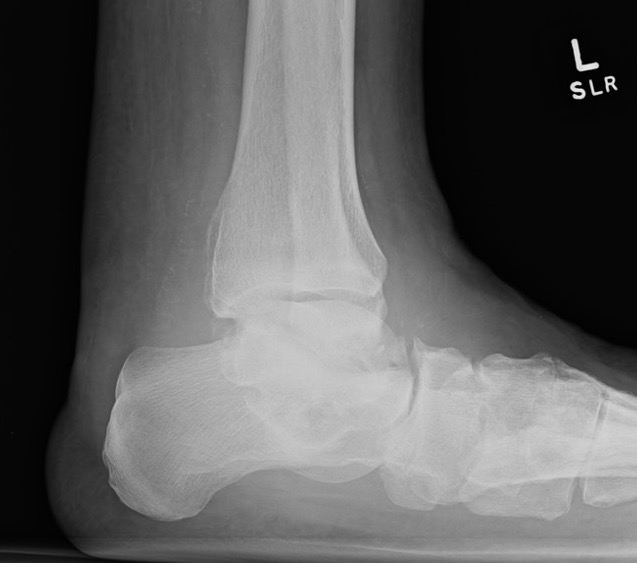
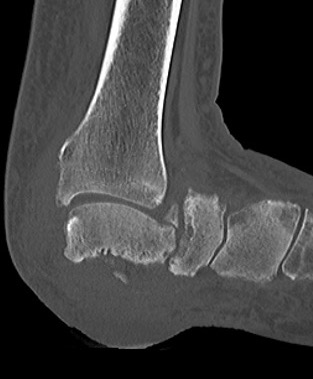
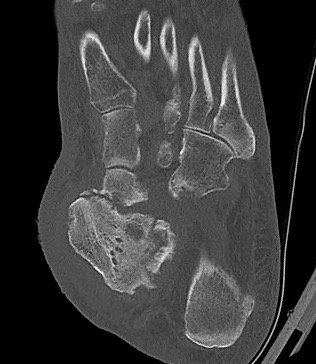
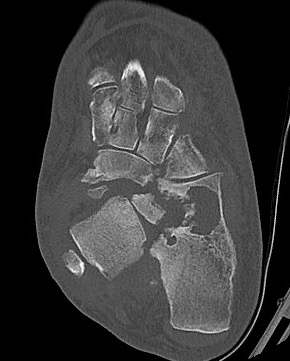

Tibiocalcaneal (TCC) arthrodesis
Options
www.boneschool.com/pantalar-fusion
Plates
Nail
External fixation
Results
DeVries et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2012
- 52 patients with Brodsky type 3a Charcot destruction of the ankle
- TCC arthrodesis
- 75% limb salvage rate
Caravaggi et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2012
- 45 patients treated with TCC arthrodesis with nail
- 4% had tibial fracture above the nail
Yammine et al J Orthop Surg 2019
- systematic review of TCC fusion in charcot hindfoot
- external fixation v IM nail
- IM nail double fusion rate and faster
