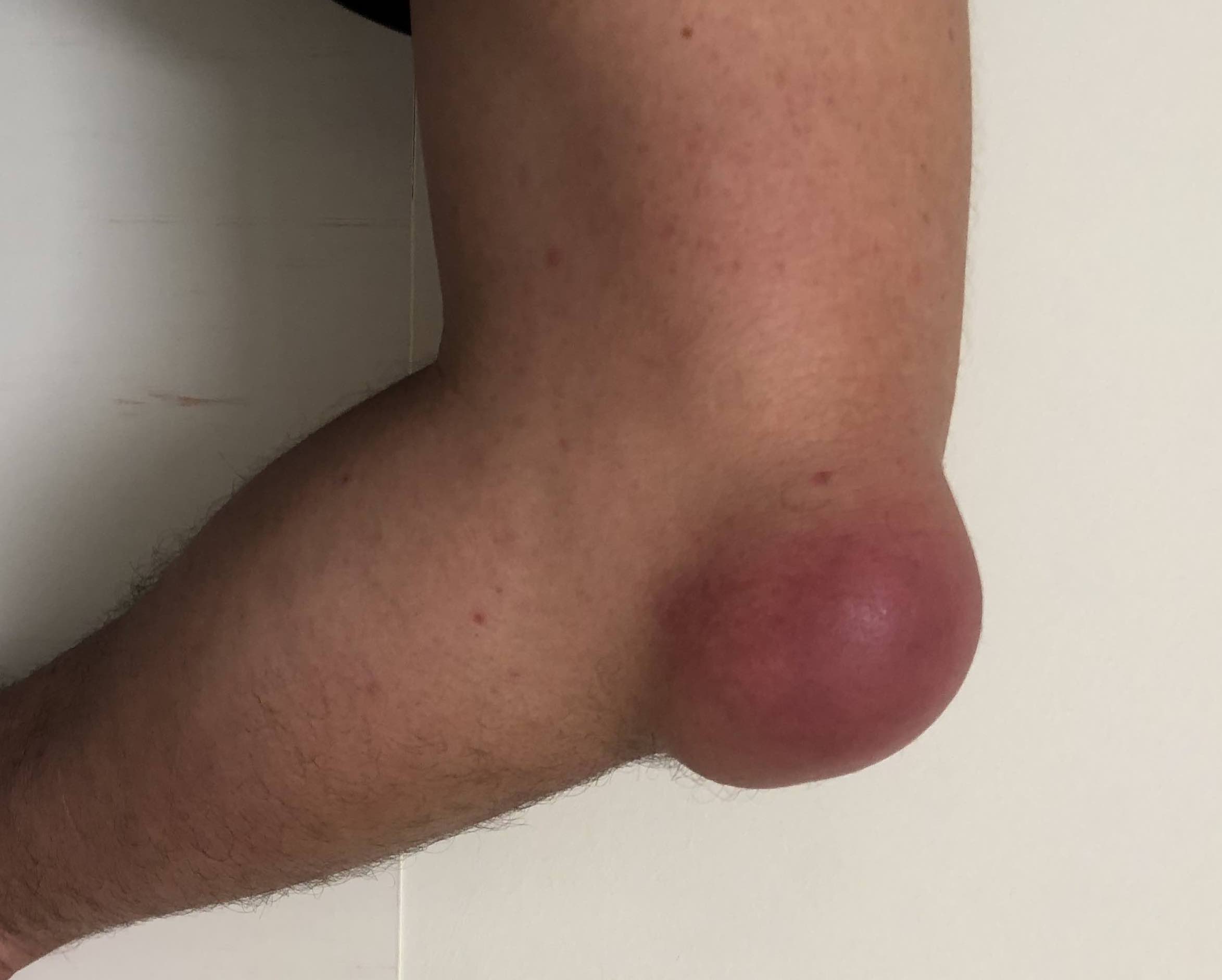
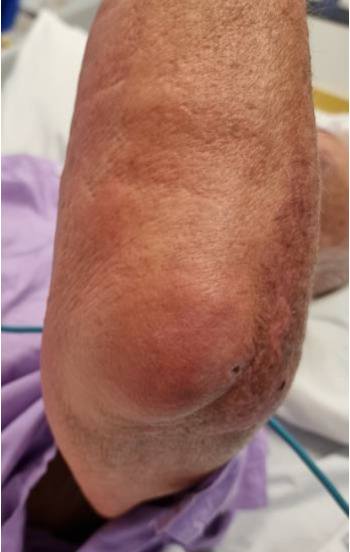
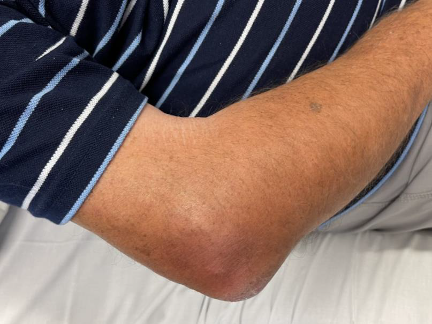
Nonseptic olecranon bursitis
Definition
Abnormal increase in fluid in the olecranon bursa
Most commonly inflammed of all 150 bursa in human body
Anatomy
Olecranon bursa
- bursal lining is poorly vascularized synovial lining
- allows skin to move back and forward with flexion and extension
Etiology
Repetitive microtrauma
Medical conditions
- 10,000 patients with olecranon bursitis
- increased risk males / hyperlipidemia / high BMI / older age / smoking
Xray
Exclude olecranon spur
Nonoperative management options
Avoid trauma
Compression bandaging
NSAIDs
Aspiration
Cortisone injections
- RCT of 90 patients with olecranon bursitis
- NSAIDS v Aspiration v Aspiration + cortisone injection
- no difference between 3 groups at 4 weeks
- average resolution 85%
- earlier resolution with cortisone injection
Operative options
Open excision
Arthroscopic excision
Open bursectomy
Technique
Vumedi open olecranon bursectomy video
Results
- open excision of 190 cases olecranon bursitis
- revision rate 12%
- more likely women / diabetes / rheumatoid
- 4% delayed wound healing
- 2% need a flap, more commonly rheumatoid arthritis
Endoscopic bursectomy
Advantage
Reduced risk of wound complications and recurrence
Technique
Arthroscopy techniques endoscopic bursectomy PDF
Vumedi endoscopic olecranon bursectomy video
Vumedi endoscopic olecranon bursectomy video 2
Results
Shen et al J Orthop Surg Res 2024
