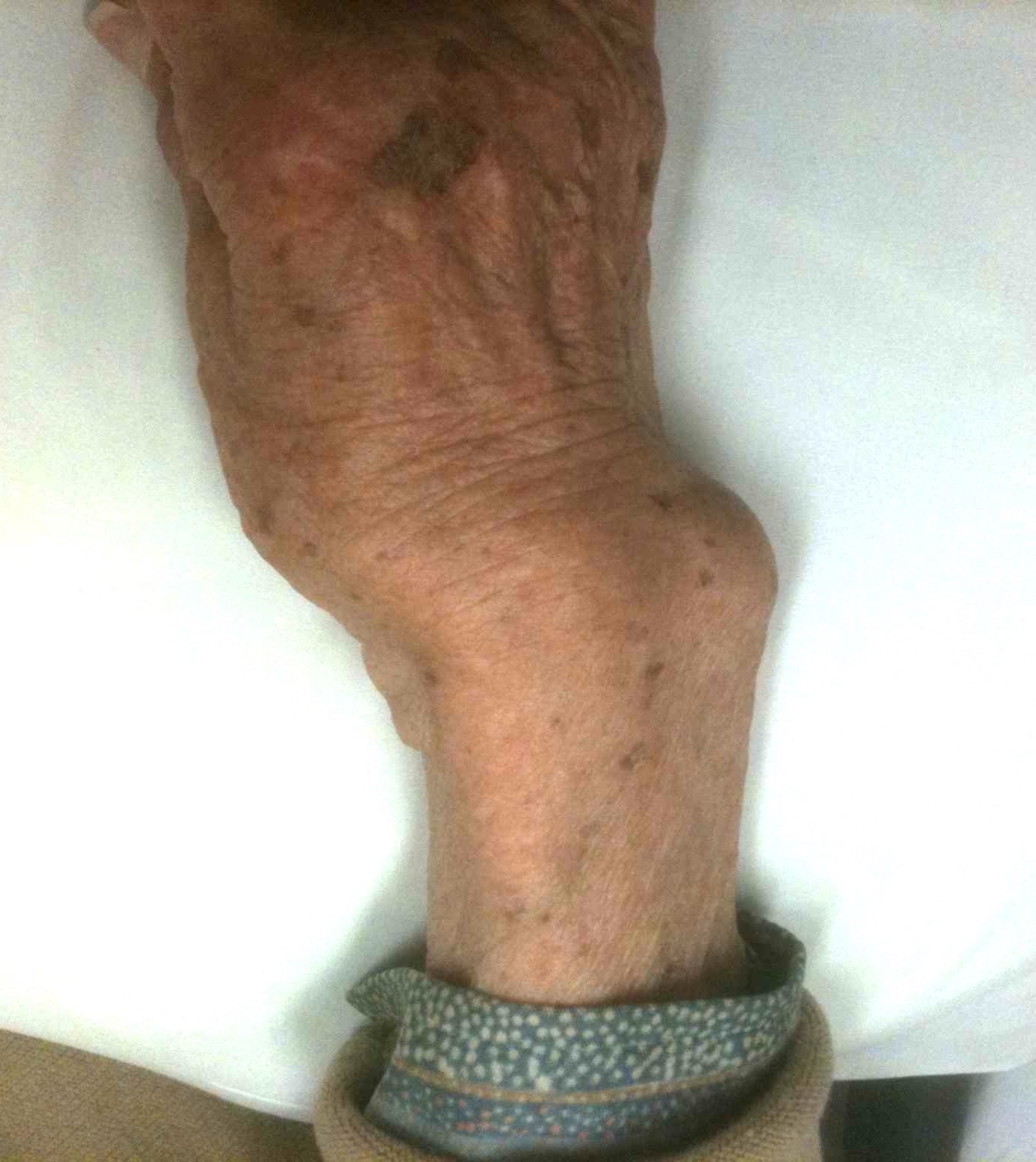
Epidemiology
Wrist commonly affected in RA
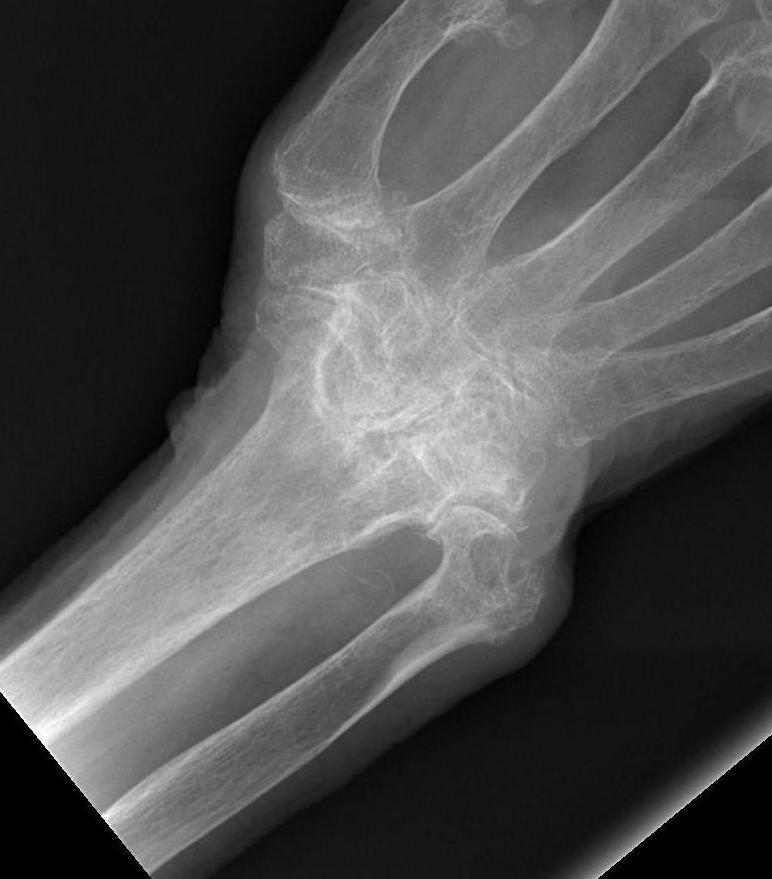
Pathology
1. Synovitis
Starts
- ulna styloid
- ulna head
- scaphoid midportion
Radial side
- synovitis scaphoid midportion
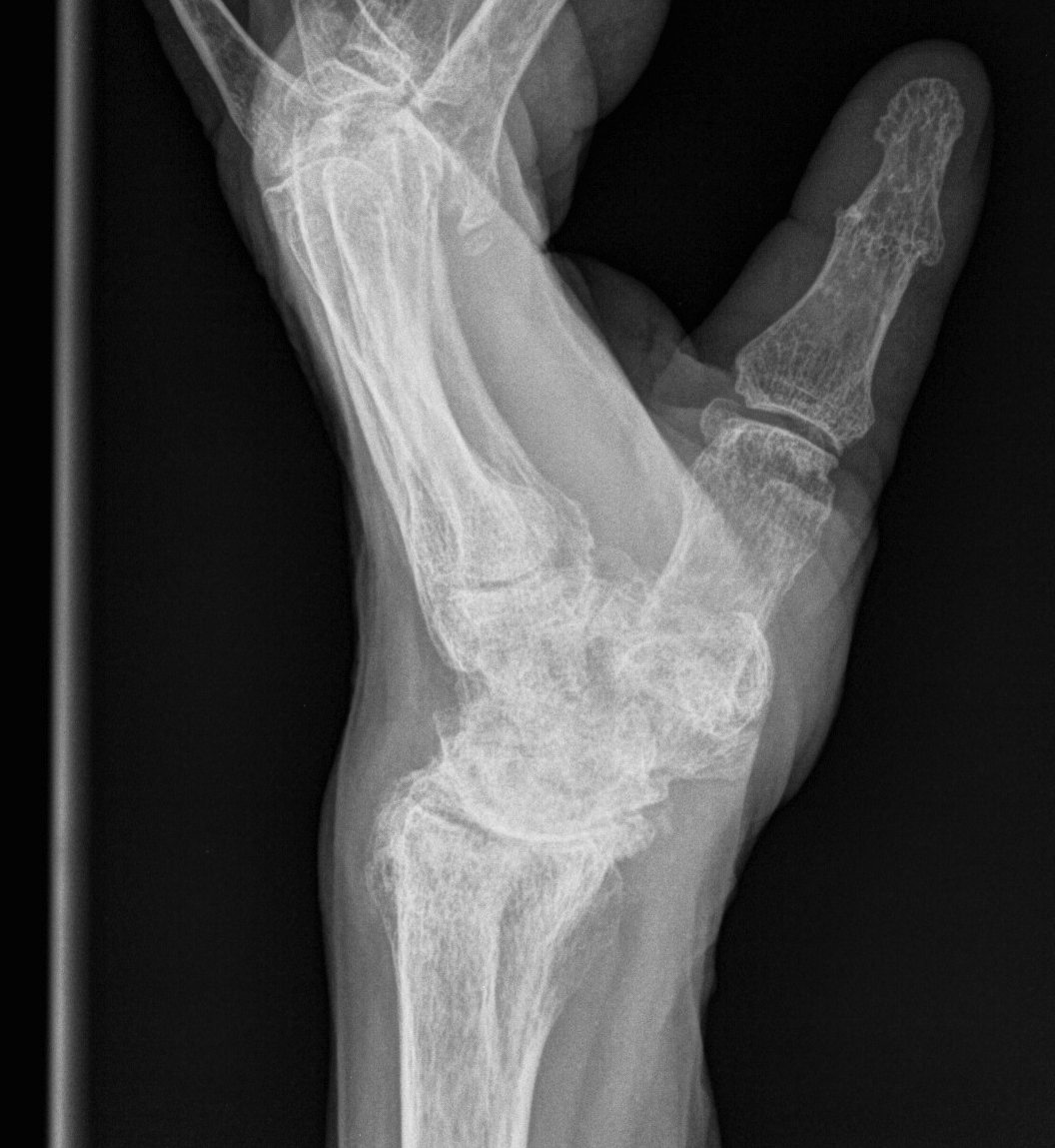
- RCL & RSCL become attenuated
- subluxation of scaphoid & scapholunate dissociation
- radiocarpal shortening
Ulnar side
- synovitis begins ulna styloid
- TFCC, ULL & UTL attenuated
- DRUJ stretches
- volar subluxation of ulnar carpus & supination
- develop caput ulna
- ulnar becomes prominent because carpus is falling away from it
- carpus volar translated & supinated
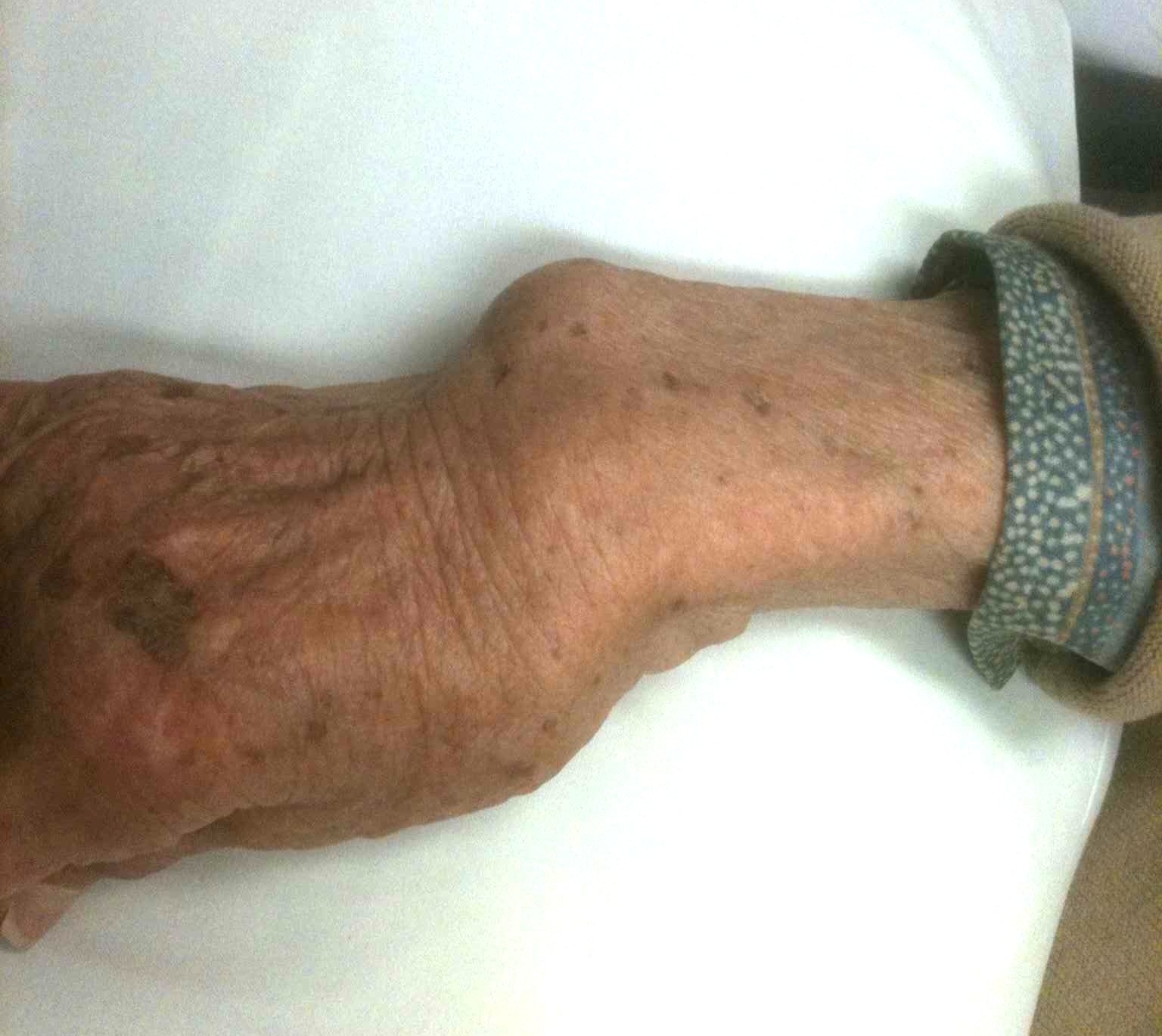
2. Loss of ECU mechanical advantage
- secondary to supinated carpus & carpal collapse
- ECU subluxes volar to flexion / extension axis
