Definition
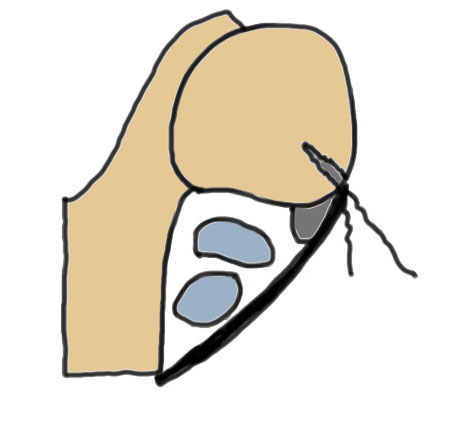
Anterior displacement of peroneal tendons out of peroneal groove
Etiology
Congenital
3% neonates - resolves spontaneously
Traumatic
Sporting activities such as skiing / football / gymnastics
- forced dorsiflexion and inversion
- tear of the superior peroneal retinaculum
- injury often misdiagnosed as an ankle sprain
Lateral calcaneal fractures / talus fractures
Anatomy
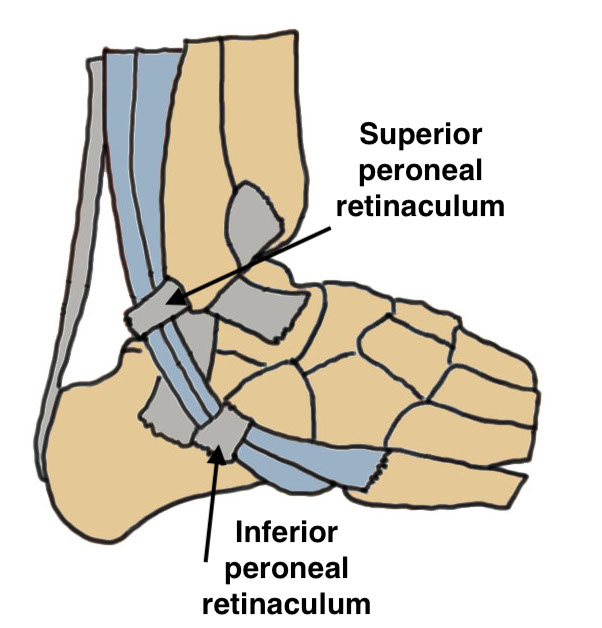
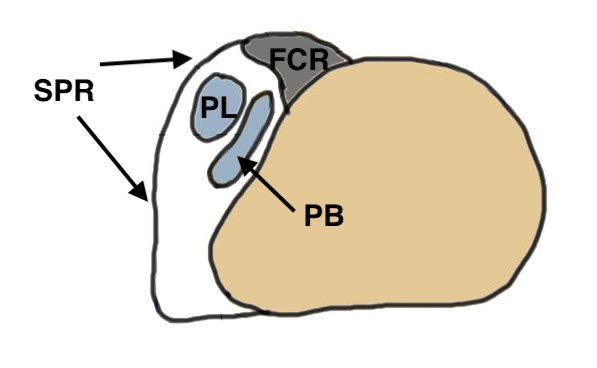
Peroneus longus (PL) posterolateral to Peroneus brevis (PB)
Run in fibro-osseous tunnel behind fibula
| Fibro-osseous tunnel | Superior Peroneal Retinaculum (SPR) | Inferior peroneal retinaculum |
|---|---|---|
|
Retro-malleolar groove lined by fibrocartilage |
Fibrocartilaginous ridge (FCR) - on fibula |
Lateral wall calcaneum below sinus tarsi No role in stability |
|
Fibular anterior PTFL / CFL / PITLF medial |
