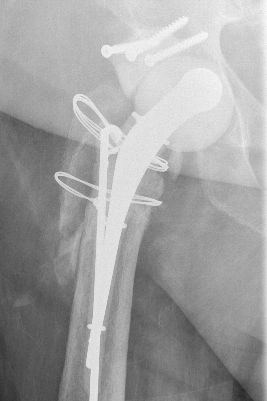
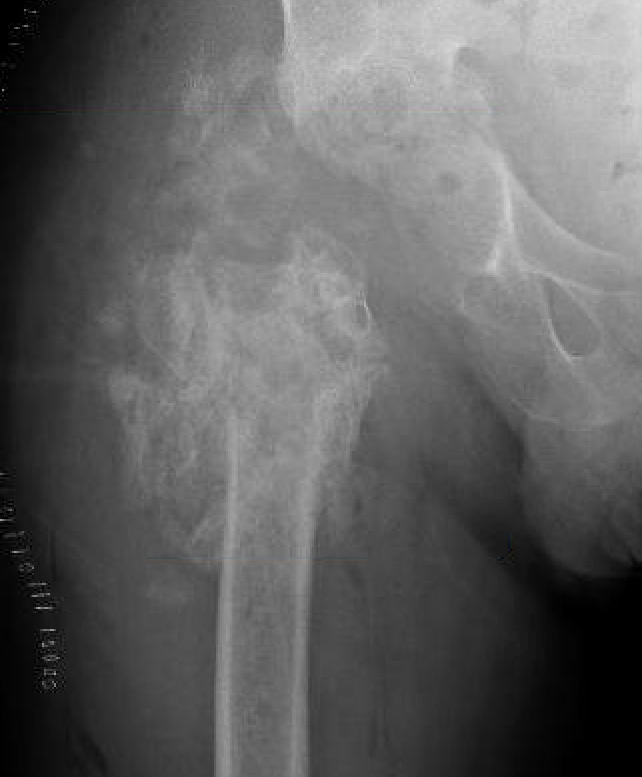
Tsukayama Classification
1. Early post-operative infection < 1 month
- < 1/12
- febrile patient with red discharging wound
2. Late chronic infection > 1 month
- indolent (low virulent)
- well patient with a healed wound and worsening of pain
3. Acute hematogenous
- previously well functioning THA now very painful
- secondary to another source of infection
4. Positive intra-operative culture
- revision for aseptic loosening