- 28 cases treated with endoscopic bursectomy
- elbow function normal after one month
- no recurrence or complications
Infected olecranon bursitis
Etiology
Most common S aureus (90%)
Diagnosis
Can be difficult to septic from aseptic olecranon bursitis
- systematic review of septic v aseptic olecranon bursitis
- tenderness (88% septic, 36% aseptic)
- erythema/cellulitis (83% septic, 27% aseptic)
- fever (38% septic, 0% aseptic)
Aspiration
- leucocytosis > 10,000 mm3
- > 50% neutrophils
Management options
Antibiotics
Aspirate + antibiotics
Open v endoscopic bursectomy
Results
Reasonable to treat initially with antibiotics, then consider endoscopic bursectomy to reduce wound complications
Antibiotics
Beyde et al Acad Emerg Med 2022
- 134 cases septic olecranon bursitis treated with empiric oral antibiotics
- no aspirations
- 88% resolution
- 7% readmitted for IV antibiotics
Aspiration + Antibiotics
Deal Jr et al J Hand Surg Am 2020
- 30 cases of septic olecranon bursitis
- aspiration + antibiotics versus antibiotics alone
- increased risk of surgical intervention in aspiration group
Open bursectomy
Uckay et al Mayo Clin Proc 2017
- RCT of 130 septic olecranon bursitis
- open bursectomy (one stage) v antibiotics and delayed open bursectomy (two stage)
- treatment failure one stage: 10%
- treatment failure two stage: 16% with higher rate of wound dehiscence
Endoscopic Bursectomy
- 14 cases of septic olecranon bursitis treated with endoscopic bursectomy
- no wound healing issues
- 1 minor recurrence