2 bands - fibula to lateral Tendo Achilles - fibula to posterolateral calcaneum |
Pathology
1. Injury to superior peroneal retinaculum (SPR) / fibrocartilaginous ridge (FCR)
Peroneal tendons sublux out of grove
2. Intra-sheath subluxation with intact superior peroneal retinaculum
- 14 patients with painful snapping but could not dislocated out of groove
- ultrasound demonstrated peroneal tendons switching positions
- at surgery superior retinaculum intact with convex peroneal groove
- 10/14 had peroneal tendons switching positions
- 4/14 had a tear in PB through which PL could sublux
- patients treated with groove deepening and retinaculum reefing
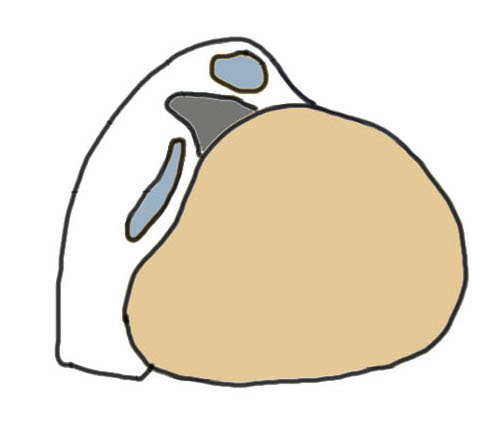
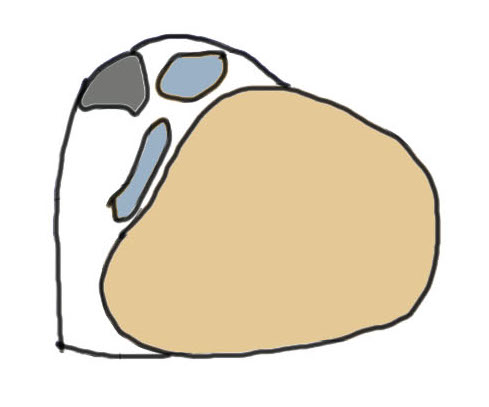
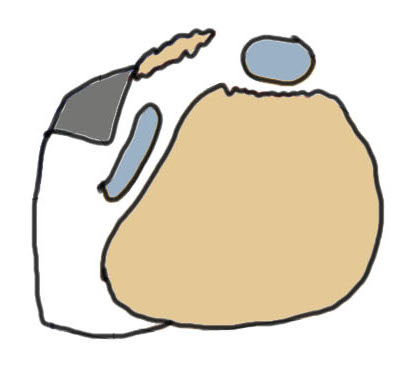
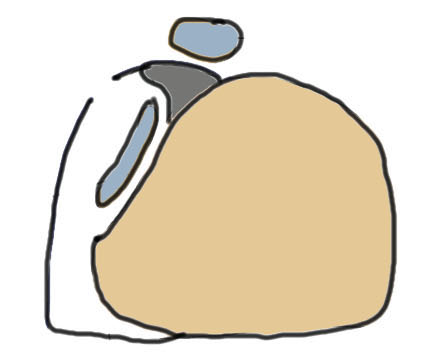
Eckert Classification
| Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 3 | Type 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPR detaches from FCR | SPR and FCR detached | Bony avulsion of SPR and FCR | Midsubstance rupture of SCR |
