Incidence
- Nordic Arthroplasty Registry of 430,000 THA
- revision for infection 0.7%
Risk factors
- obesity
- diabetes
- rheumatoid arthritis
- biologics
- revision THA
Symptoms
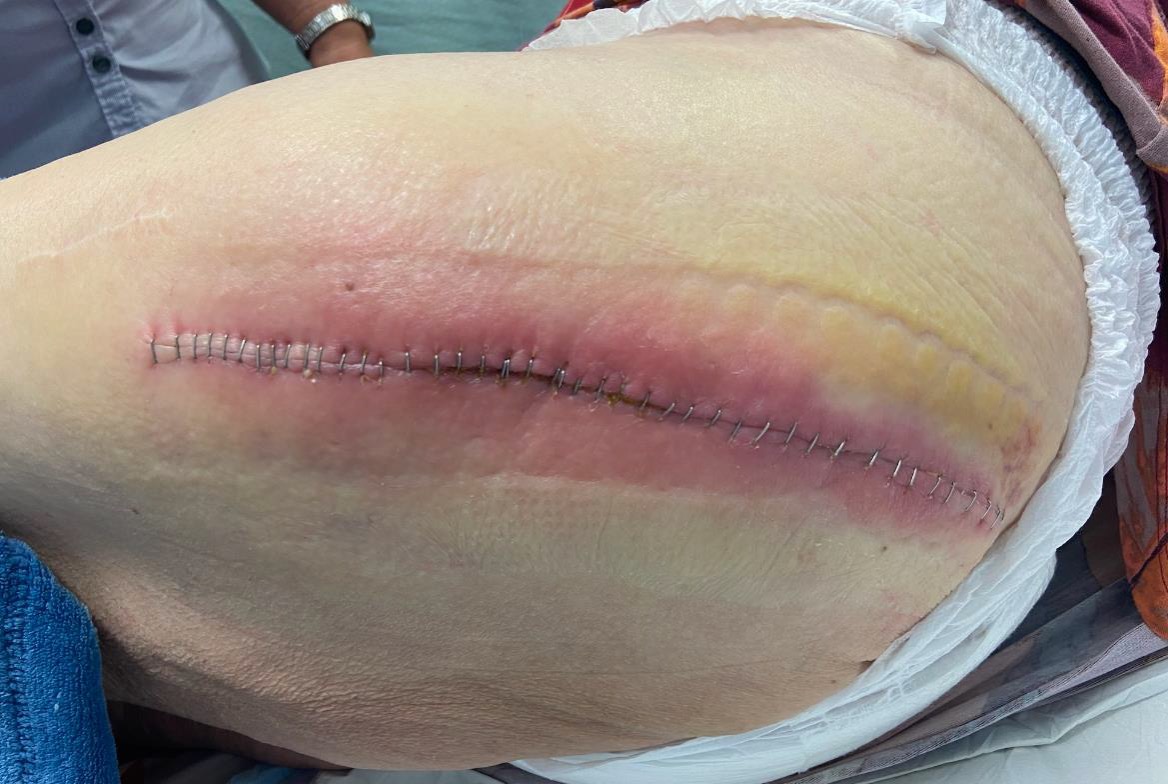
Pain
Wound drainage
Microbiology
Gram positive cocci 70%
- Staph aureus
- coagulase negative Staph Epidermidis
- Streptococcus < 10%