- increases mechanical advantage of radial wrist extensors
- radial deviation of carpus
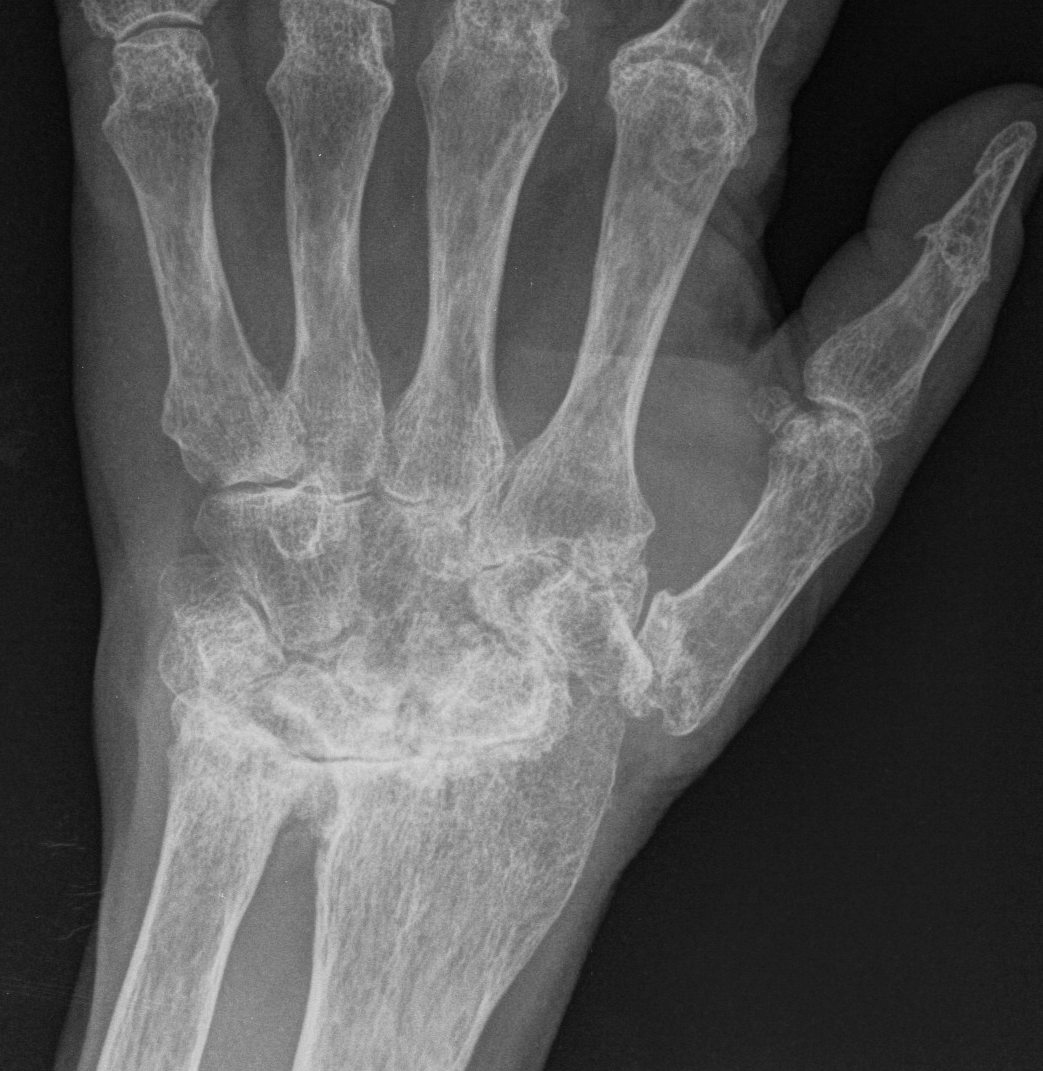
3. Carpal Collapse
- decreases mechanical advantage of long finger flexors / extensors
- leads to intrinsic plus deformity
Xray
Operative Management
Principle
Failure to address wrist deformity will lead to failure of MP or IP reconstruction
Options
Early disease
- synovectomy
- tendon transfers for flexor tendon / extensor tendon rupture
- DRUJ
End stage disease
- arthrodesis
- arthroplasty
Zhu et al J Hand Surg Eur 2021
- systematic review of arthrodesis v arthroplasty for end stage RA wrist
- 23 studies - 343 arthrodesis and 618 arthroplasty
- complication rate: arthrodesis 17%, arthroplasty 19%
Synovectomy
Indications
Persistent painful wrist synovitis not settling with medical management