- intraoperative cultures comes back positive (2 out of 5)
Options
Antibiotic suppression
Debridement and prosthesis retention
One stage revision
Two stage revision
Resection arthroplasty
Antibiotic Suppression
Indications
Elderly and frail
Not suitable for surgery
Require
Known sensitive organism
Stable prosthesis
Tolerable oral antibiotics
Results
Pavoni et al Clin Microbiol Infect 2004
- infection suppression with antibiotics in 34 patients
- failure of treatment in 13 patients
Debridement, Antibiotics, Implant Retention (DAIR)
Indications
Acute infection, < 4/52, no sinus
Stable, well-fixed prosthesis
Known sensitive organism
- reduced efficacy with S. aureus unless rifampicin used
- poor results with MRSA
Technique
Surgery
Excision of all necrotic and infected tissue
- ensure implant well fixed
- exchange liner (if uncemented)
- wash +++
Antibiotics
IV antibiotics 4 - 6 weeks
Results
- systematic review of 1300 PPI hip treated with DAIR
- infection eradication 72%
- < 7 days: infection eradication 76%
- exchange modular implants: infection eradication 78%
One-Stage Revision
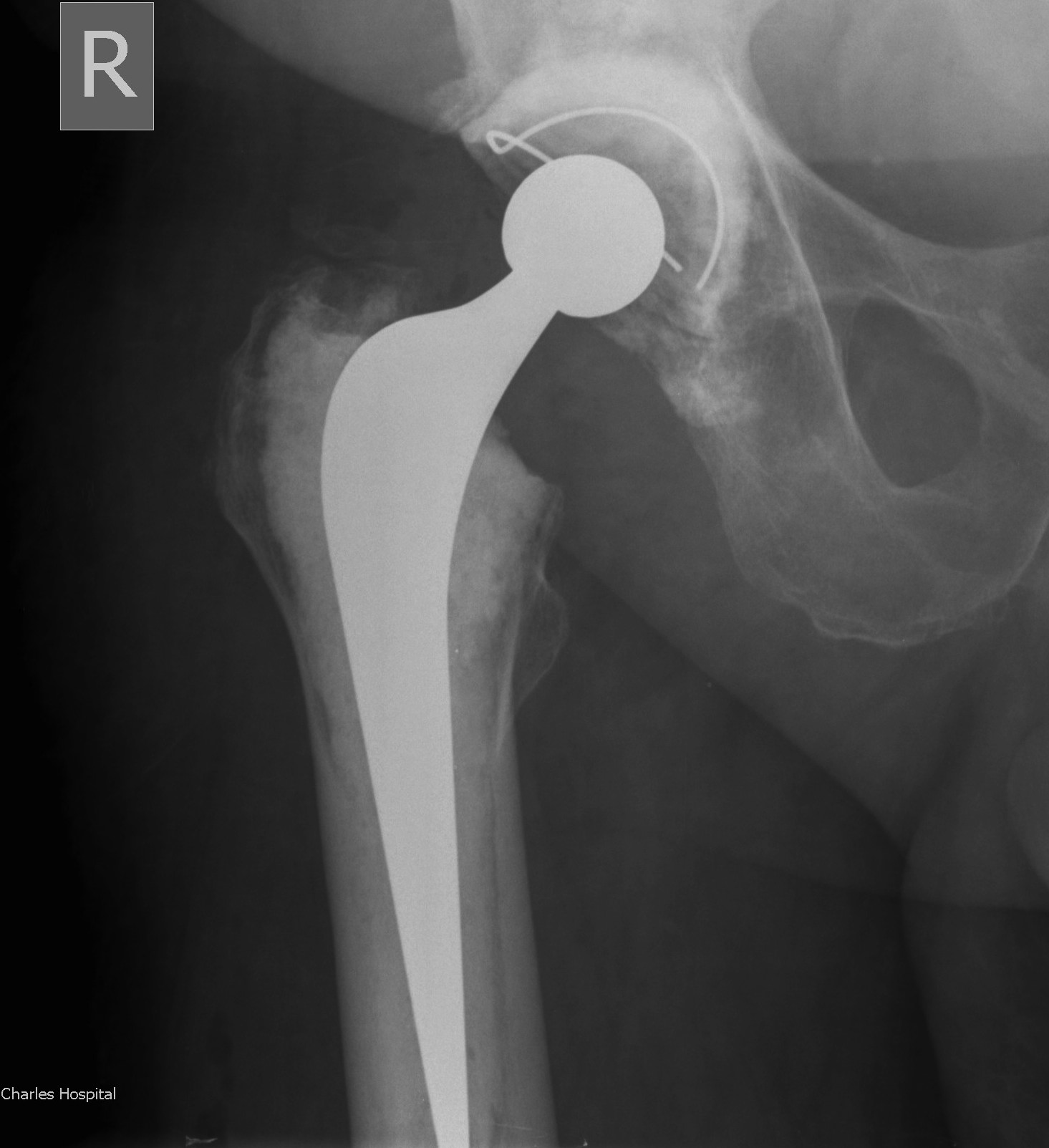
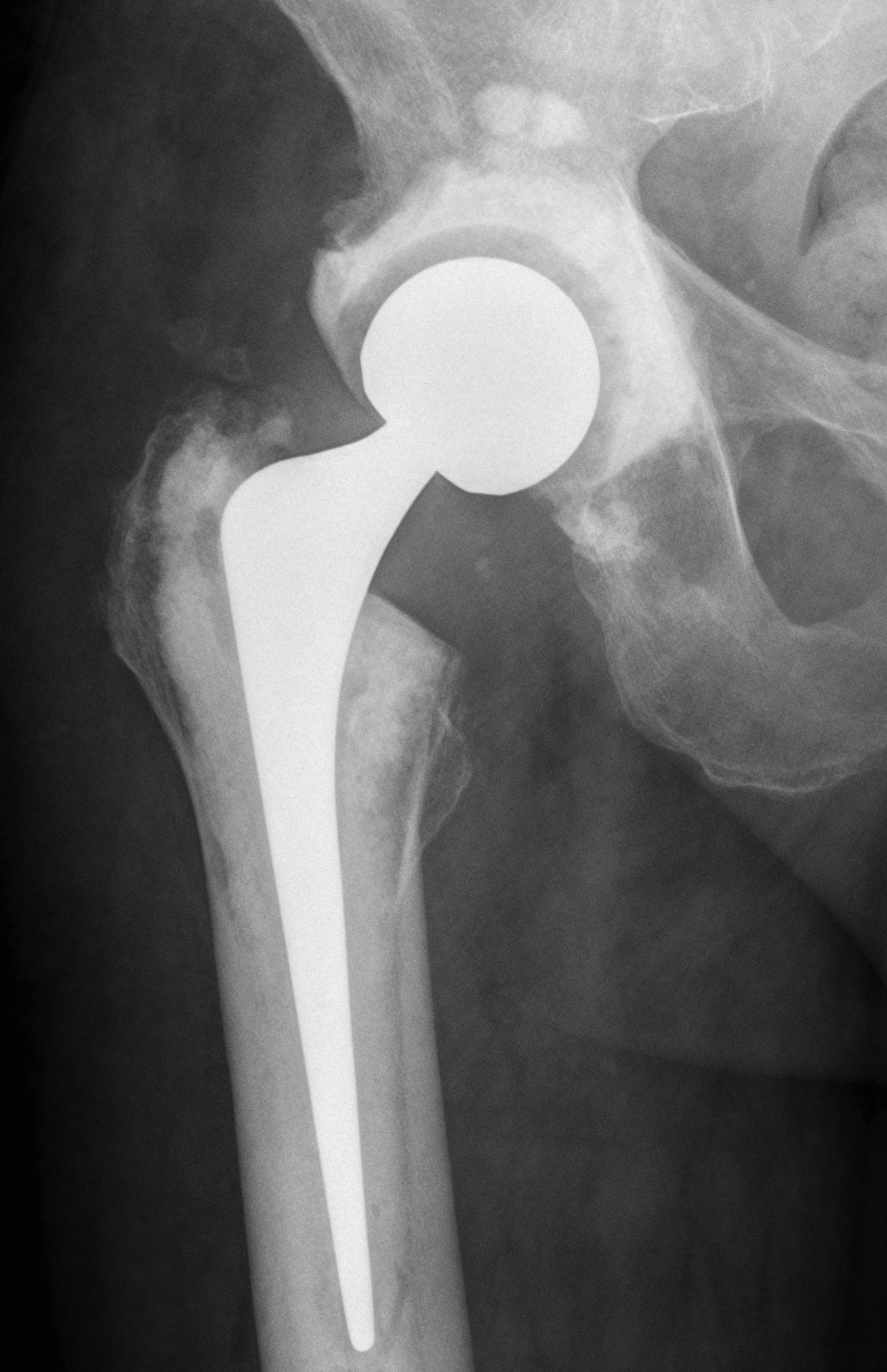
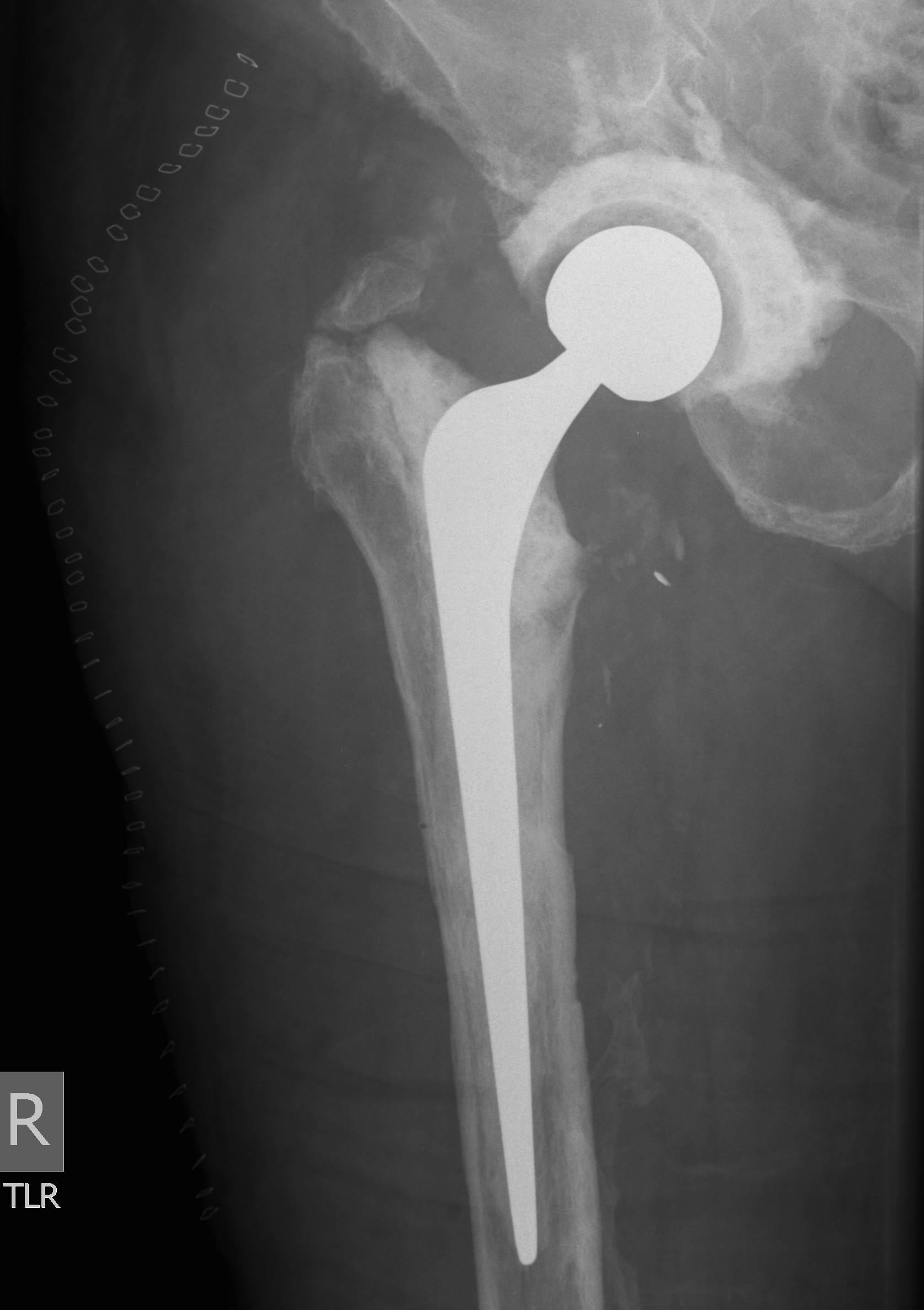
Concept
Remove prosthesis, debride and replace at single sitting
- meticulous debridement critical
- antibiotic cement both femur and acetabulum
Technique
Debridement + removal of implants and all cement
- wash +++
- re-drape, new instruments
Implant cemented polished femur and all poly cup
- must use antibiotic cement
- guidance on antibiotic choice from multidisciplinary team (ID)