| 51% | 33% | 13% | ? |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Predisposition
- MRI and CT of 30 patients with peroneal dislocation
- compared to 30 controls
- no difference in retromalleolar groove
- peroneal dislocation associated with low lying PB muscle belly
History
Acute - sudden significant pain behind lateral malleolus
Chronic
- painful snapping of lateral ankle with activity
- feeling of tendon subluxation
Examination
Tenderness & swelling behind lateral malleolus
Snapping - pain or dislocation reproduced by active eversion & dorsiflexion
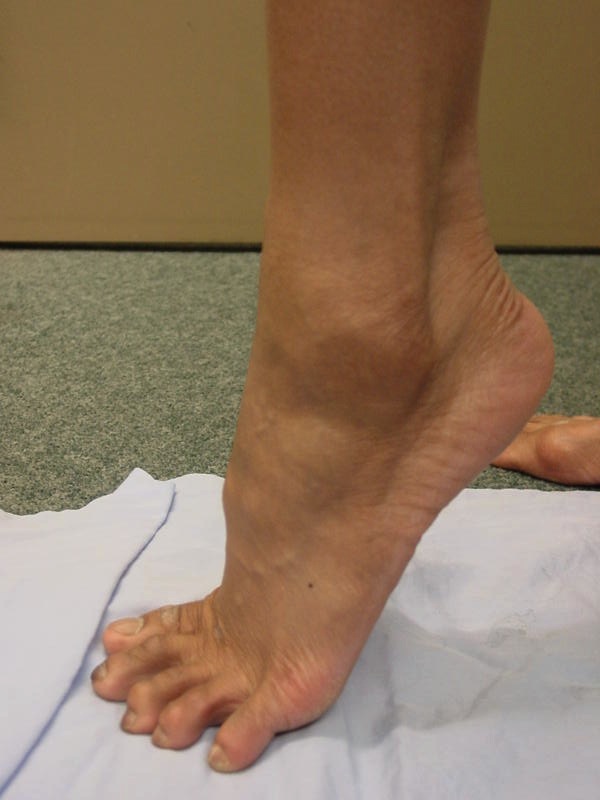
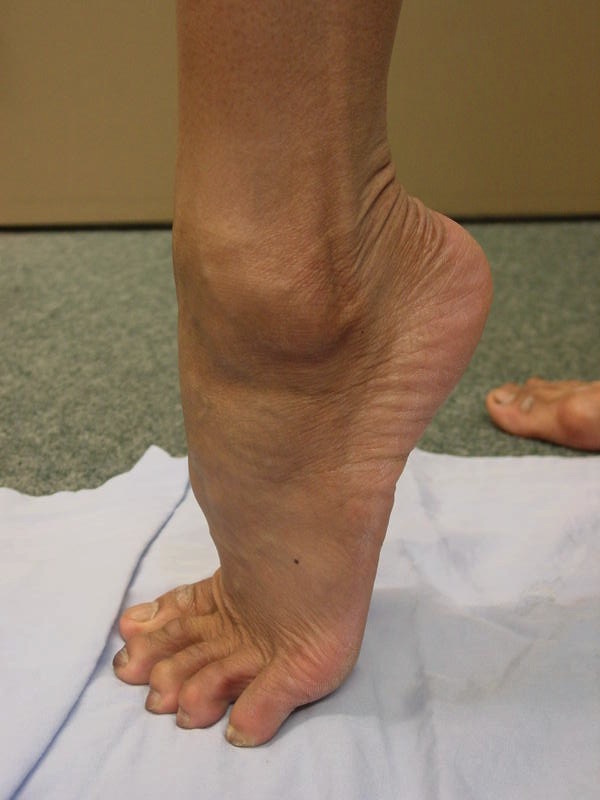
Anterior subluxation of the peroneal tendons with dorsiflexion
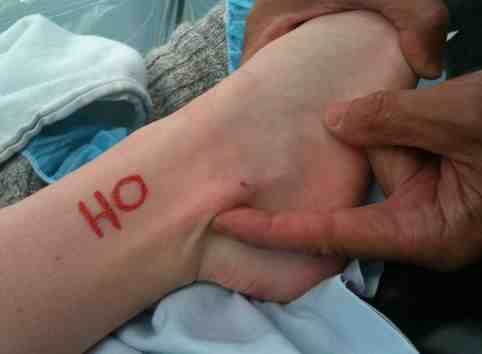
Peroneal tendons easily subluxed out of joint
X-ray
Usually normal
Fleck sign
