Definition
A glenohumeral dislocation which has been missed for a significant period of time
- time period is arbitrary
- > 3-6 weeks
Pathology
Anterior glenoid bone deficiency
Large Hill Sachs lesions
Rotator cuff tears
Etiology
Poor historians
- developmental delay
- dementia
Issues
Closed reduction may be unsuccessful / locked
Open reduction - unstable due to bony deficiency / rotator cuff tears
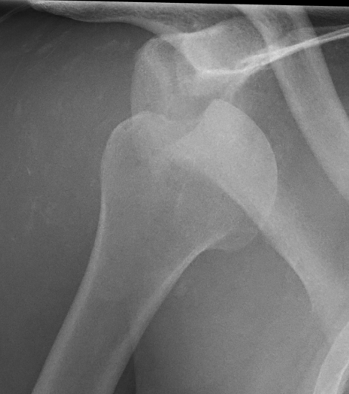
Xray
Signs of chronic shoulder dislocation
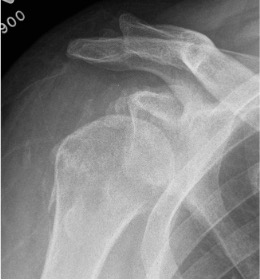
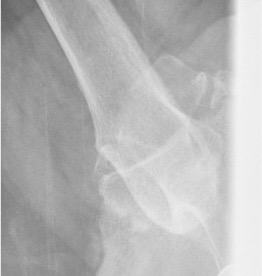
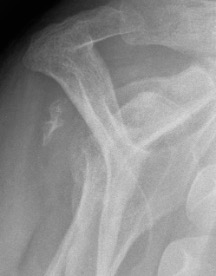
CT
Assess bone stock / glenoid bone loss / Hill Sachs lesions
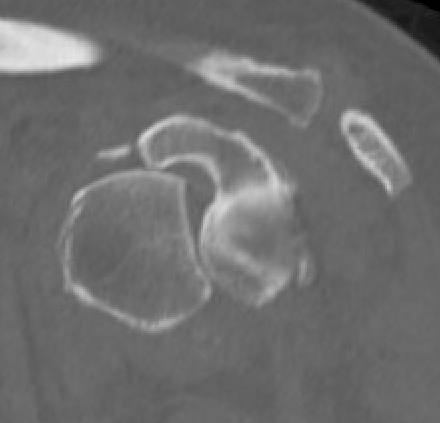
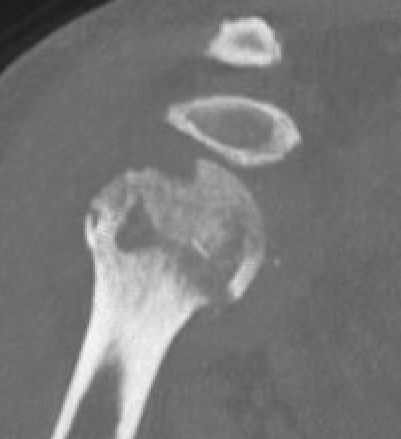
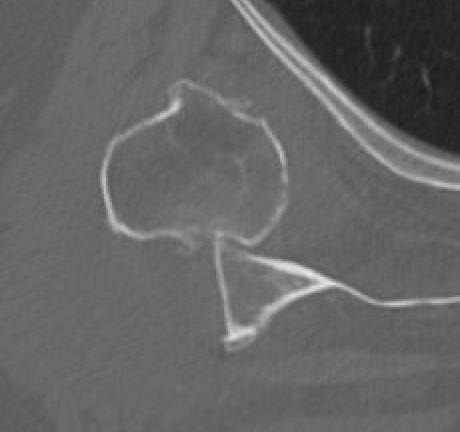
Chronic shoulder dislocation with large Hill Sachs and minimal glenoid deficiency