- for example add powder form vancomycin
- 2-3 gram vancomycin in each 40g packet of cement
Results
Lange et al Clin Epidemiol 2012
- systematic review of one- versus two-stage revision for hip PJI
- recurrent infection 13% one-stage
- recurrent infection 10% two-stage
Two-Stage Revision
Technique
First stage
- debridement + removal of implants and all cement
- insert antibiotic impregnated cement spacer
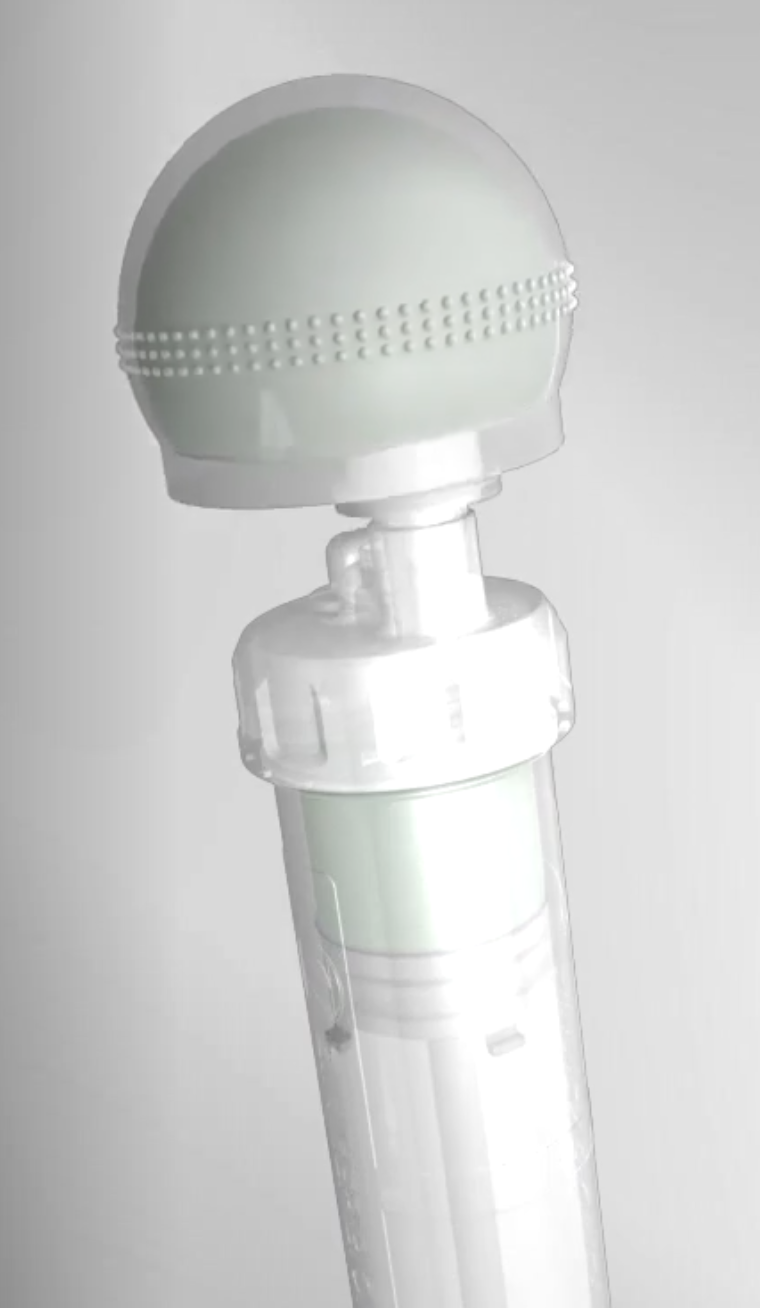
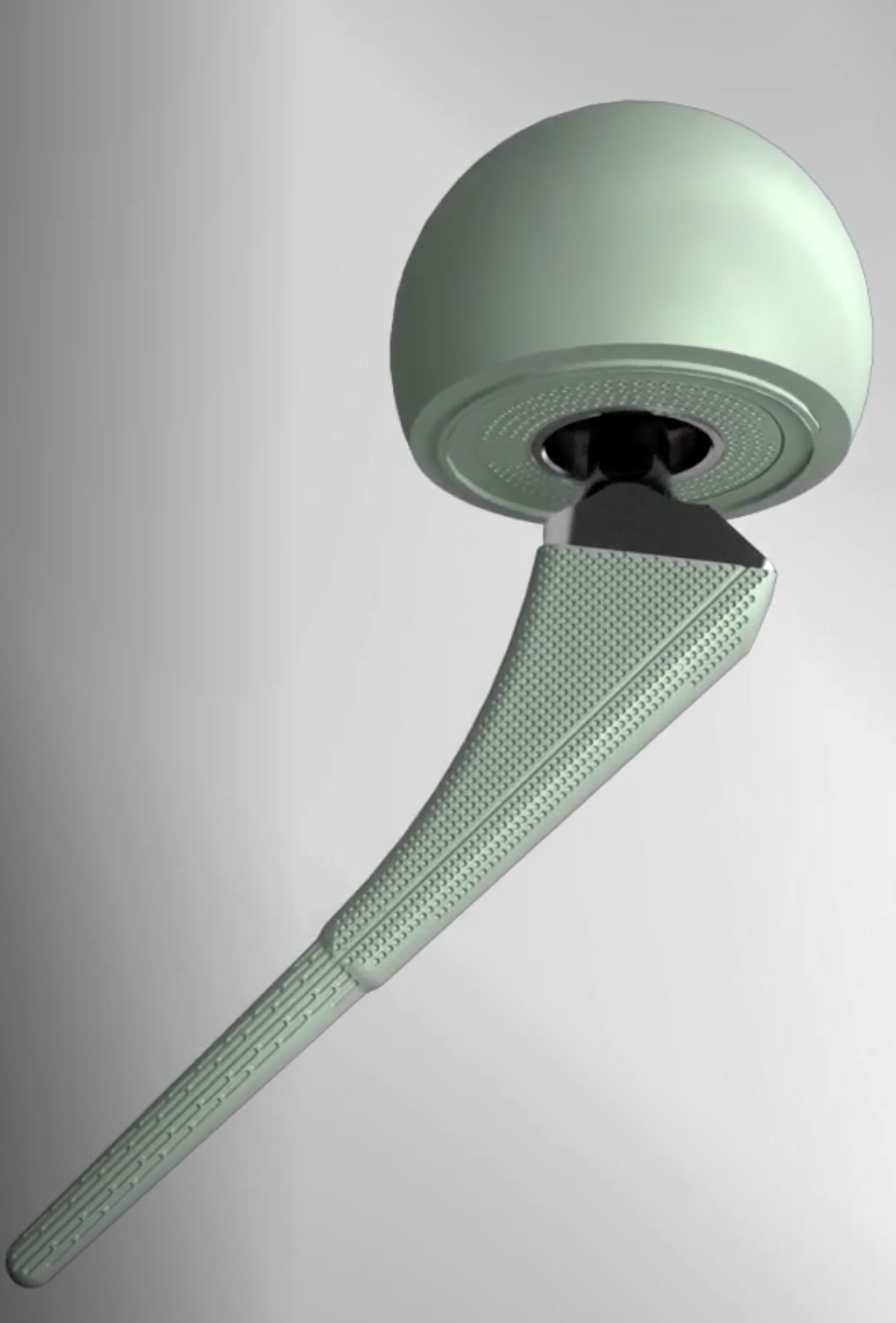
Types of spacers
- hand made +/- metal reinforcement
