Definition
Benign enlargement of the common digital branch
Epidemiology
Women between 40 and 60
Usually 3rd webspace
Etiology
Repetitive chronic trauma of interdigital nerve against deep intermetatarsal ligament
- narrow shoes
- high heel shoes
- sustain micro damage to nerve
- perineural fibrosis, neural edema and demyelination
History
Pain with weight bearing
Clicking symptom
Numbness / tingling in the affected toes
Examination
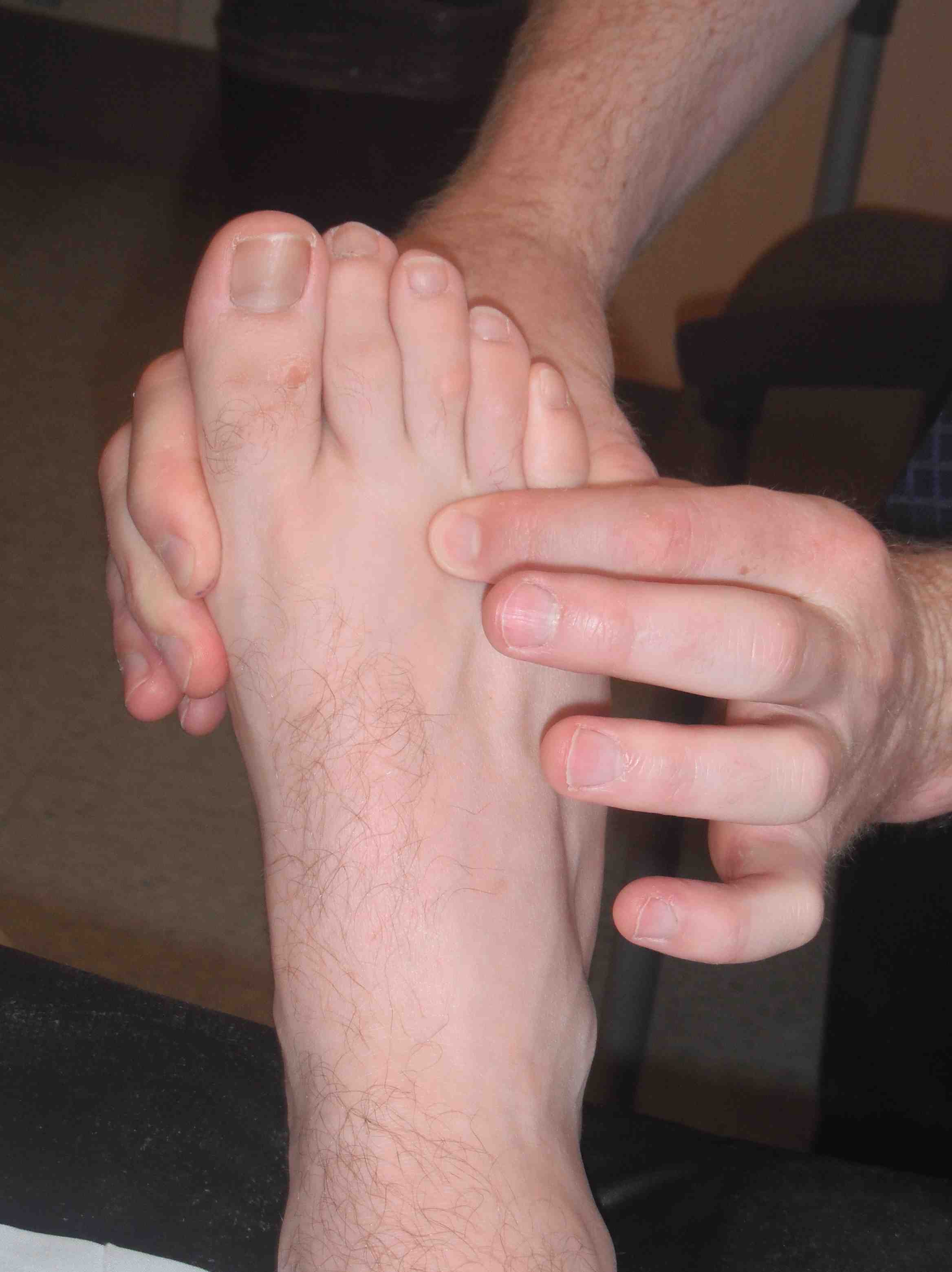