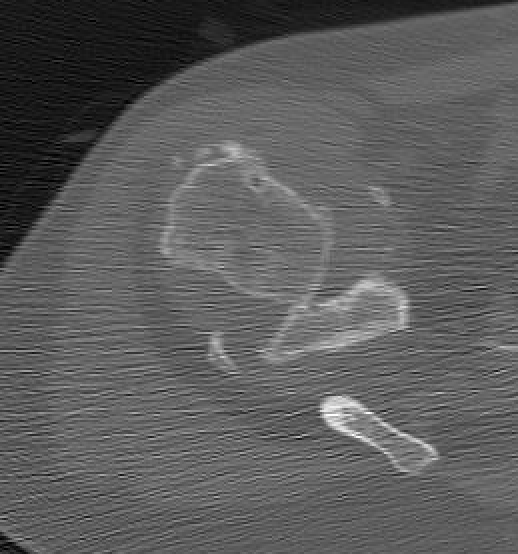
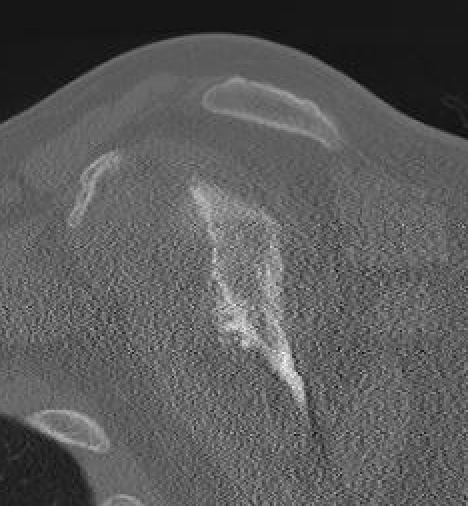
Chronic shoulder dislocation with large Hill Sachs and significant glenoid deficiency
MRI
Rotator cuff tears
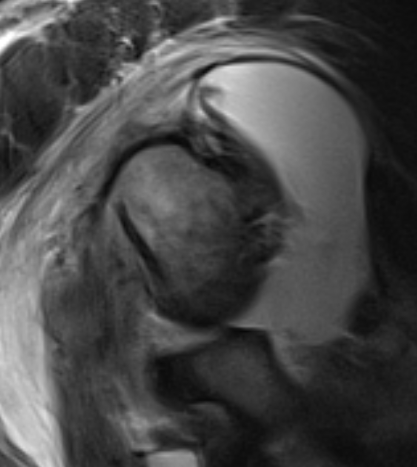
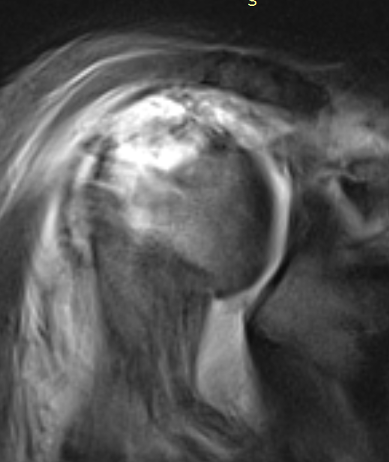

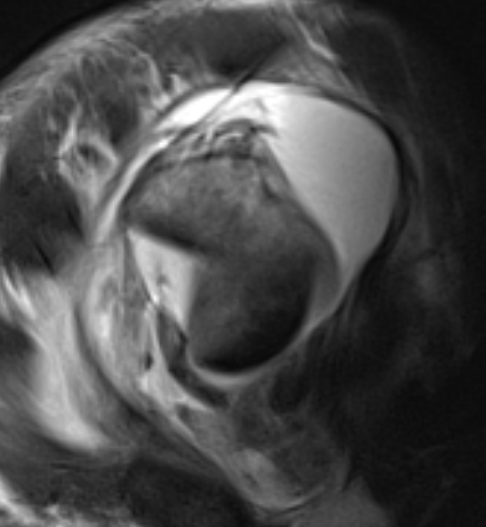
MRI with massive supraspinatus tear, subscapularis tear, and large Hill Sachs lesion
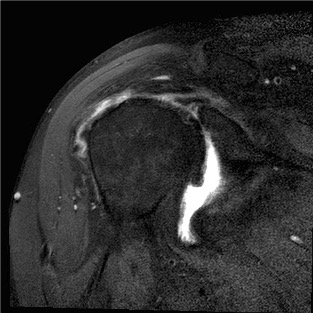