- Enteroccus - more common acute infection
Aerobic gram negative bacilli 10%
- more common acute infection
Culture negative 6%
Fungus / Candida < 1%
- revision / immunosuppression
Pathology
Glycocalyx / Biofilm
- slime layer of polysaccharides produced by bacteria
- protective barrier against antimicrobial and host defense
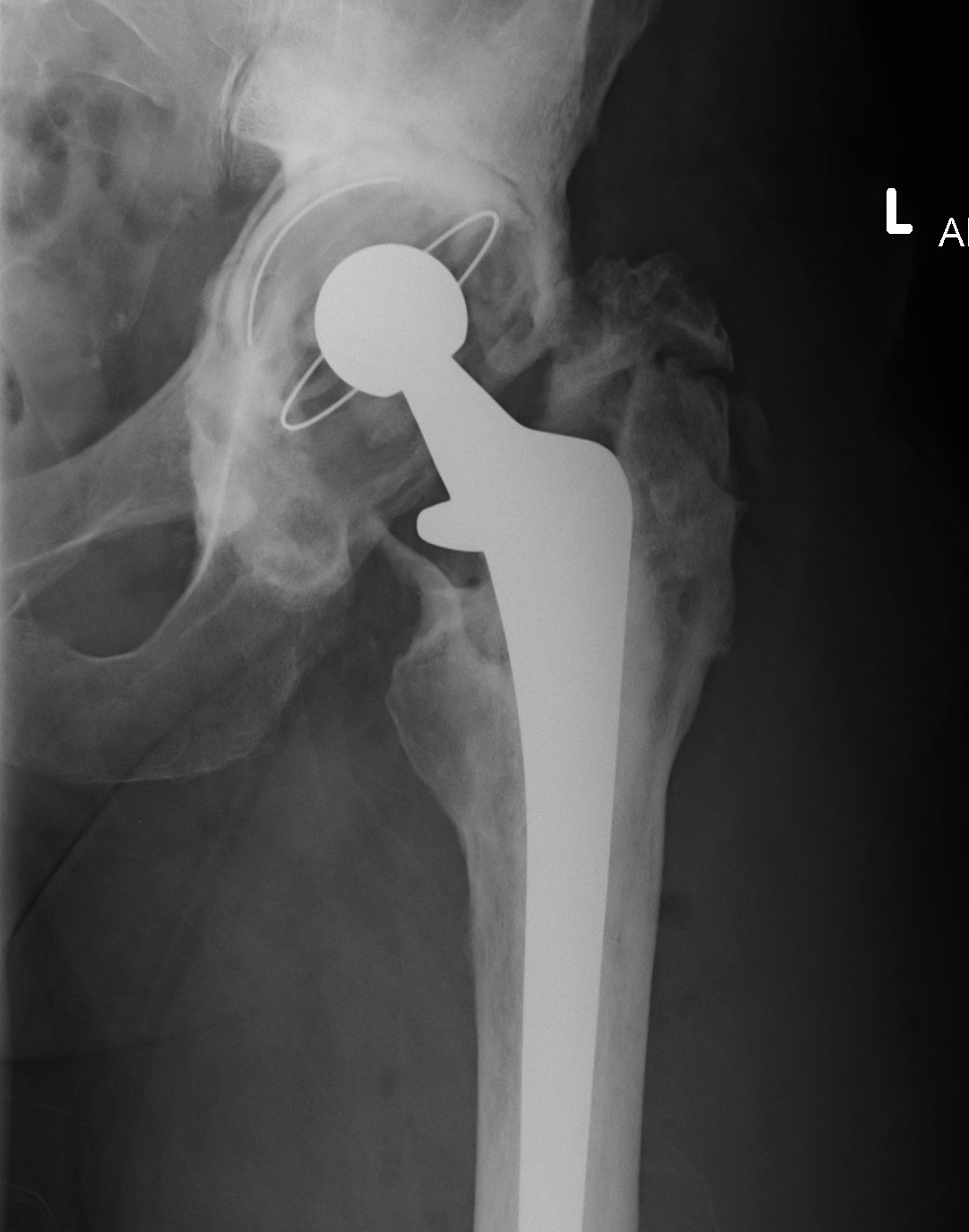