Mulder sign
- palpate webspace with fingers superiorly and inferiorly
- with other hand compress metatarsal heads together
- either palpate the lump or feel a click

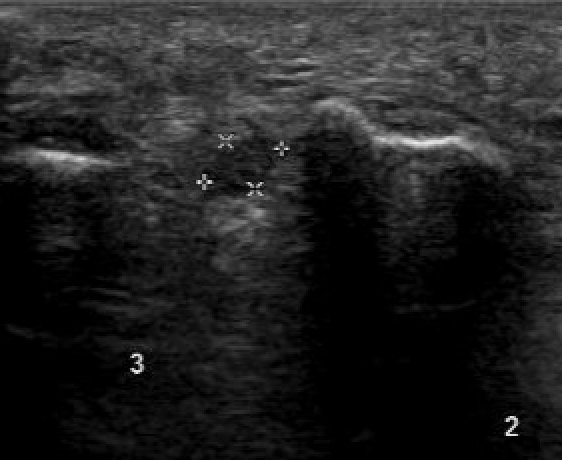
Ultrasound
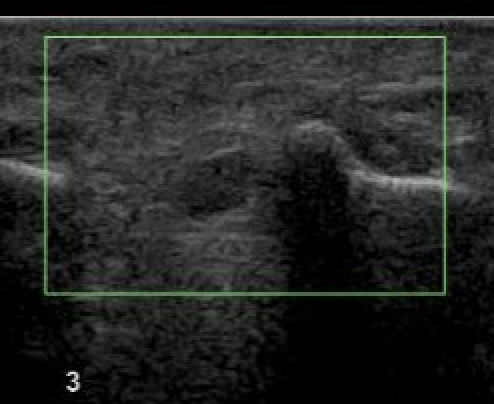

Bignotti et al Eur J Radiol 2015
- systematic review of US versus MRI for Mortons
- equal accuracy
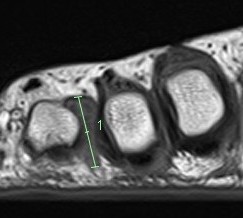
MRI
Obliteration of fat pad
Dumbbell shaped lesion between metatarsal heads