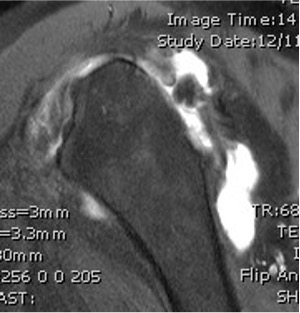
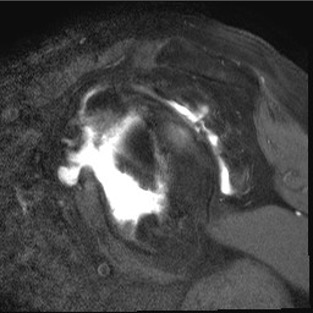
MRI with supraspinatus tear, Hill Sachs lesion and significant glenoid bony deficiency
Nonoperative management
Indications
Elderly with significant medial issues
Operative management
Options
1. Humeral head preservation: open reduction +/- glenoid bone graft +/- Hill Sachs allograft +/- rotator cuff repair
2. Arthroplasty +/- glenoid bone graft
Results
Latarjet
- 25 patients undergoing latarjet for chronic locked anterior dislocations
- Latarjet procedure: recurrent instability 50%
- Latarjet + humeral head replacement: recurrent instability 80%
Humeral head replacement v reverse TSA
- 19 chronic locked anterior dislocations
- 10 hemiathroplasties / anatomic TSA: 6/10 unstable
- 9 reverse TSA: 0/10 unstable
reverse TSA
- 24 cases of chronic locked anterior dislocations treated with rTSA
