Medial subluxation of long head biceps
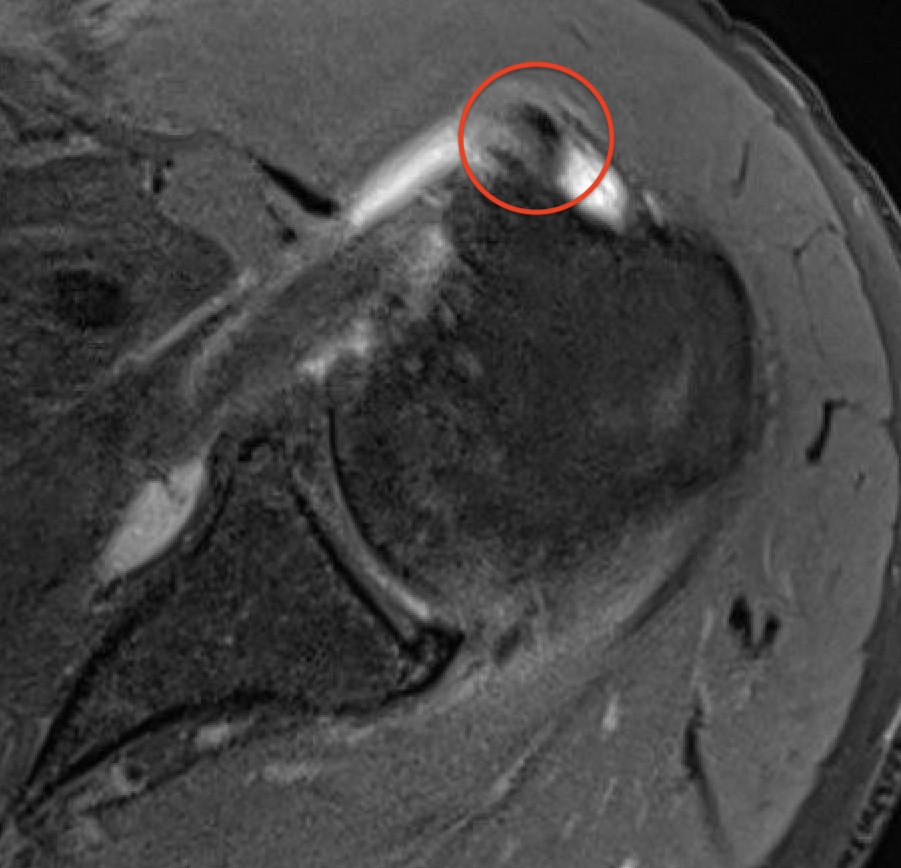
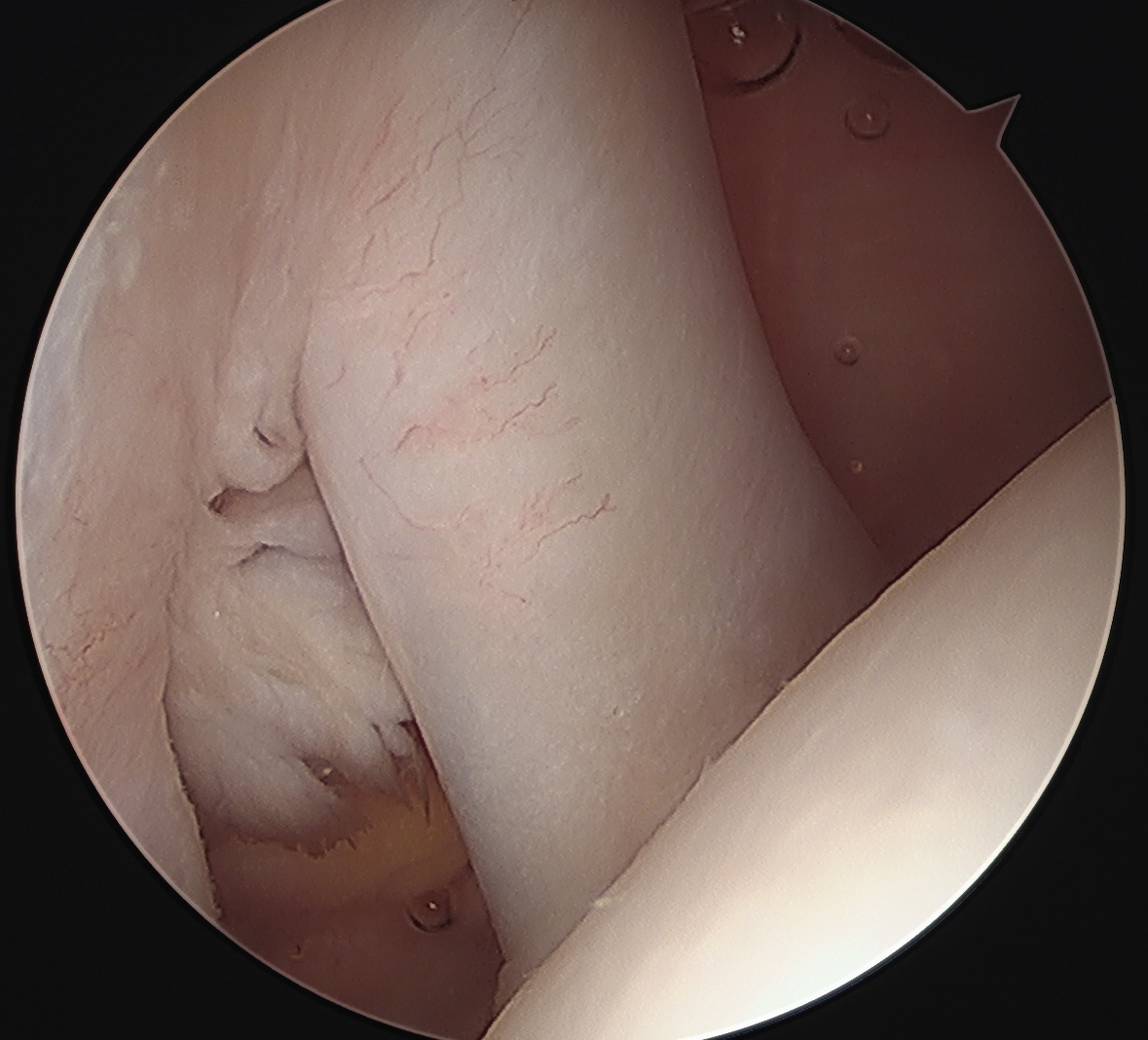
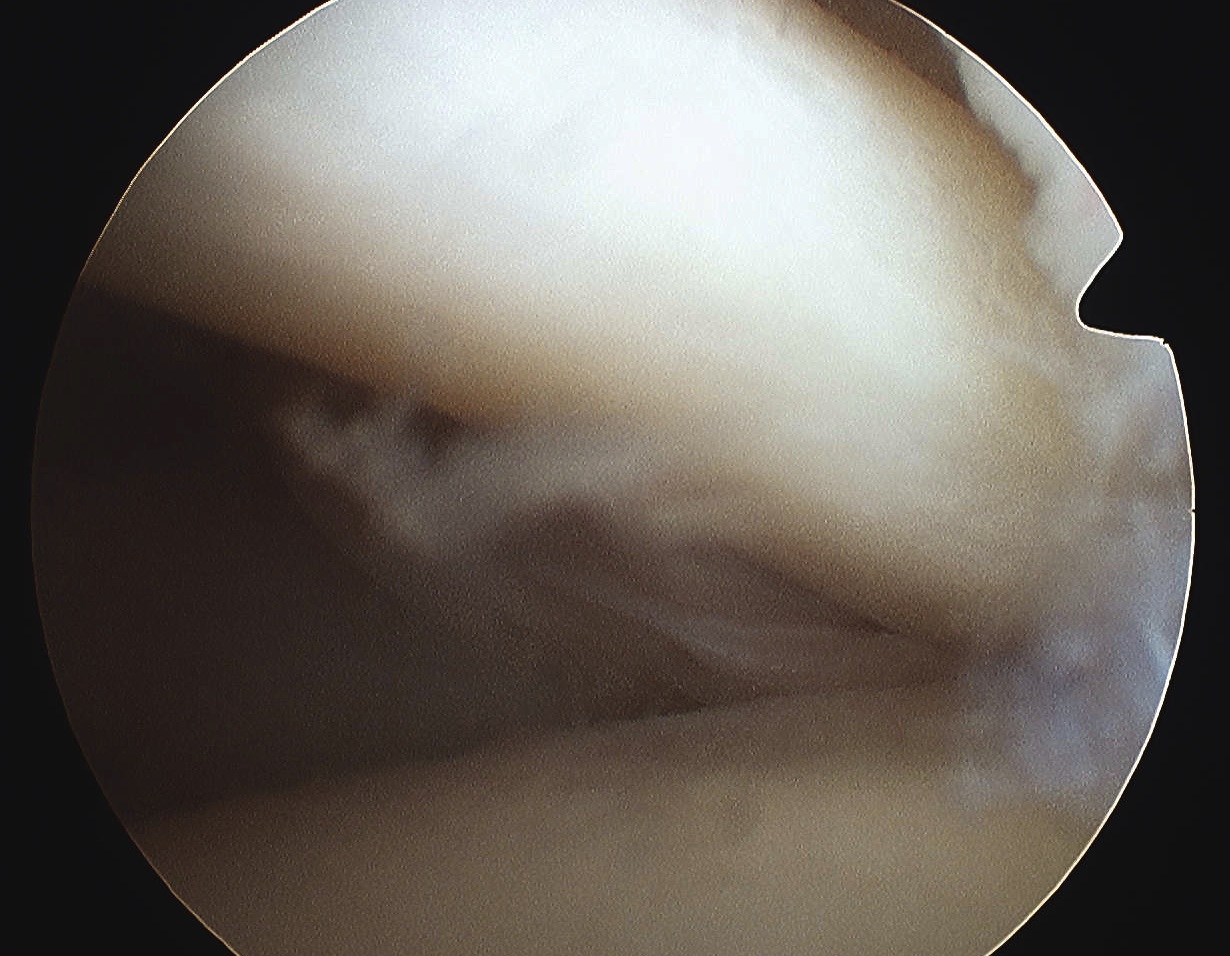
Definition
Medial subluxation of long head of biceps tendon out of groove and into rotator interval


Medial subluxation of long head of biceps tendon out of groove and into rotator interval
LHB primary function is humeral head depressor
Also accelerate / decelerate arm in overhead sports
Biceps problems usually occur with other pathology
- rotator cuff / instability
3 main problems
1. Degeneration
6 /100 000
- second most common dislocation after shoulder
FOOSH
Diagnosis
Pisotriquetral view
- forearm positioned 30° supinated off the neutral position
- loss of symmetry between the pisiform and triquetrum is required for the diagnosis
- carpal tunnel view may be helpful in further assessment of the joint
Clinical
More common problem
6th compartment
- fibro-osseous tunnel overlying 1.5 cm to 2.0 cm of distal ulna
- held tight by the extensor carpi ulnaris tendon sheath
- the extensor retinaculum passes around the ulna to insert on the palmar aspect of the carpus
- extensor retinaculum is a separate structure from the ECU tendon sheath
Forced supination, palmar flexion, and ulnar deviation
Stenosing tenosynovitis of the first dorsal compartment of wrist
Most are middle aged women
Repetitive thumb movements
- abduction & extension
- combined with RD & UD movements
Any mechanical irritation
- foreign body
- prominent bony surface
- restricted fascial compartment
Extremely uncommon
Stability provided by joint capsule /costoclavicular & interclavicular ligaments
Recurrent instability uncommon
Many apparent dislocations in adolescents may be growth plate injuries
-will remodel without treatment
If OA from chronic dislocation may resect SCJ