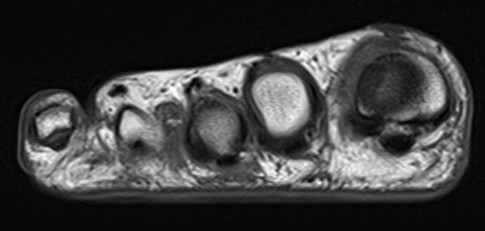
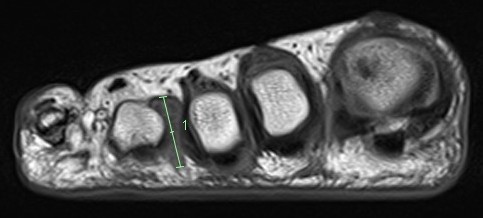
Morton's neuroma 3rd webspace
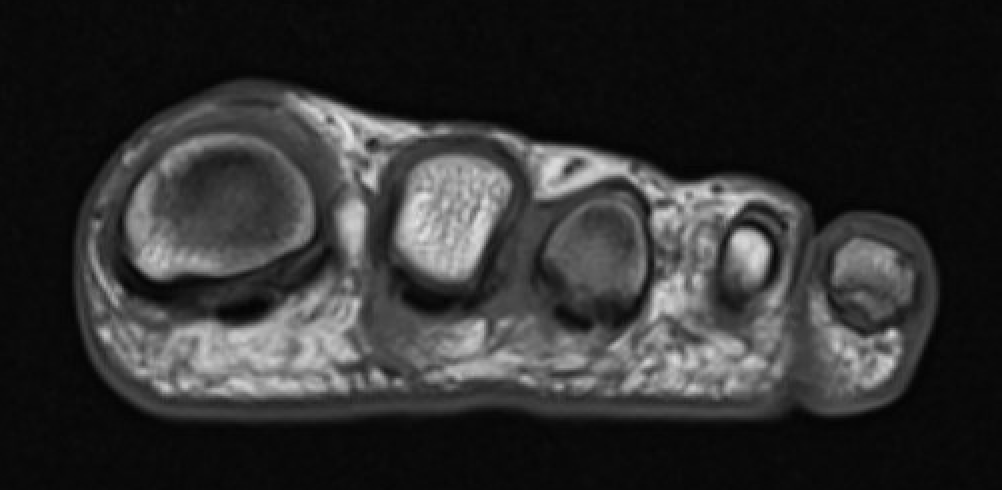
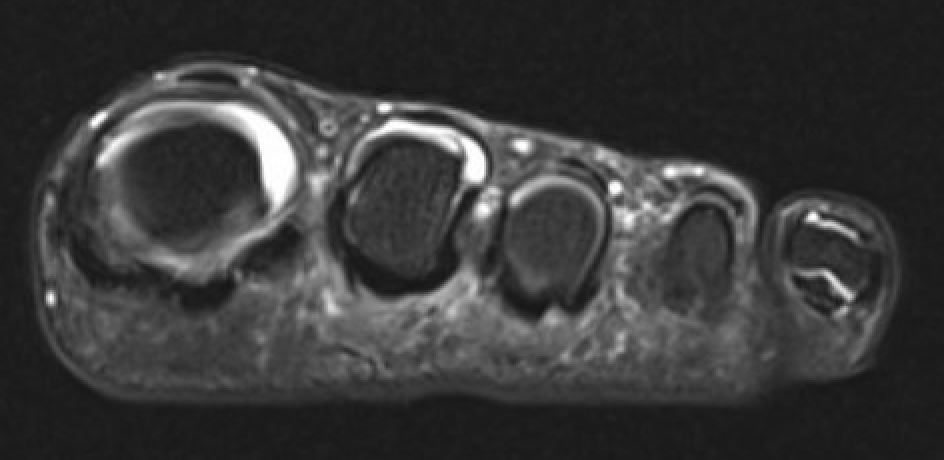
Morton's neuroma 2nd webspace
Non operative management
Wide toe box / metatarsal dome
Cortisone injection
Edwards et al J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2021
- systematic review of efficacy cortisone injection for Morton's neuroma