- compared to control rTSA
- increased need for glenoid bone graft
- increased used of larger glenospere
- increase rate of acromial stress fractures
Open reduction +/- glenoid bone graft +/- Hill Sachs allograft +/- rotator cuff repair
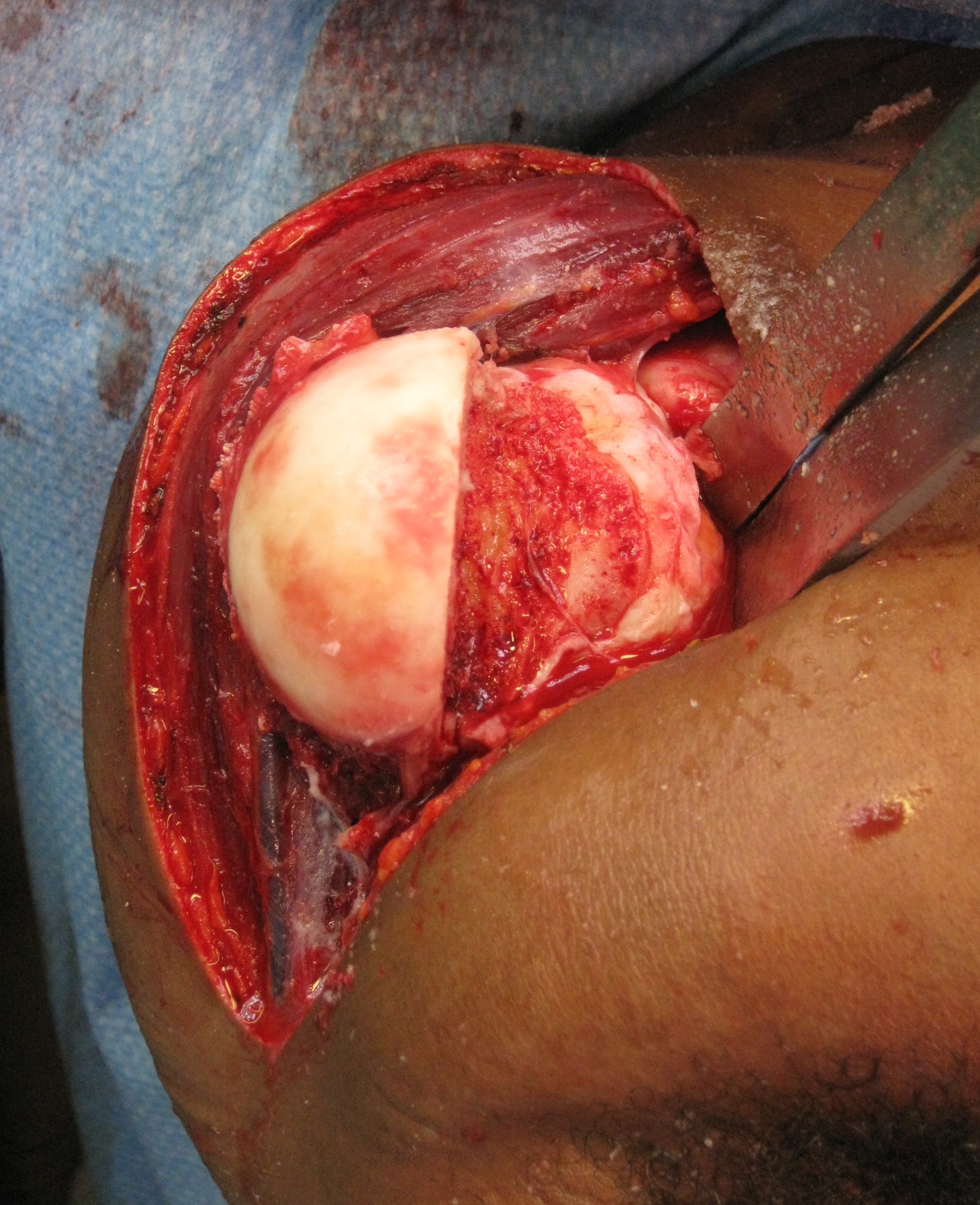
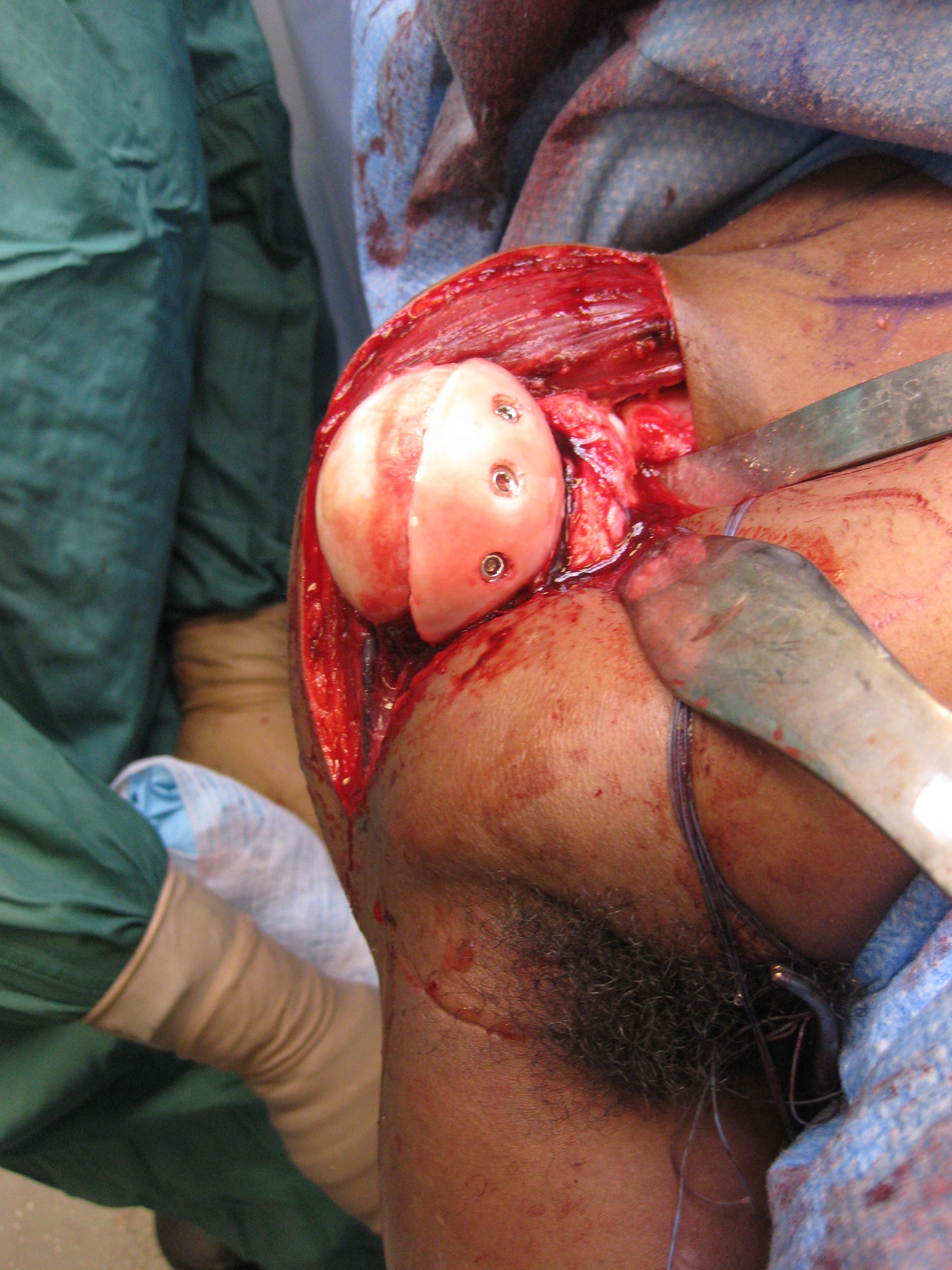
Humeral head replacement + glenoid autograft + rotator cuff repair
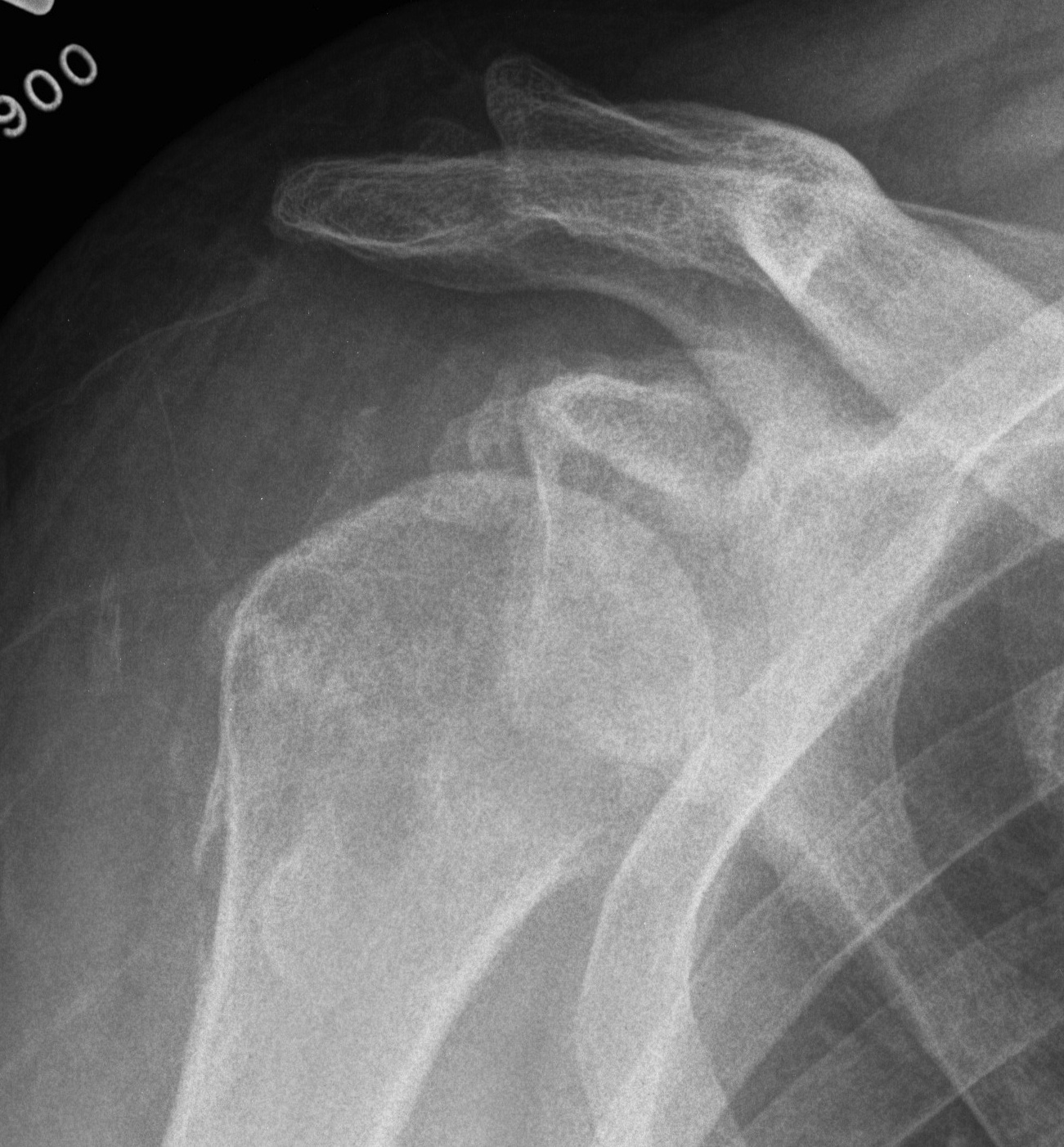