- avulsed fragment of cortical bone lateral to lateral malleolus
Dynamic Ultrasound
Demonstrates dynamic subluxation
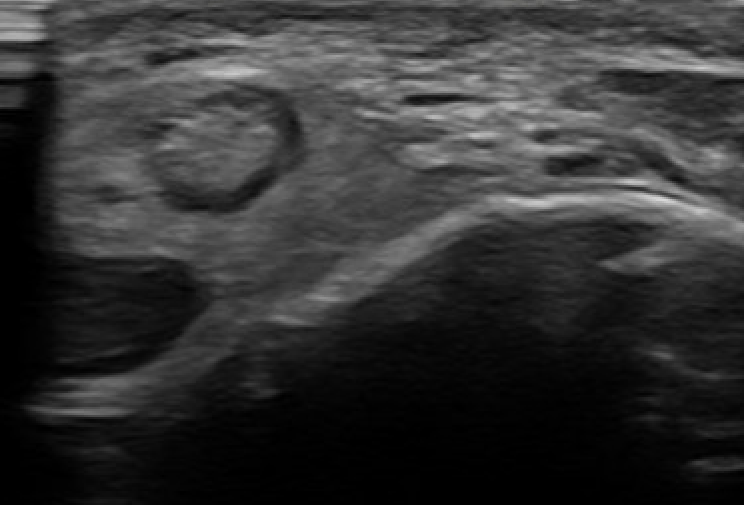
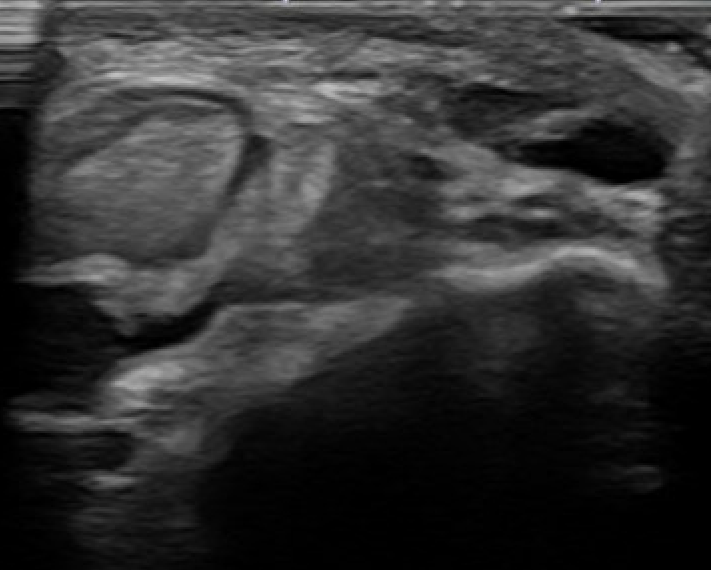
MRI
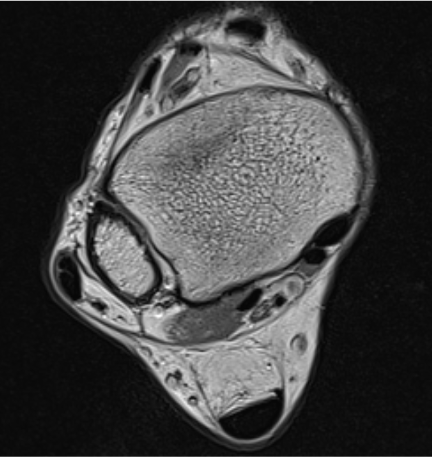
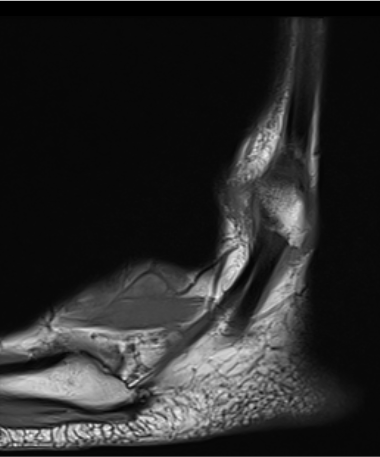
Anterior subluxation of peroneal tendons
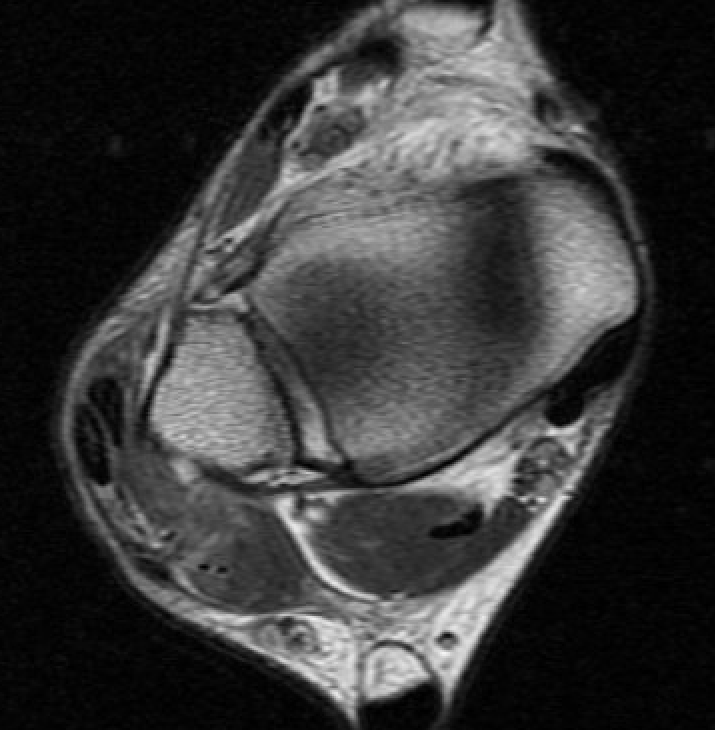
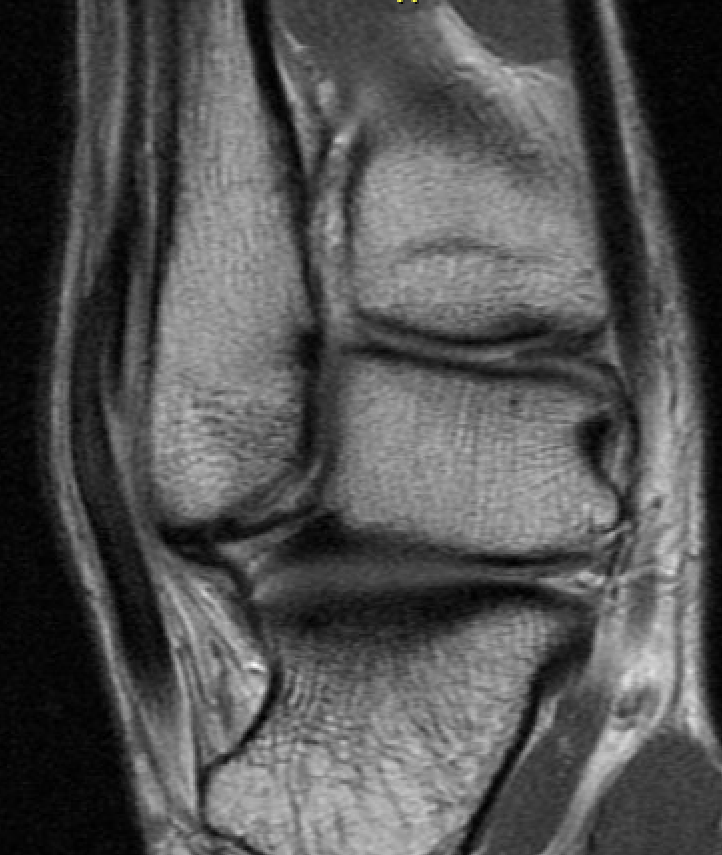
Anterior subluxation of peroneal tendons
Non-operative management
Acute injuries
Cast in plantarflexion for 6 weeks
Operative management
Indications
Acute injury in athletes
Chronic injuries with painful snapping
Acute Repair
Options
1. SPR avulsed - reattach to fibula via trans-osseous sutures / anchors
2. SPR bony avulsion - fragment reattached with sutures / screws / anchors
3. SPR torn midsubstance - primary repair
Chronic management
Options
1. Superior peroneal retinaculum repair / reconstruction
2. Groove deepening