Minimal xray changes
Options
Open
Arthroscopic
Results
- arthroscopic synovectomy in 56 RA wrists with mean 8 year follow up
- 75% controlled synovitis
Technique
| Flexor tenosynovectomy | Extensor tenosynovectomy |
|---|---|
|
Difficult to diagnose Limited active finger flexion Carpal tunnel syndome |
Dorsal synovitis Dumbbell shape under extensor retinaculum |
| Carpal tunnel incision |
Midline dorsal incision |
Dorsal Tenosynovectomy + Carpal Synovectomy
- dorsal incision
- divide extensor compartment between 5th (EDM) and 6th (ECU) extensor compartment
- elevate radially based flap to 1st compartment
- perform partial wrist denervation (PIN in floor of 4th extensor compartment)
- expose radial carpal and & intercarpal joints using ligament sparing arthrotomy (between DRC and DIC ligaments)
- synovectomy
- DRUJ synovectomy +/- excision through longitudinal capsular incision
- ECRL to ECU transfer to prevent radial deviation
- repair extensor retinaculum underneath tendons to protect bed
Tendon Transfer
Extensor tendon rupture
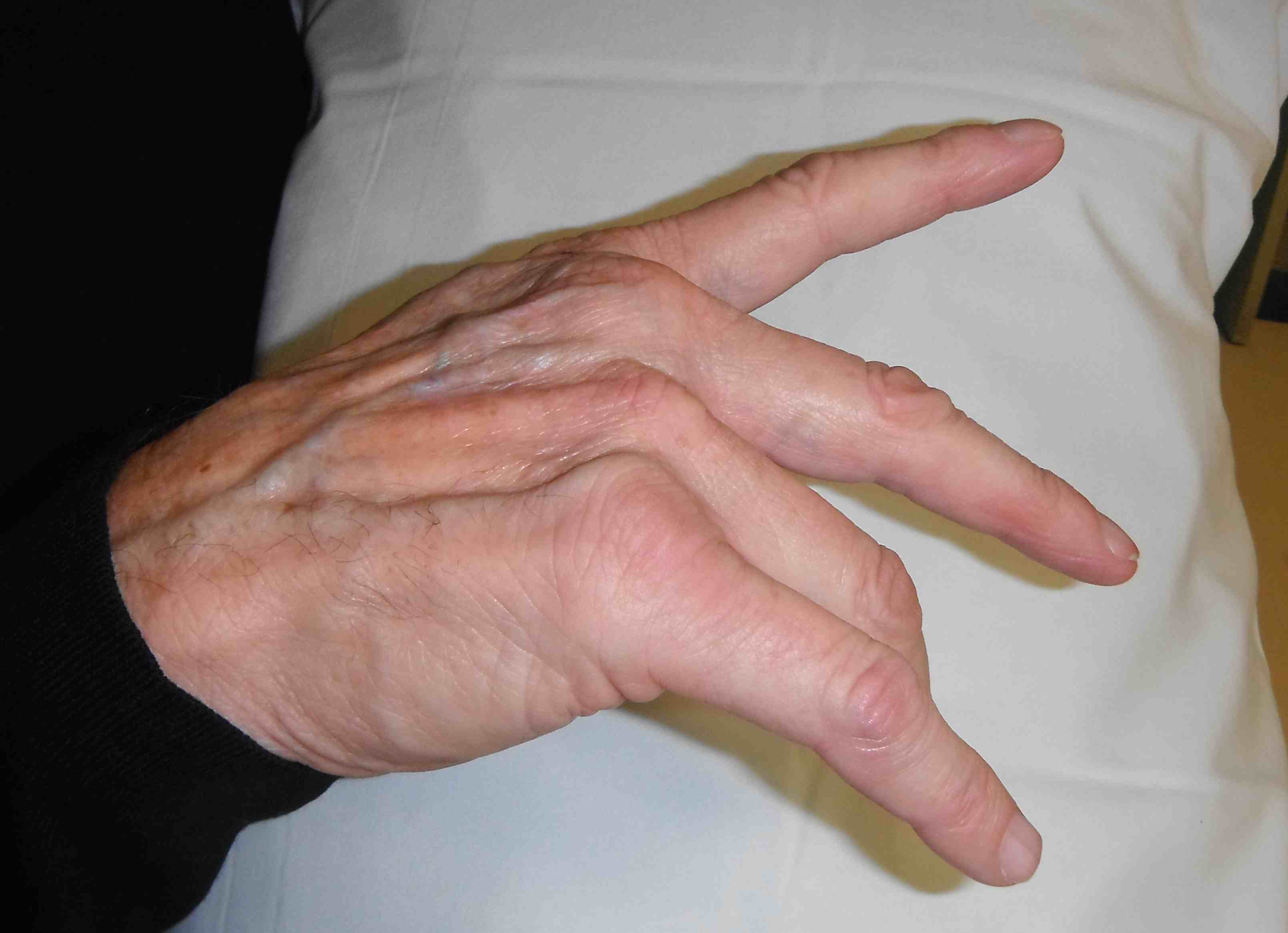
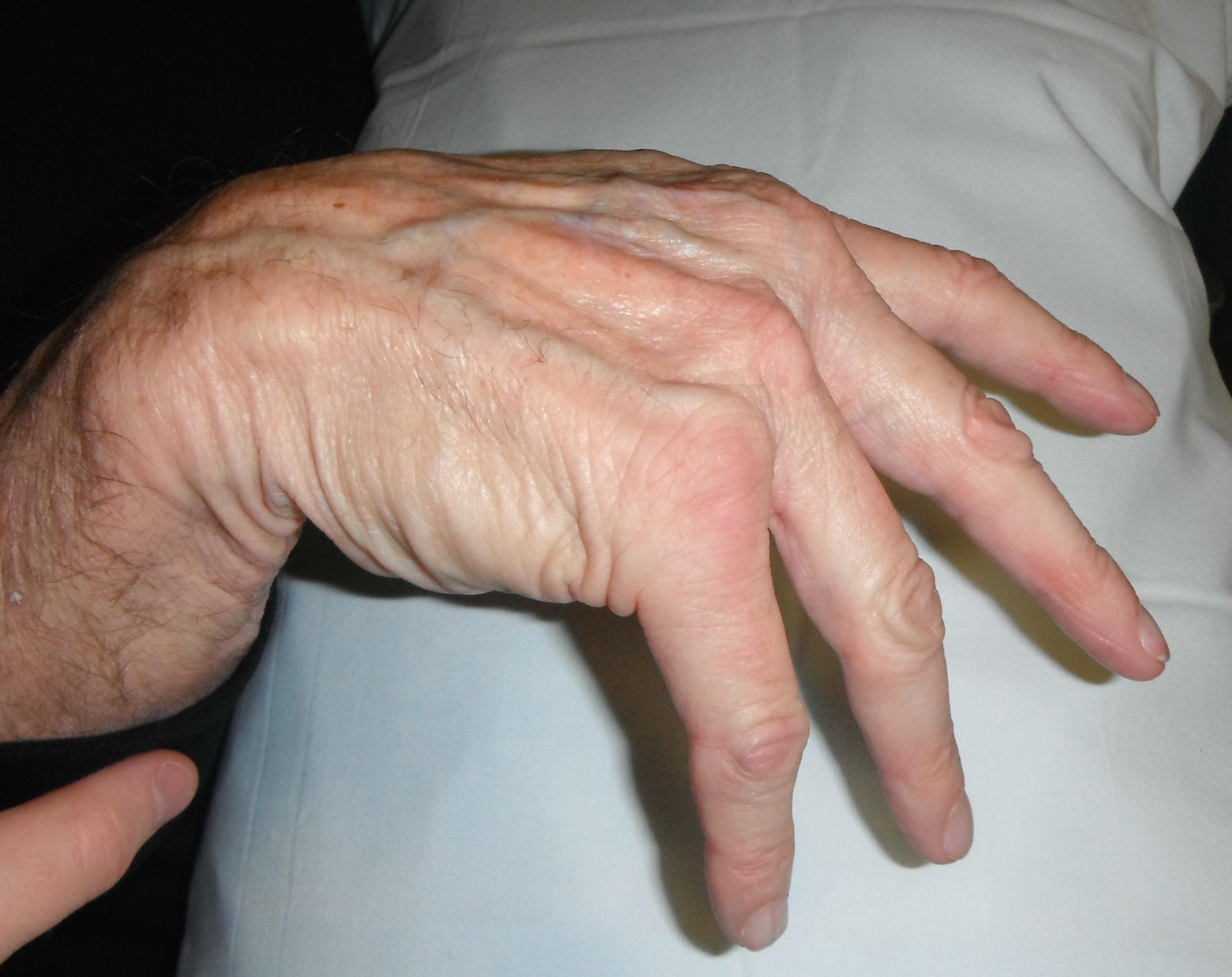
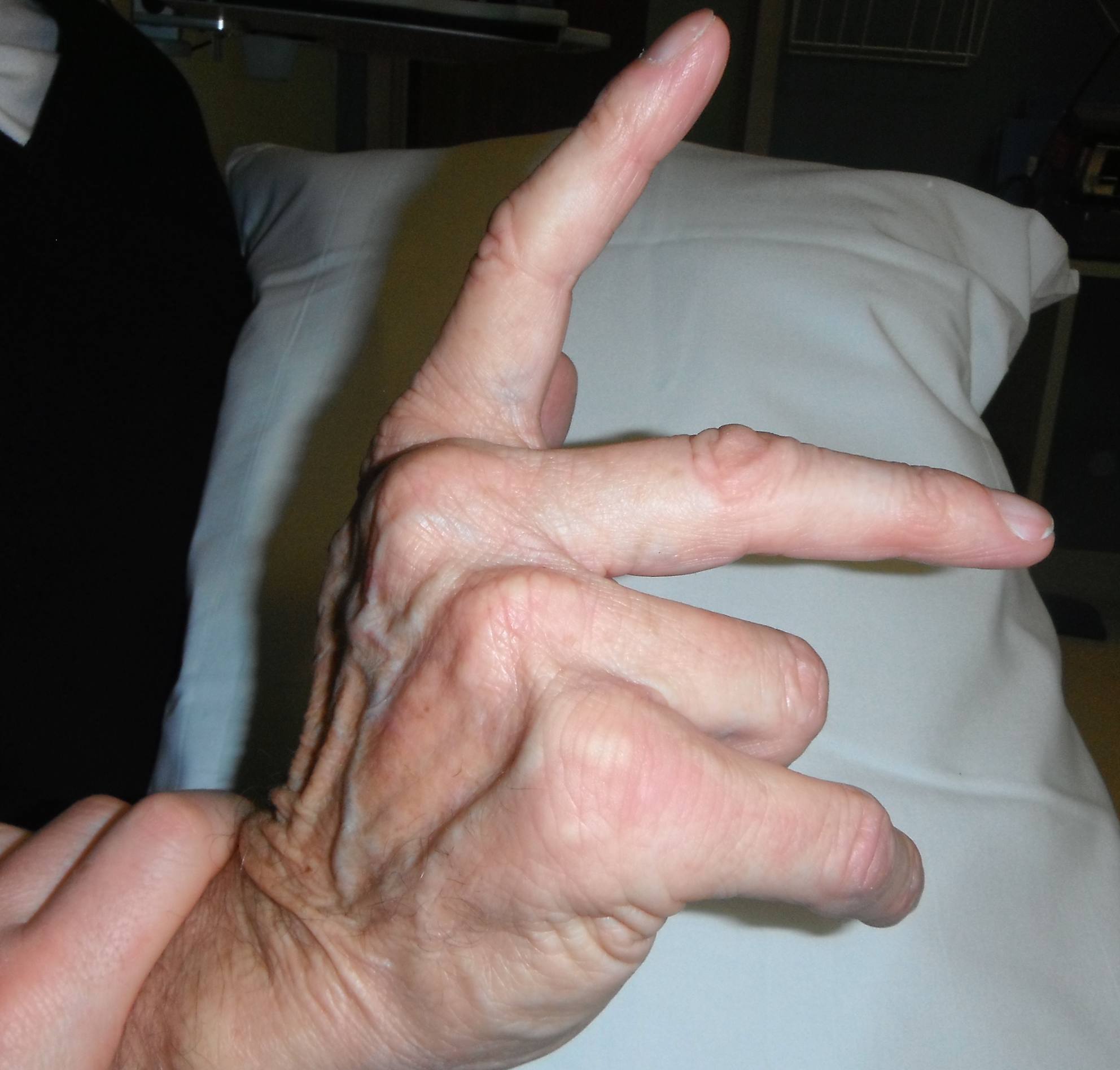
Sequence of extensor tendon rupture
- goes ulna to radial
- EDQ > LF > RF > MF > IF > EI
- opposite to flexor tendons
Extensor Digiti Quinti / Vaughan-Jackson syndrome
- 5th dorsal compartment
- can be clinically silent as EDC and compensate
- attempt to hold LF extended whilst other fingers flexed
DDx dropped finger - extensor tendon subluxation / MCPJ dislocation
Extensor Tendon transfers
| LF rupture | LF & RF rupture | LF / RF / MF rupture | LF / RF / MF / EI / IF rupture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Side to side RF EDC | Side to side MF EDC |