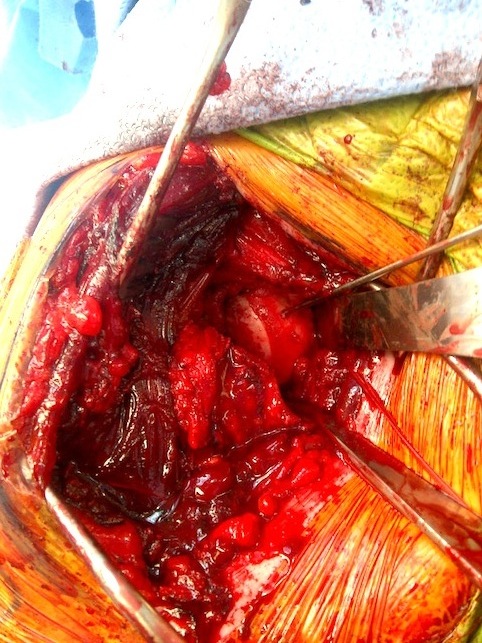

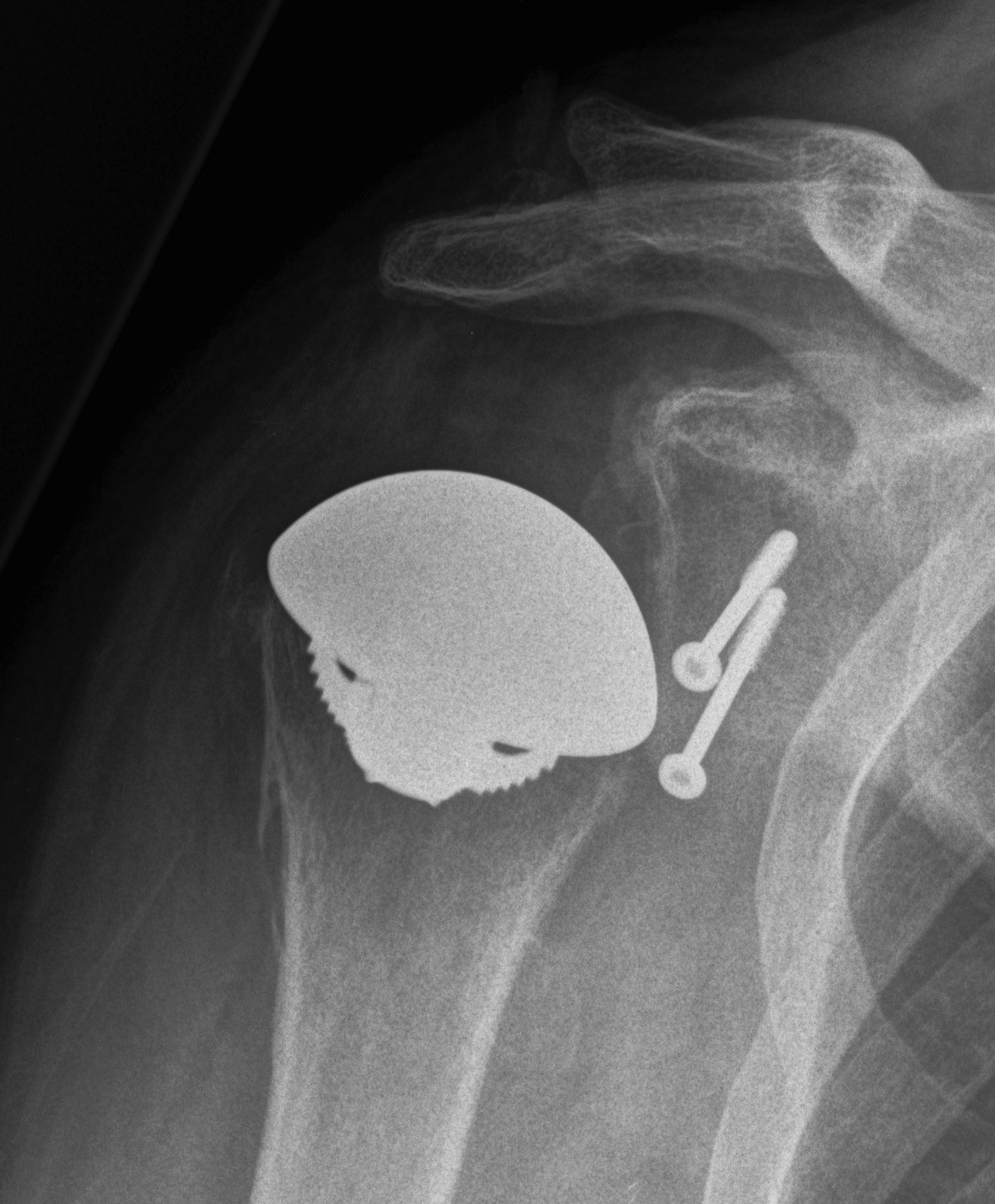
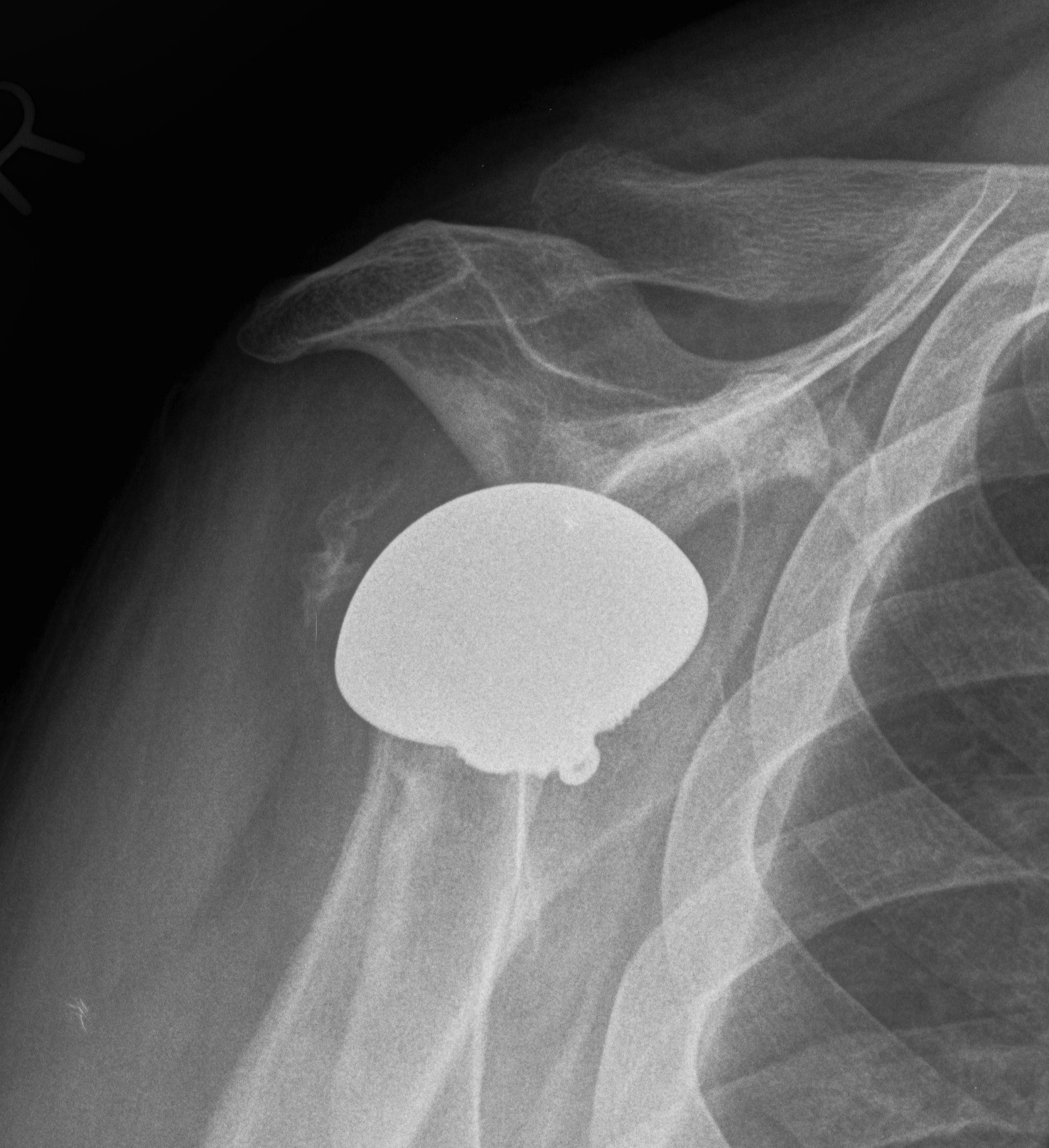
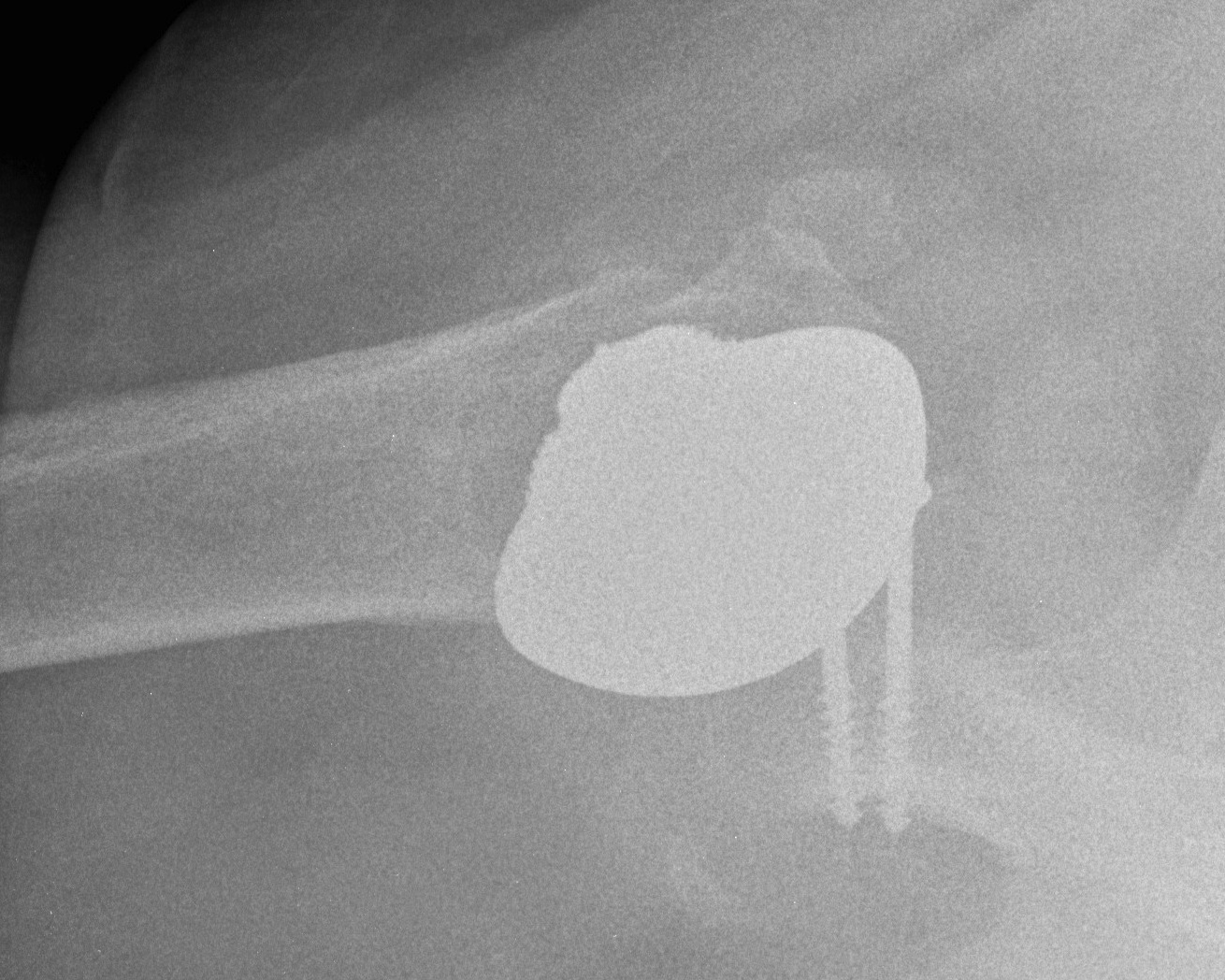
Post humeral head replacement / glenoid autograft / rotator cuff repair
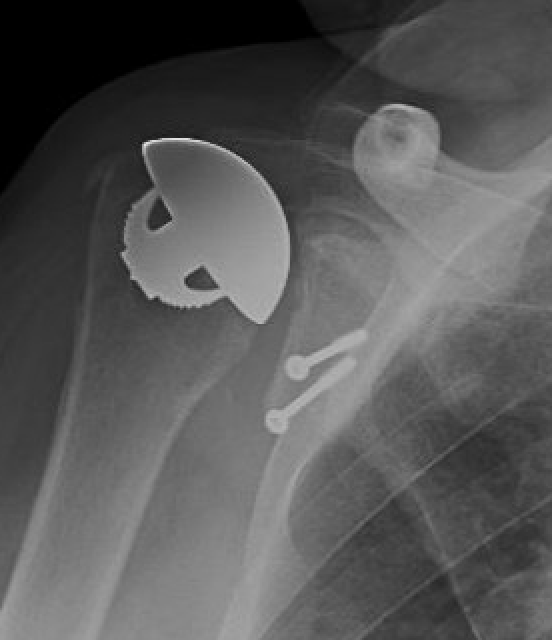
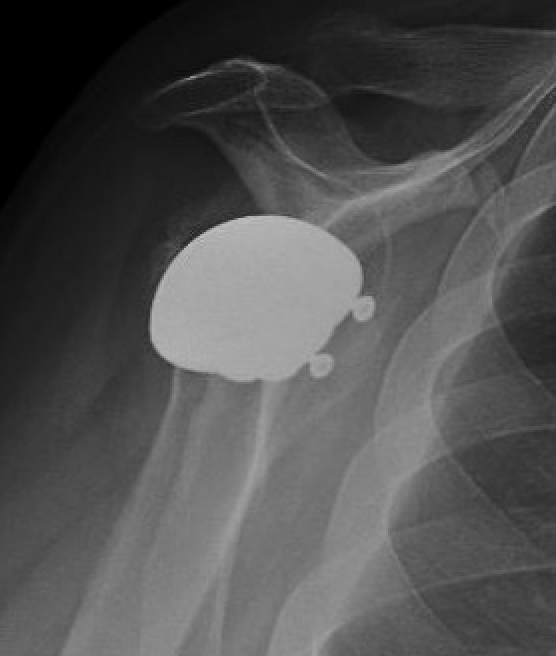
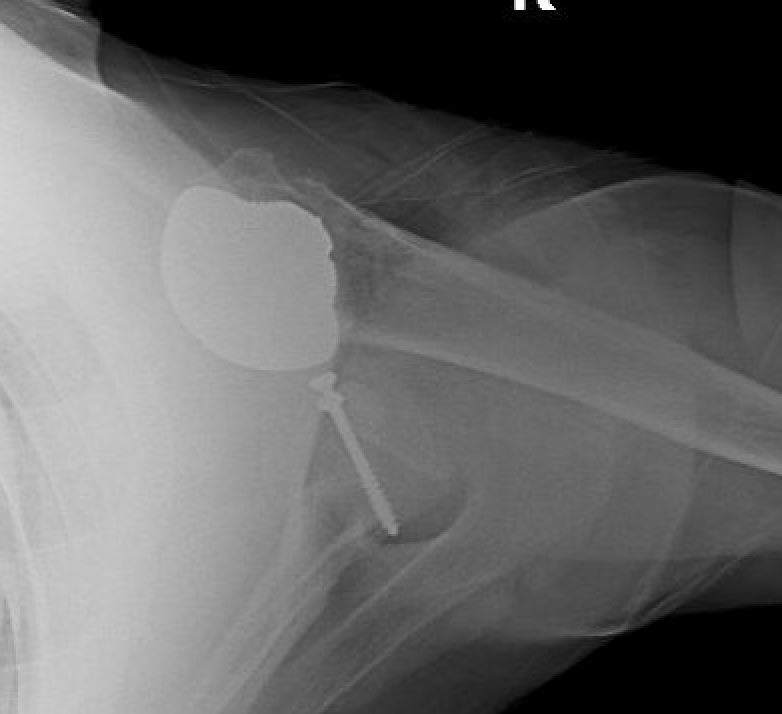
Rotator cuff failure and development of anterosuperior escape