- moulds +/- metal reinforcement
- prefabricated
- antibiotic-coated prosthesis
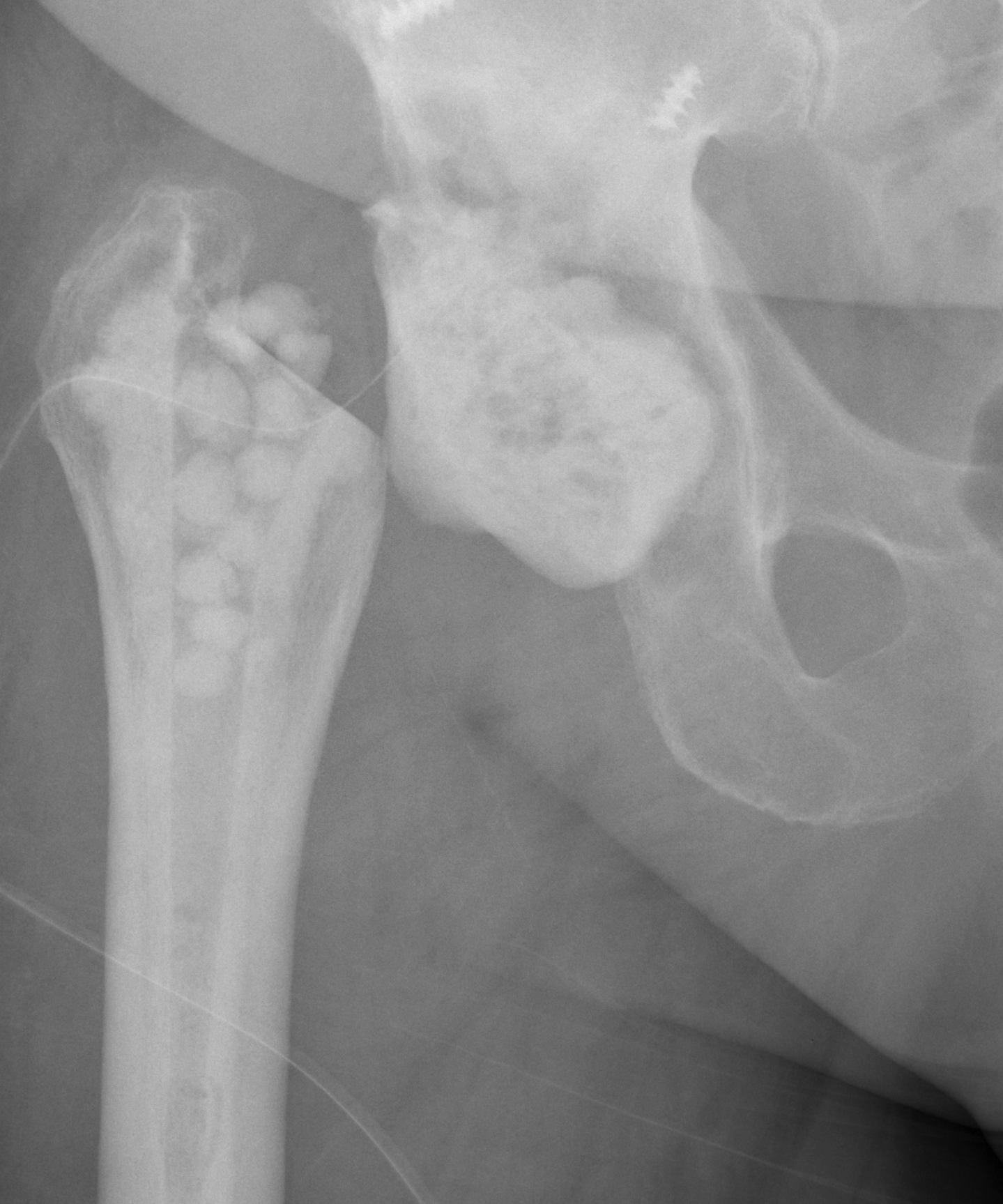
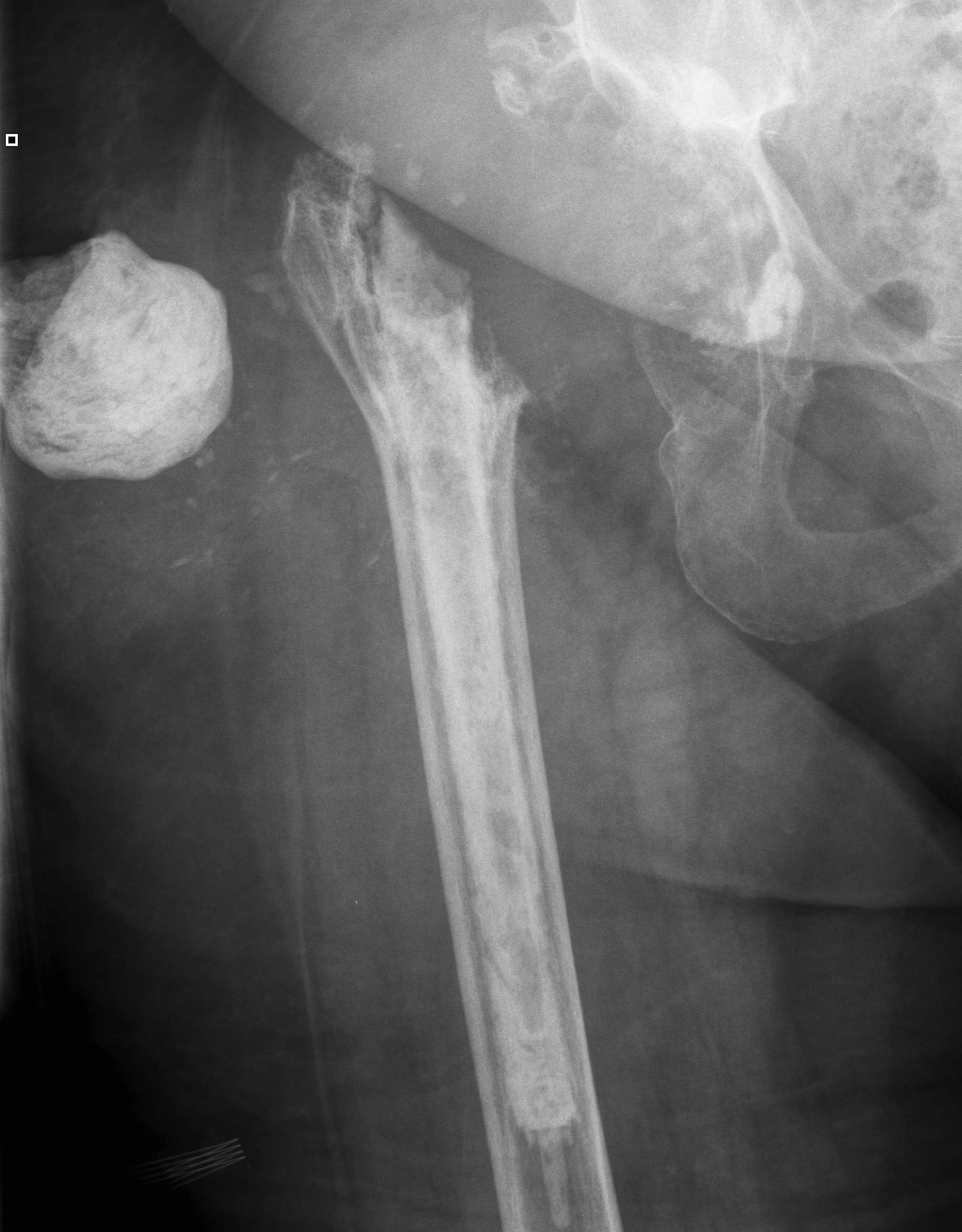
Ball antibiotic cement Mold
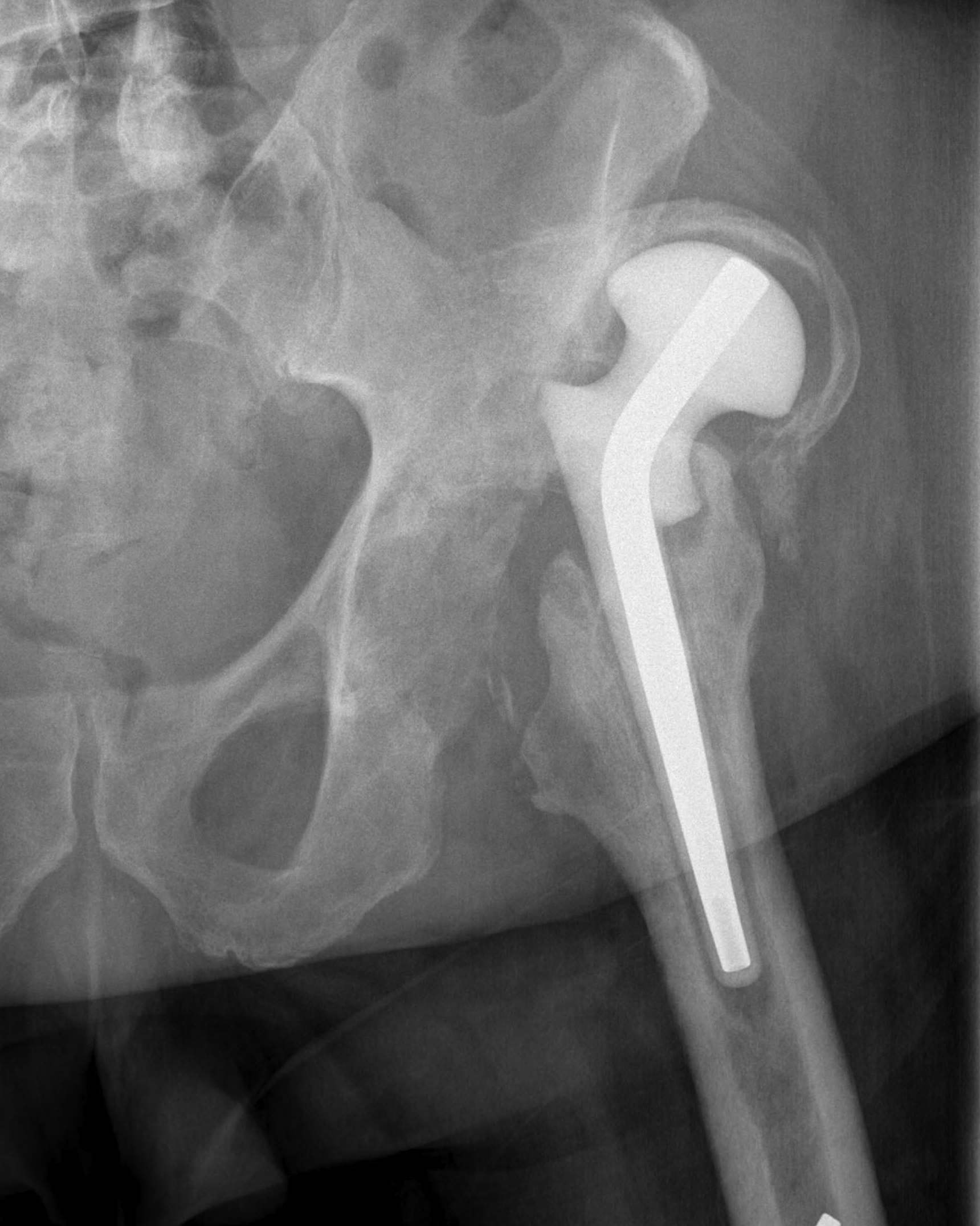
Prefabricated Handmade

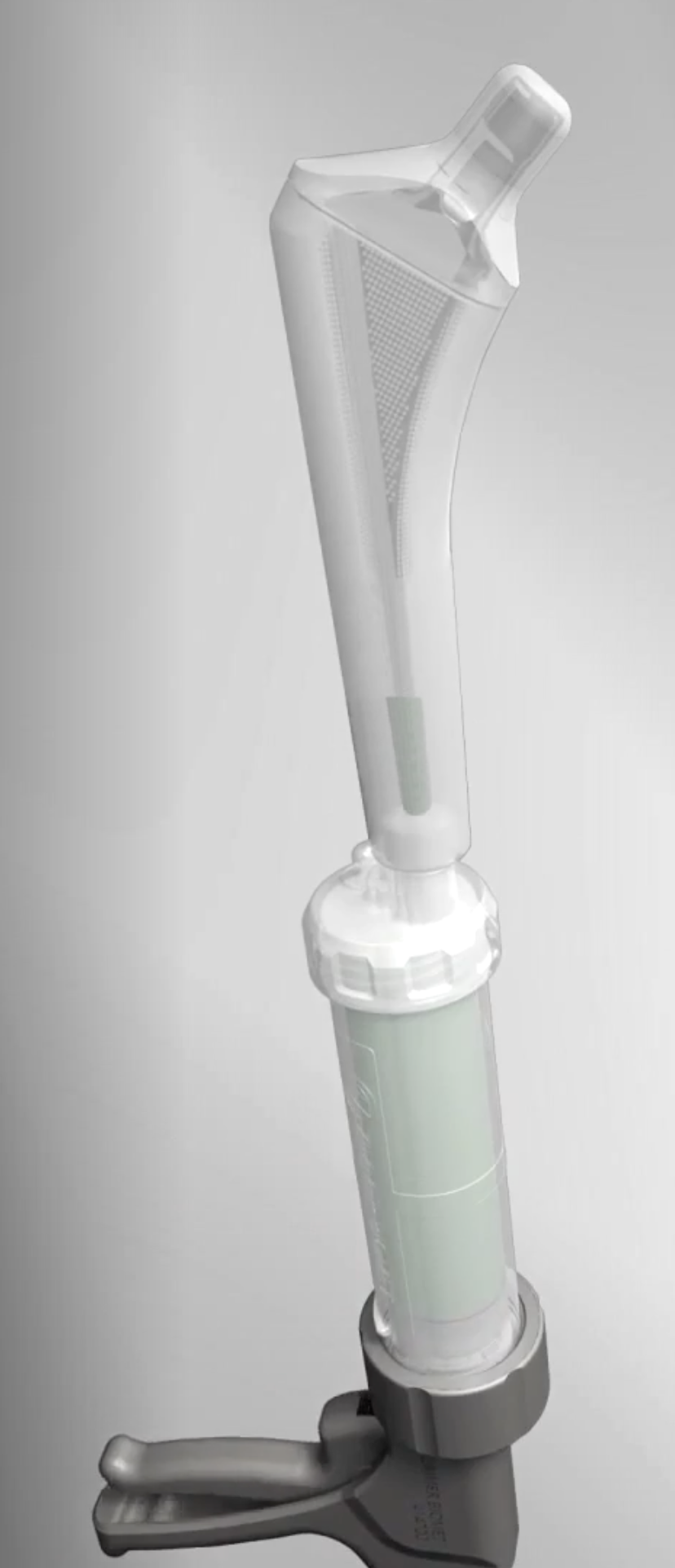

Zimmer StageOne Select Hip Cement Spacer Molds
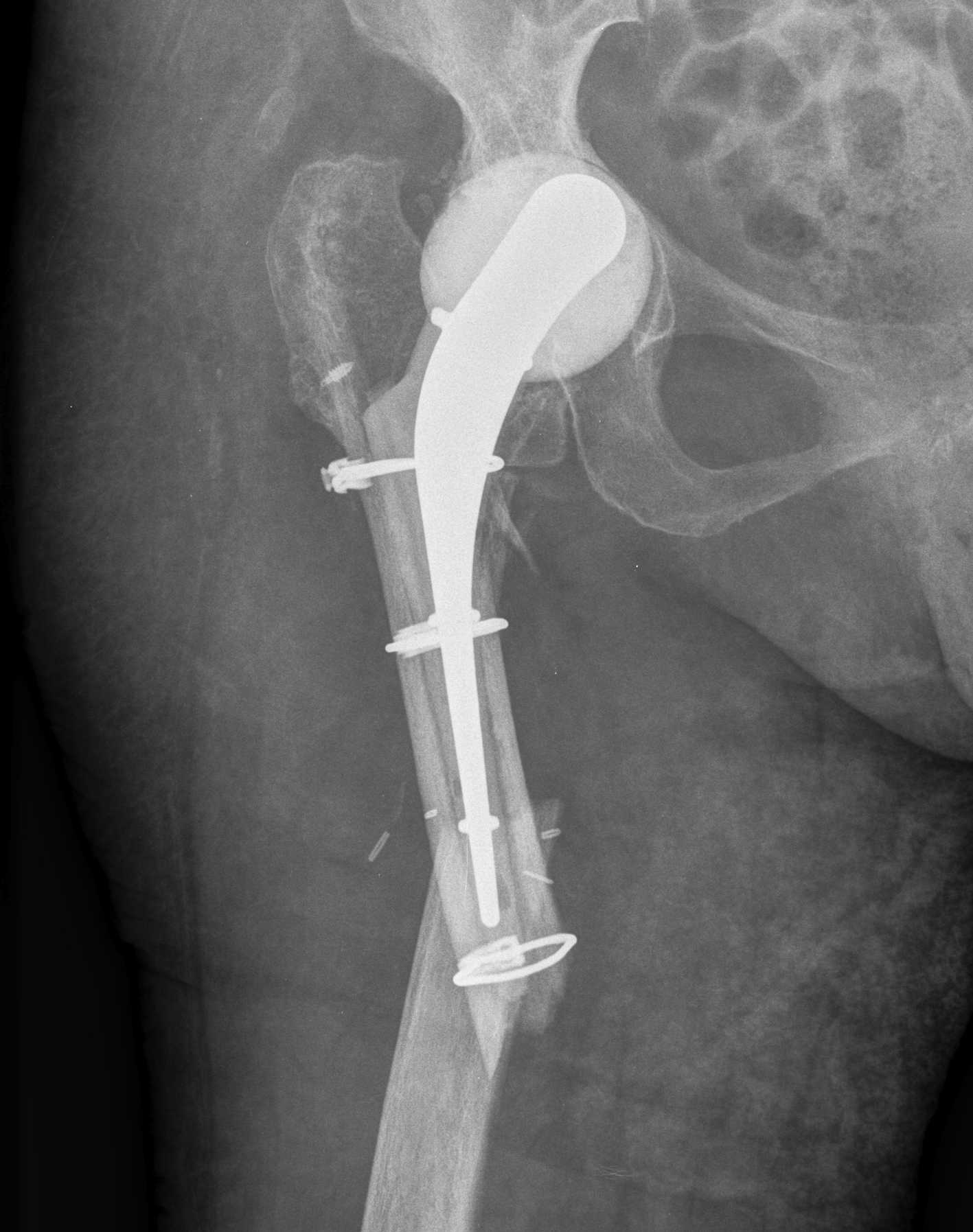
Second stage
- definitive revision
- at least 2 - 4 weeks off antibiotics and normal CRP / ESR
- consider hip aspiration