MF to IF EDC Extensor indicis to IF +/- RF and MF FDC to EDC |
RF and MF FDC to EDC |
Flexor tendon rupture
Pathology / Mannerfelt lesion
- distal pole of scaphoid and trapezium erode through volar capsule
- FPL most common
- then FDP IF / FDS IF / MF
- opposite direction to extensors
Management
Carpal tunnel incision / debride bony prominences
| FPL rupture | IF FDP | IF FDS & FDP |
|---|---|---|
| Fuse thumb IPJ | Fuse DIPJ | Fuse DIPJ |
| Transfer FDS IF / RF +/- PL graft | MF FDS transfer |
Distal radio-ulna joint
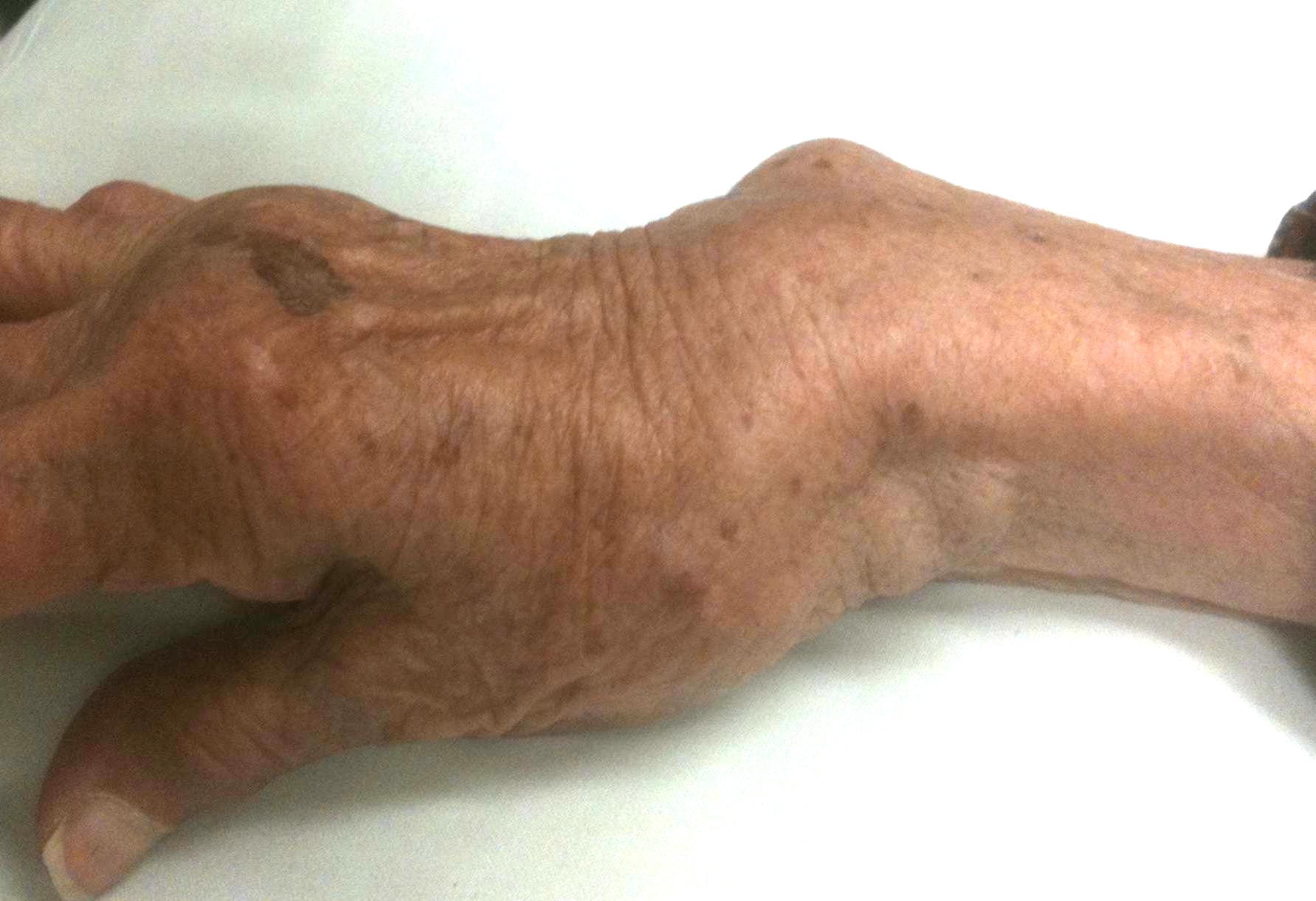
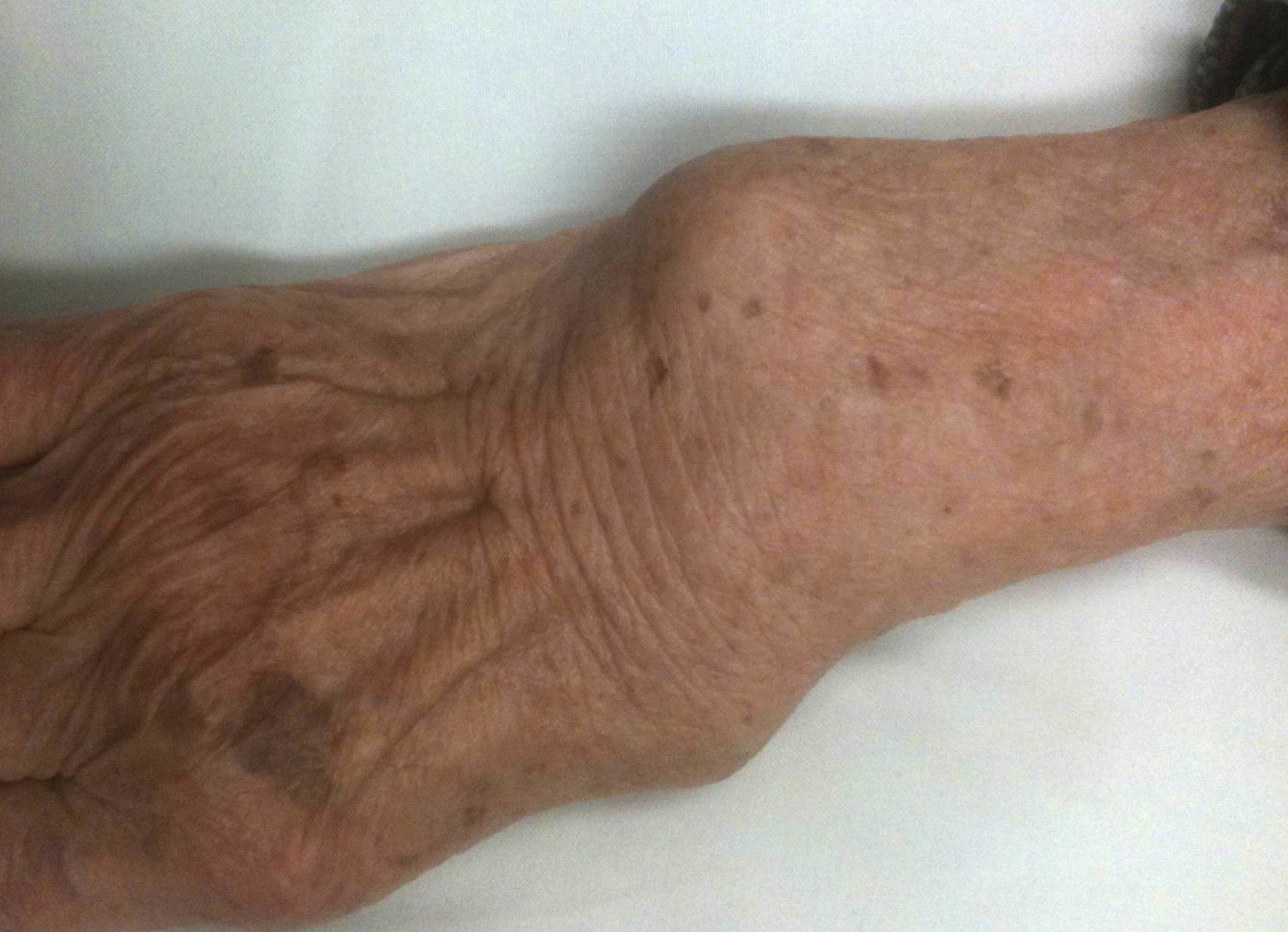
Pathology
Frequently subluxes dorsally
Pain with wrist rotation
Piano key sign - reduce the ulna, it simply redislocates
Options
A. Darrach's