- evidence of short to medium term efficacy single cortisone shot
Radiofrequency ablation
Llombart et al Am J Phys Med Rehab 2024
- systematic review of 8 studies and 247 patients
- radiofrequency ablation Morton's
- 48% complete symptom relief
- 16% no relief
Operative management
Options
Neurolysis
Neurectomy / resection
- systematic review of neurolysis v neurectomy
- complete pain relief: neurolysis 68% neurectomy 74%
- complete satisfaction: neurolysis 63% neurectomy 57%
- revision surgery: neurolysis 2% neurectomy 5%
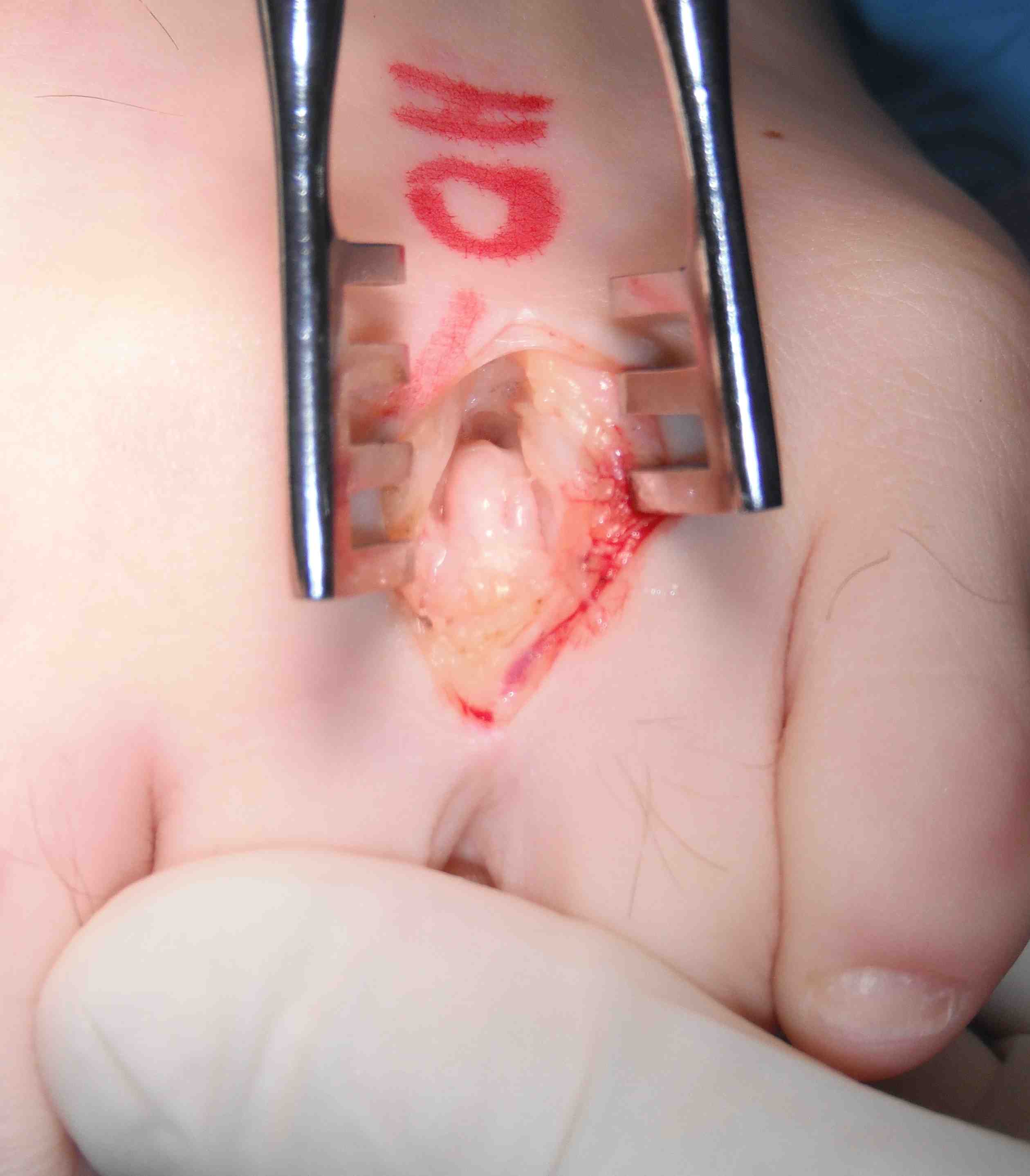
Resection Morton's neuroma
Technique
Vumedi Morton neuroma resection
Dorsal incision over the webspace
- separate metatarsals with lamina spreader / retractor
- divide deep metatarsal ligament
Identify common digital nerve proximally
- identify neuroma / place forceps under
- resect proximal to neuroma
- resect distal to bifurcation
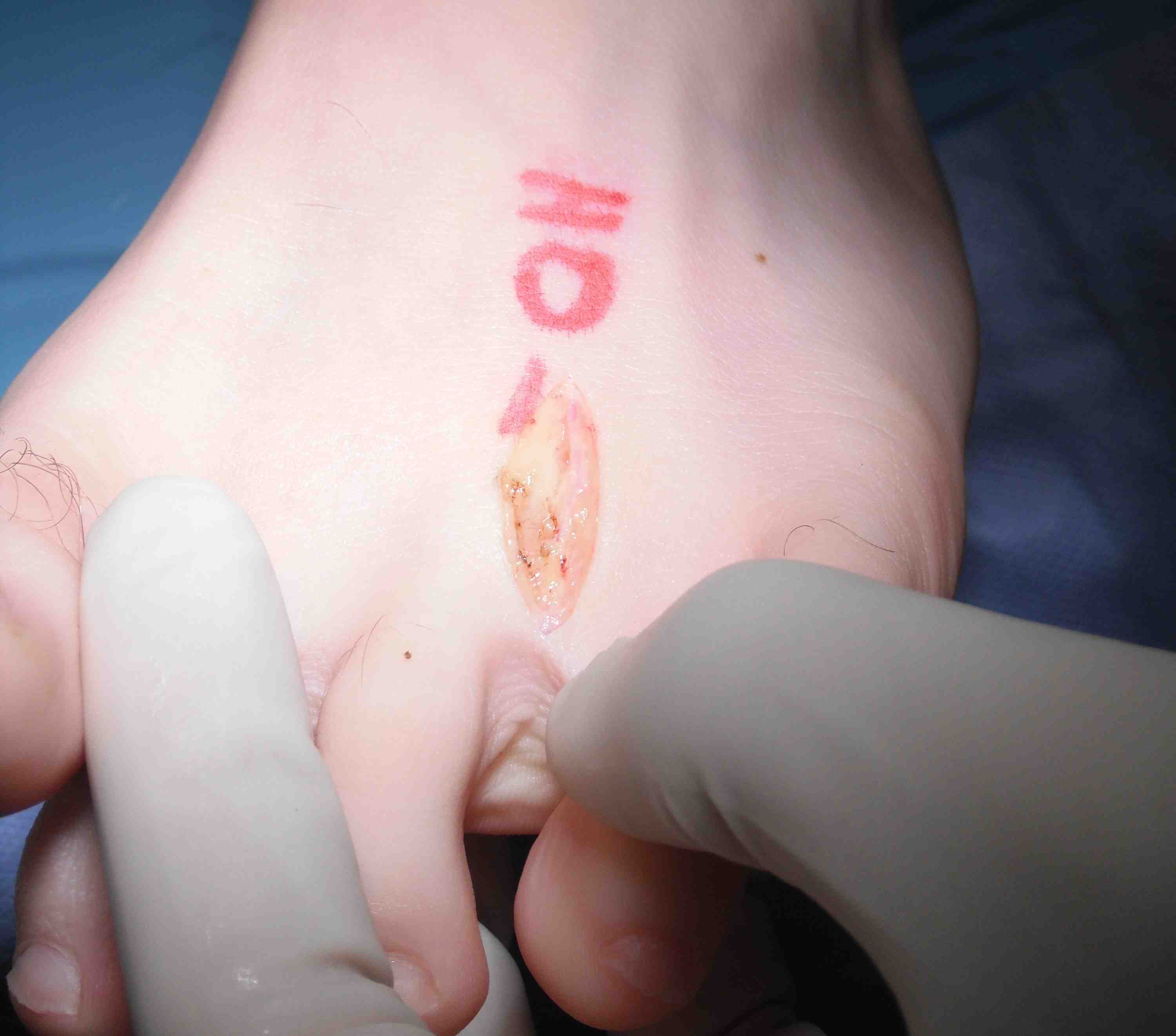

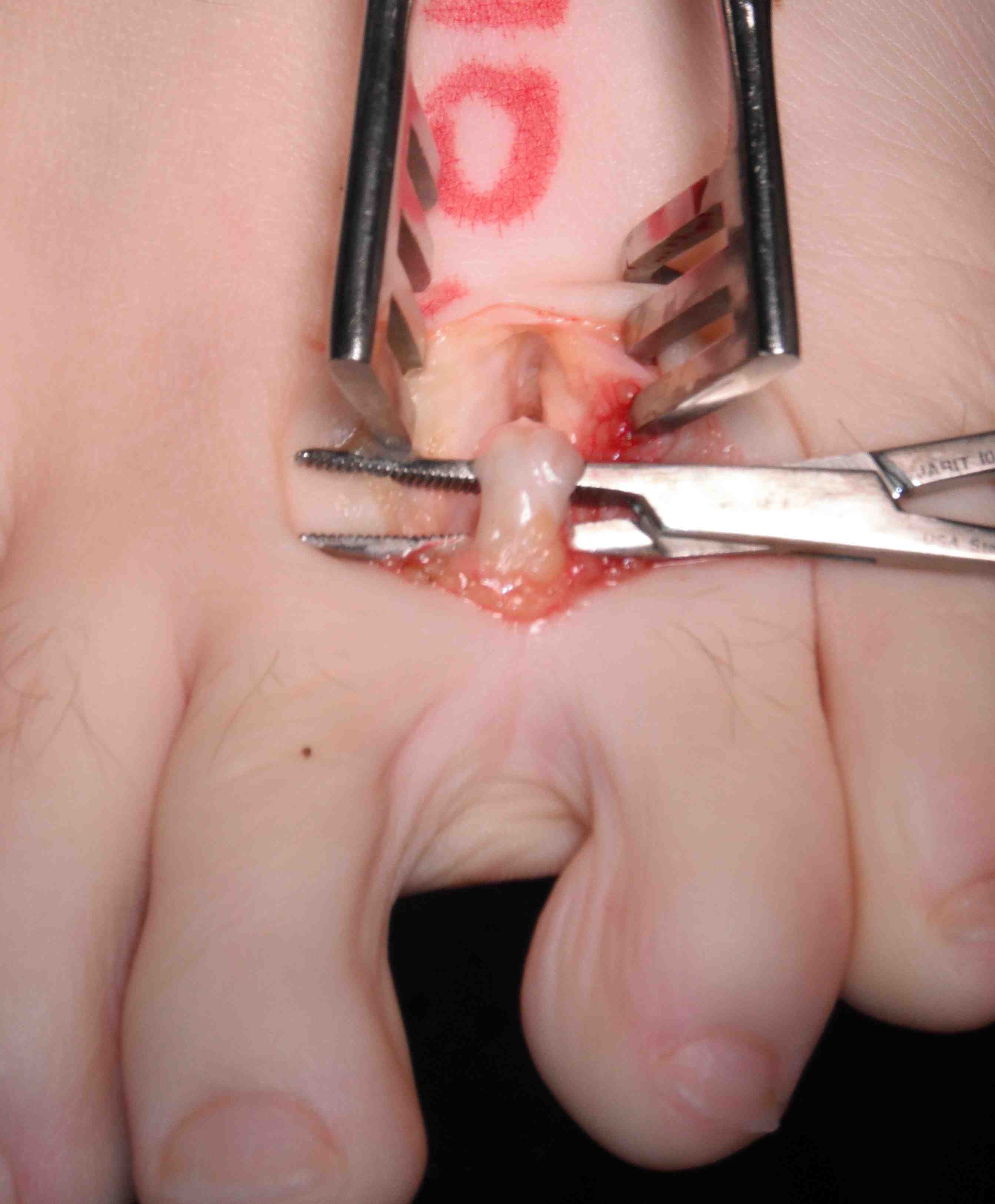