- intra-operative FFS at time of surgery
Complications
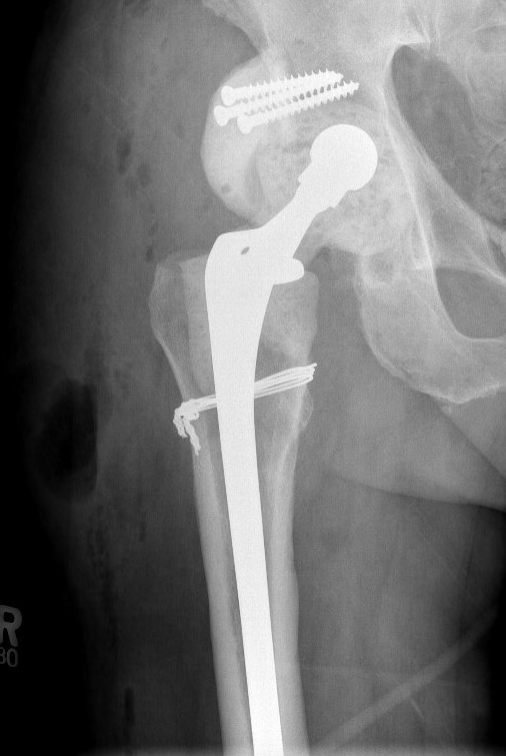
Dislocation / bone loss / prosthesis fracture / femur fracture
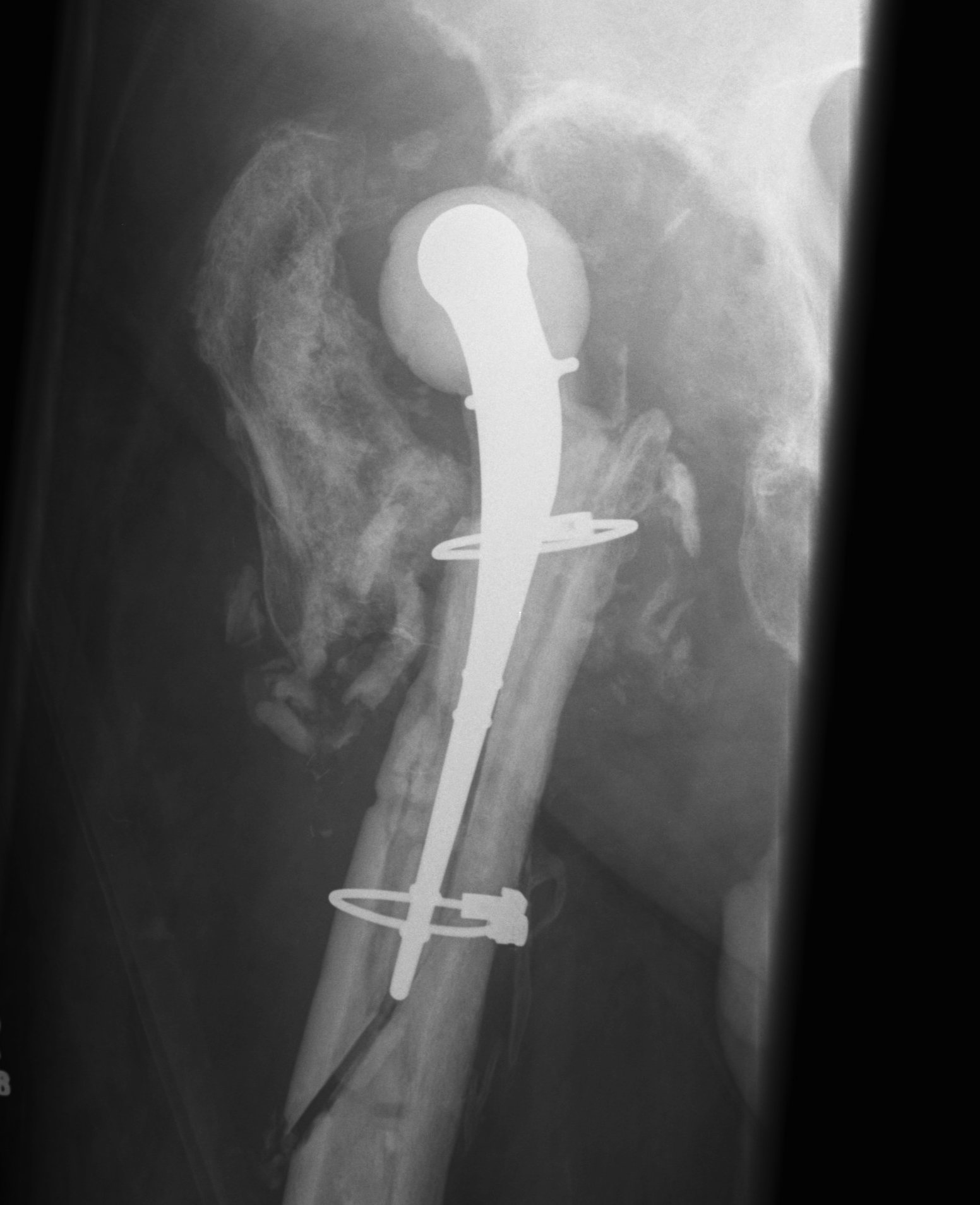

Jones et al J Arthroplasty 2019
- 185 antibiotic cement spacers
- 53% molds / 30% antibiotic coated prosthesis / 12% handmade / 4% prefabricated
- 9% dislocation
- 8% spacer fracture
- 7% periprosthetic fracture
Results
- 221 patients with two-stage revision average 6 year follow up
- 12% recurrent infection