+/- address tears in peroneal tendons
Results
Groove deepening
- systematic review of surgery for peroneal tendon dislocation
- redislocation rate < 1.5%
- best results with SPR repair and groove deepening v SPR repair alone
Open versus endoscopic
Wang et al Orthop Surg 2024
- 46 patients
- equal outcomes been open and endoscopic techniques
Superior peroneal retinaculum
Options
SPR repair
- most common
- direct repair / advancement / tightening / bone block
Rerouting under CFL
- if SPR deficient
- detach CFL from fibular and reroute tendons under, reattach CFL
- divide peroneal tendons, reroute under CFL, suture tendons
SPR reconstruction
- slip of T Achilles
- free plantaris
- peroneal brevis
Direct repair of SPR +/- groove deepening
Technique
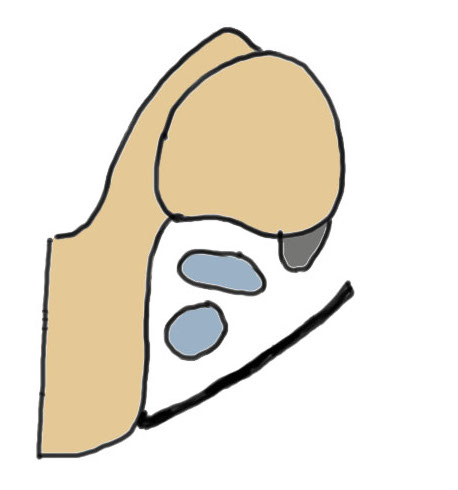
Vumedi open SPR repair with transosseous sutures and groove deepening
Vumedi open SPR repair with suture anchors
Vumedi open SPR repair with suture anchors and groove deepening