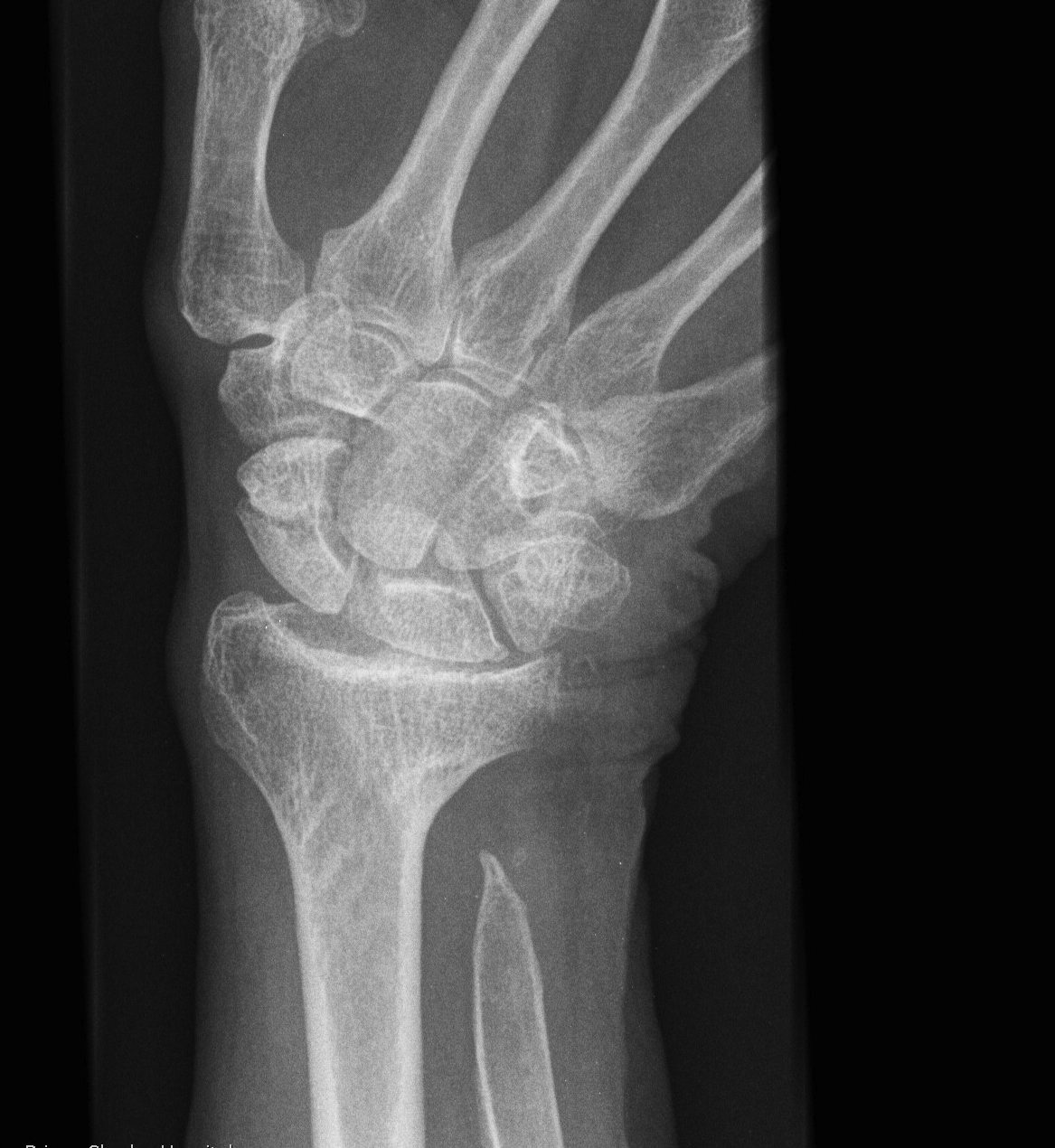
Principle
- excision arthroplasty
Indications
- older patient
Technique
- same dorsal approach as for synovectomy
- radial based ER flap
- excise distal ulna
- proximal limit is articulation with sigmoid notch
- usually 1.5 cm
- round off radial side
- stabilise with volar capsule + ECU tenodesis
- can stabilise with Pronator Quadratus
Complications
- can be unstable
- even with ECU tenodesis
- revise by ECU / FCU tenodesis + pronator quadratus interposition
- or by further shortening!!!
B. Suave - Kapandji
Principle
- fusion DRUJ & ulna pseudoarthrosis
Indication
- younger patient
Technique
- resection of 10 - 15 mm long segment of ulna proximal to DRUJ
- resect proximal periosteum +/- interposition of pronator quadratus to prevent regrowth
- DRUJ denuded of cartilage