- risk factors for recurrent infection polymicrobial infection and resistant organisms
- revision rate 26%
- mortality rate 41%
Resection Arthroplasty / Girdlestone
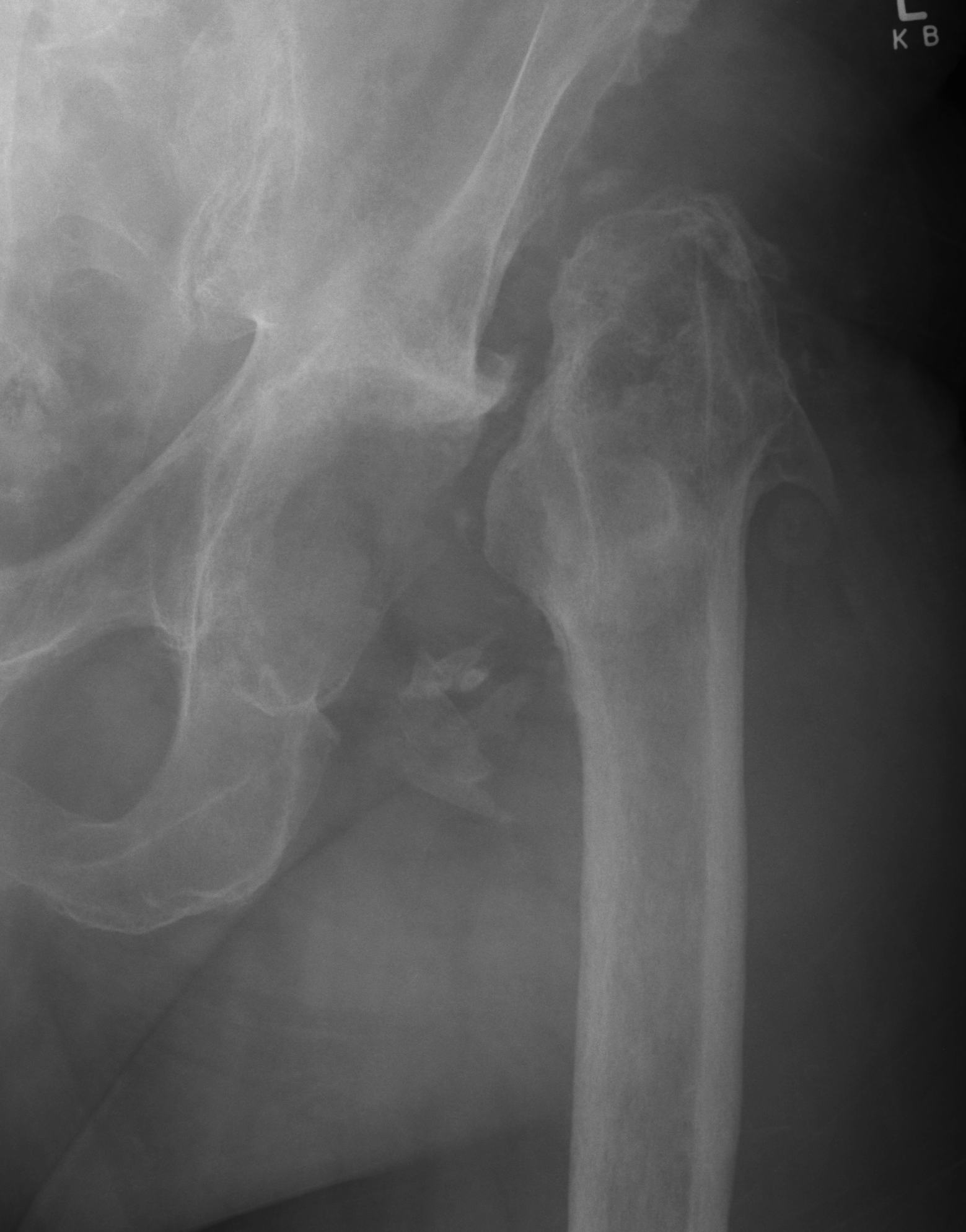

Indications
- medically unfit for further revision surgery
- refusal for further revision surgery
- sepsis control / virulent bug
- unrevisable due to bone loss
- unlikely to become mobile
Advantage
Effective control of infection (95%)
Disadvantage
Poor function
- pain / limp
- require walking aid
- 5cm average LLD
Amputation / Hip disarticulation