Reverse TSA +/- glenoid bone graft
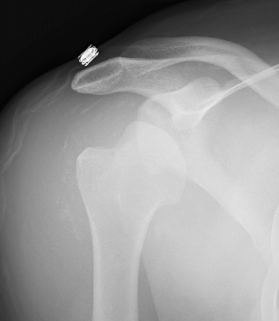
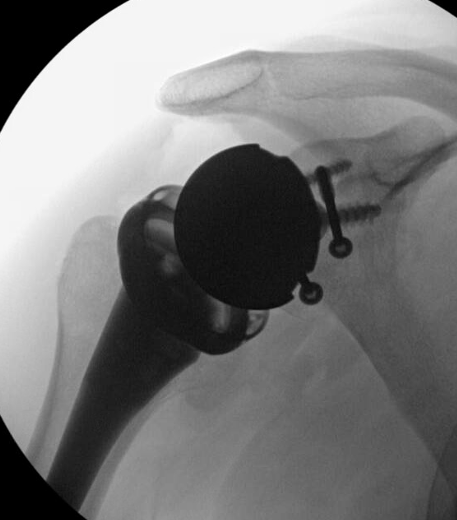
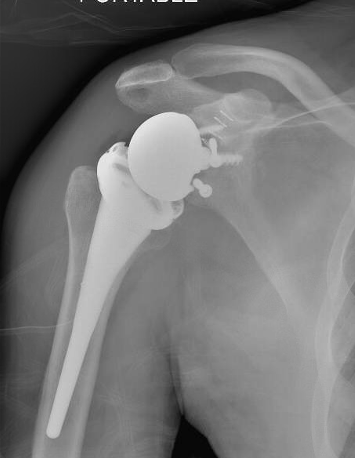
Chronic locked with large Hill Sachs treated with rTSA + glenoid bone graft
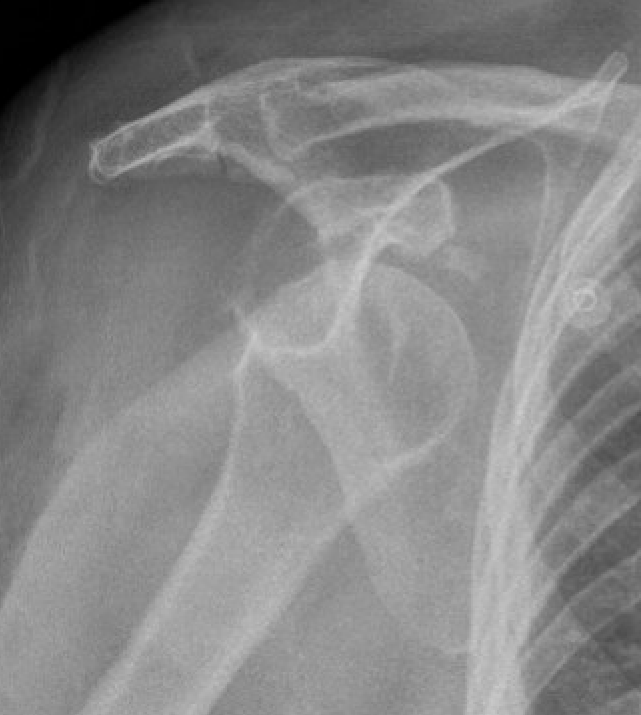
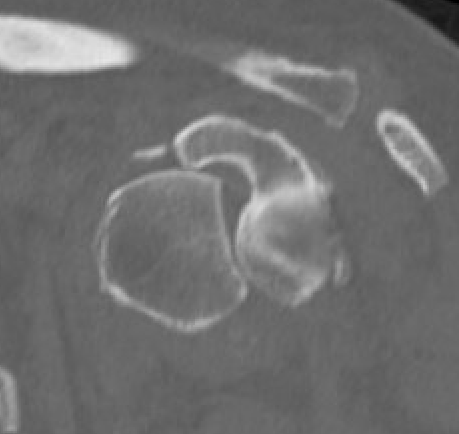
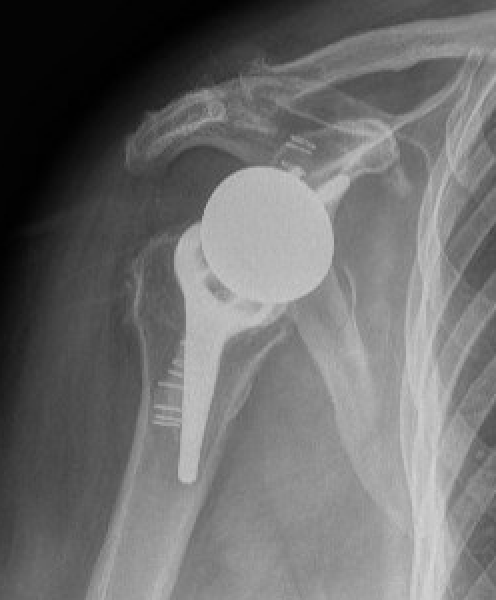
Chronic locked with large Hill Sachs and normal glenoid treated with rTSA + glenoid bone graft