- distal fragment brought slightly proximally to prevent ulno-carpal abutment
- fuse to distal radius with screws or K wires
- 4 weeks in LA POP in neutral
Results
- may have better result than Darrach's in RA
- less instability
C. Hemi-resection arthroplasty
Not usually done in RA
- TFCC and DRUJ soft tissues very poor
- indicated for DRUJ arthritis with good soft tissue stability
D. Arthroplasty
Wrist arthrodesis
Options
Partial wrist arthrodesis
- radiolunate / radioscapholunate fusion
- isolated arthritis with midcarpal joint spared
Total wrist arthrodesis
Total wrist arthrodesis
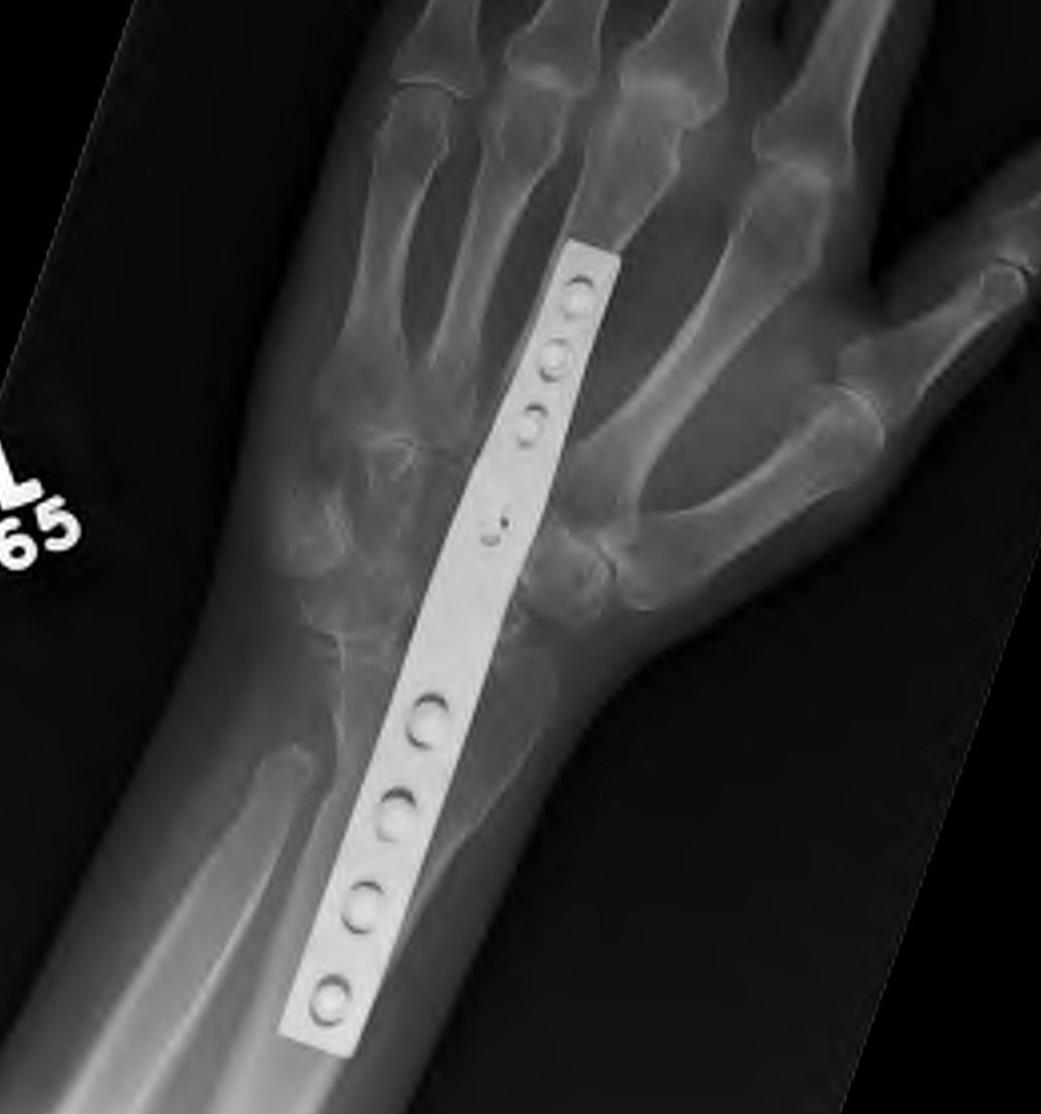
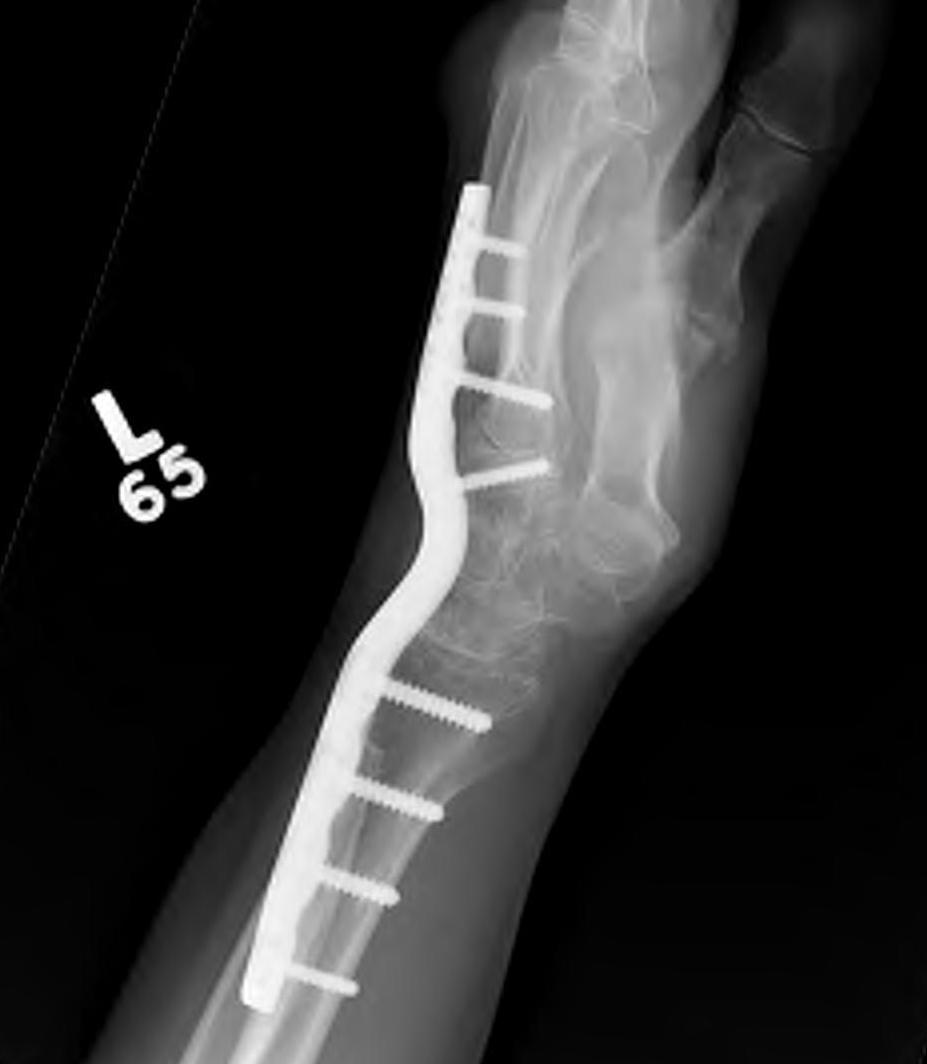
Indications
Diffuse advance radiocarpal and mid carpal OA
Poor bone stock
Stiff wrist
Loss of wrist extensors
High demand
Technique
Total wrist arthroplasty
Indications