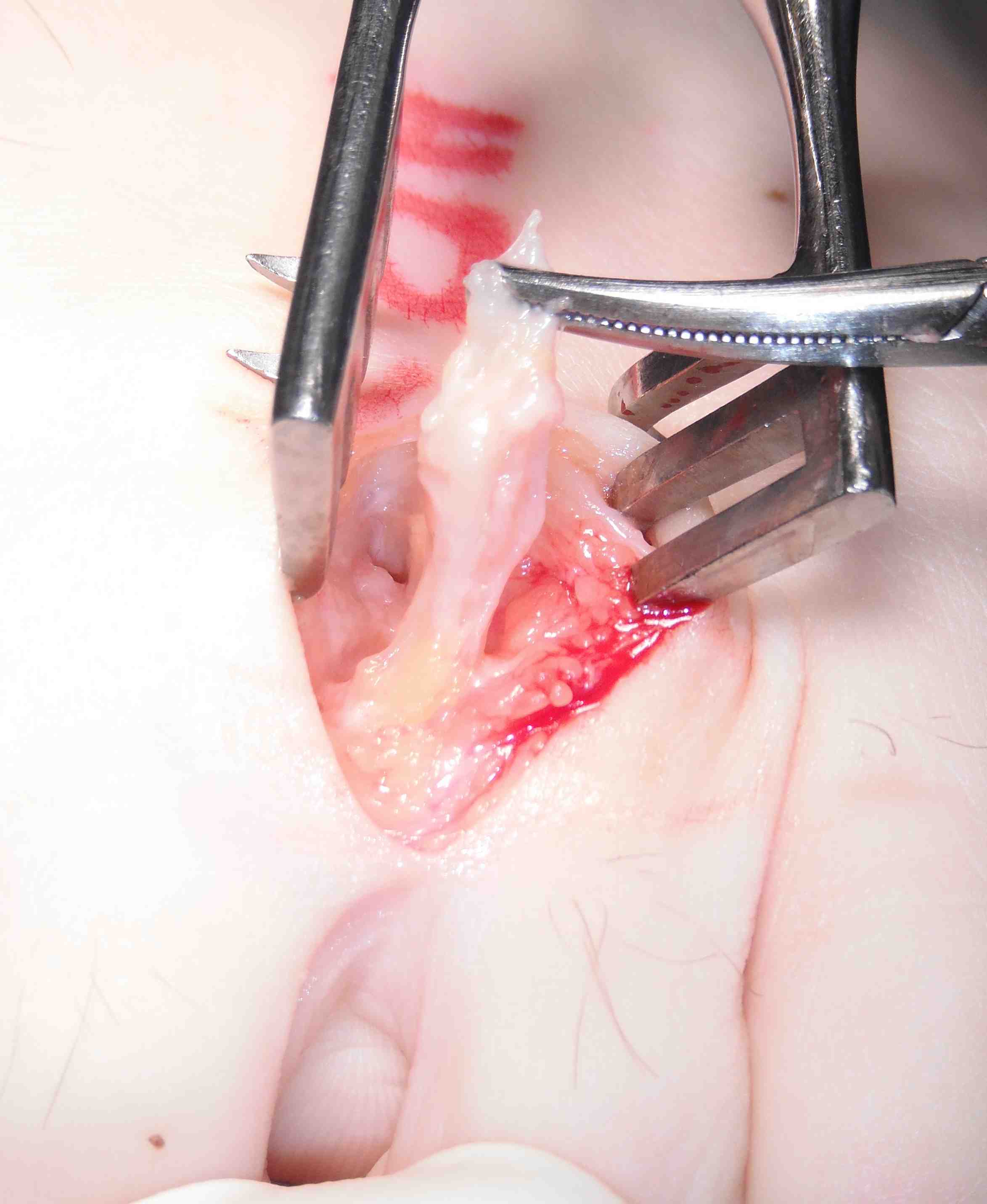
Results
Lee et al Foot Ankle Surg 2024
- systematic review of dorsal v plantar approach for excision
- increased scar tenderness in plantar group: 17% v 6%
- increased reduced sensation in dorsal group: 62% v 49%
Complications
Toe numbness
Painful stump neuroma
Hammer toe (inadvertant lumbrical resection)
Pain secondary to instability / division inter-metatarsal ligament
Neurolysis
Advantage
Prevent toe numbness
Avoid stump neuroma
Technique
Divide deep metatarsal ligament
Results
Archuleta et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2020
- minimally invasive nerve release in 27 cases
- divide deep intermetatarsal ligament
- 59% excellent / good results
- 41% poor results
- 20% required open neurectomy
Koti et al J Orthop Surg Res 2022
- open release of deep intermetatarsal ligament in 39 cases
- 69% good or excellent results
- 30% fair or poor results
- 66% had numbness in toes