Lateral decubitus
- curvi-linear incision posterior to fibula
- protect sural nerve
- divide SPR
Identify SPR pathology
- typically avulsed from fibula
- allows tendons to sublux anteriorly
Inspect peroneal tendons for pathology
- synovectomy
- repair splits
- debride low lying / excessive muscle
Groove deepening
- deepen with burr
- can elevate fibrocartilage base / deepen groove with burr / replace fibrocartilage base
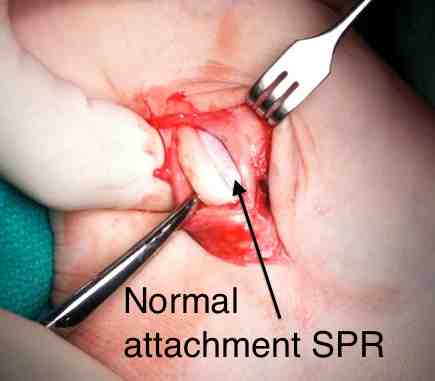
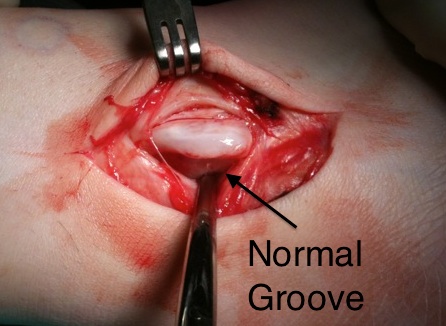
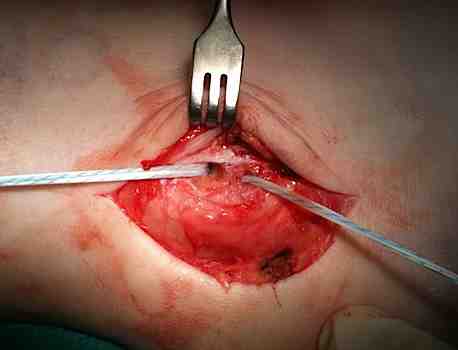
Identify avulsion of SPR from fibula, assess groove, insert anchors in fibula
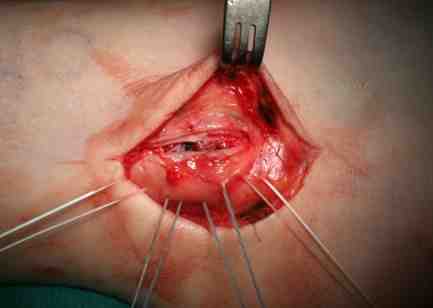
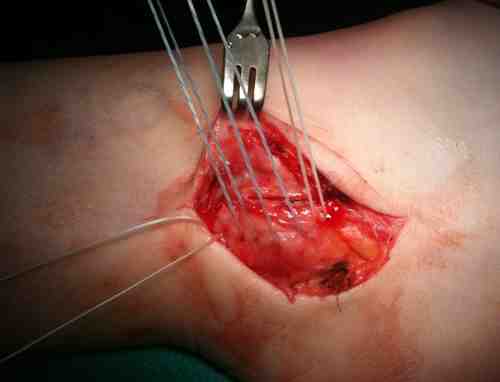
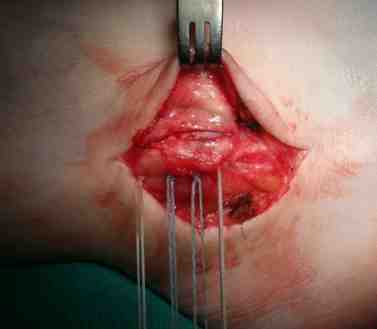
Repair + advancement / tightening of SPR with pants over vest technique
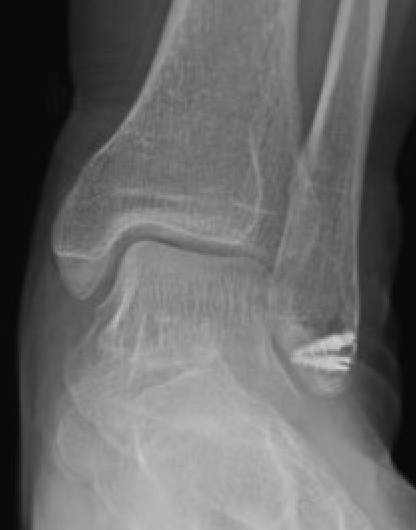
Endoscopic SPR repair
Arthroscopic technique endoscopic SPR repair PDF