Low demand patient
Intact wrist extensors
Good bone stock
Technique
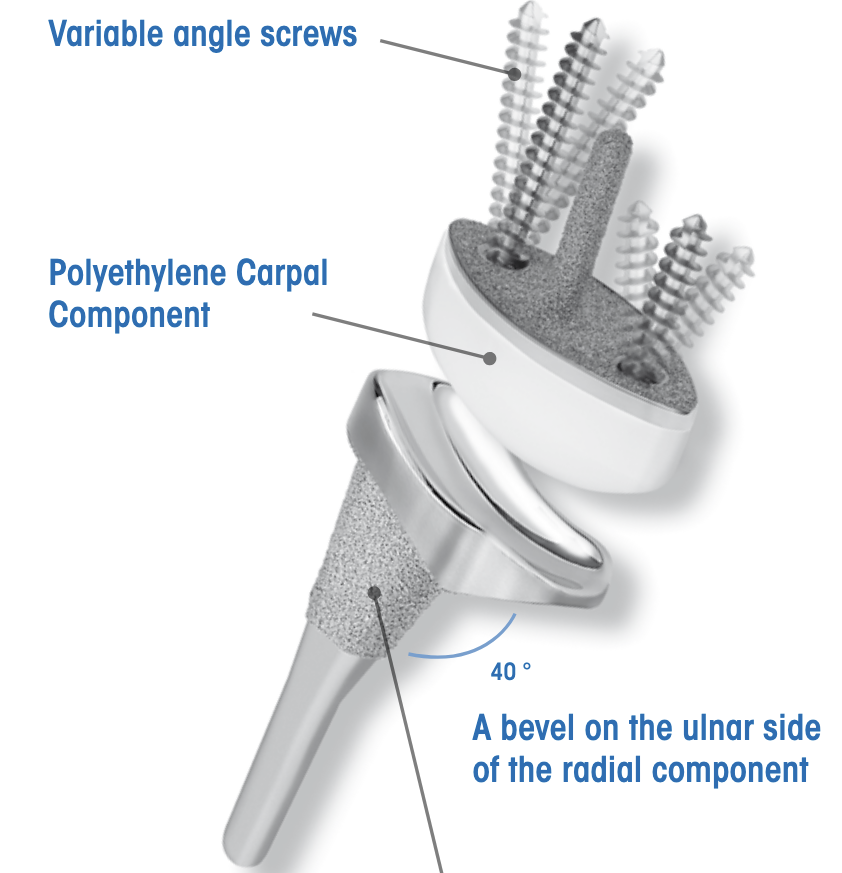
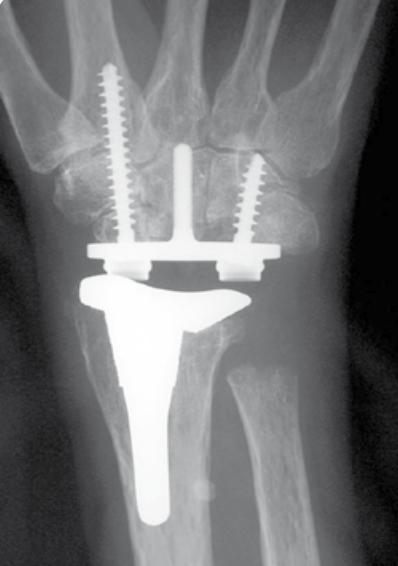
Universal 2 Total Wrist Implant system surgical technique PDF
Dorsal approach
- incision in line with 3rd meta-carpal
- divide extensor retinaculum over ECU compartment and reflect radially
- mobilize entensor tendons
- ensure ECRB and ECRL intact
- elevate wrist capsule as a distally based flap
TWA
- uncemented radial prosthesis
- excise lunate and apply carpal cutting block to capitate
- cut 1 mm hamate / capitate head / midscaphoid
- screw fixation of carpal plate
- trial polyethylene component
Results
- 425 primary total wrist arthroplasty followed for mean 2 years
- 90% inflammatory arthritis
- intra-operative fractures 2%
- postoperative fractures 2%
- 88% 10 year survival