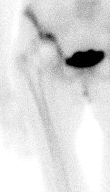
X-ray
1. Progressive radiolucent lines / rapid lysis
2. Focal osteolysis with endosteal scalloping
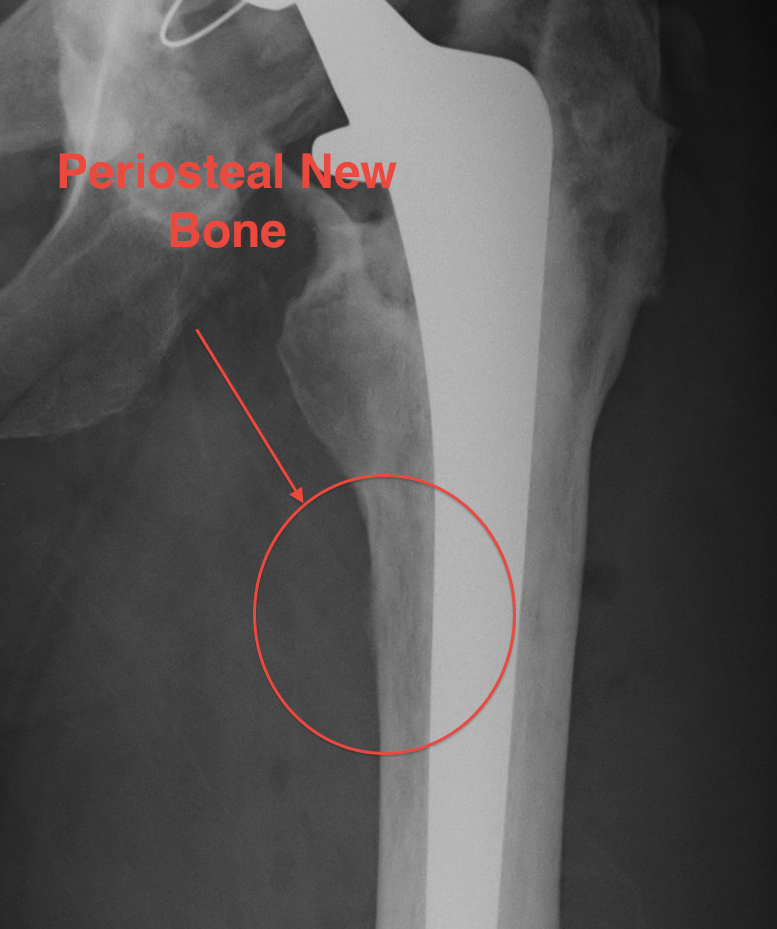
3. Periosteal new bone
- pathognomonic of infection
- usually at junction meta / diaphysis on medial side
- uncommon

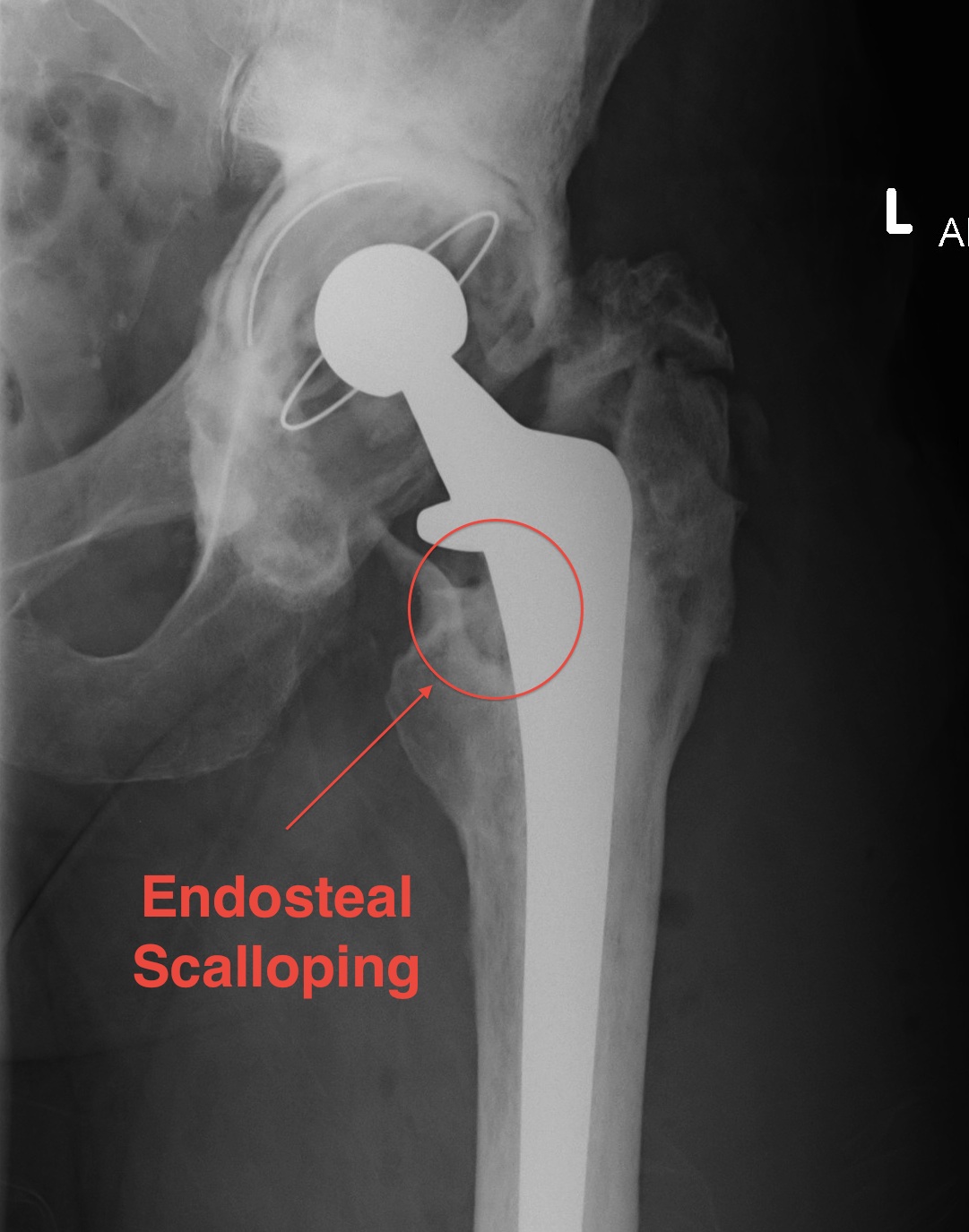
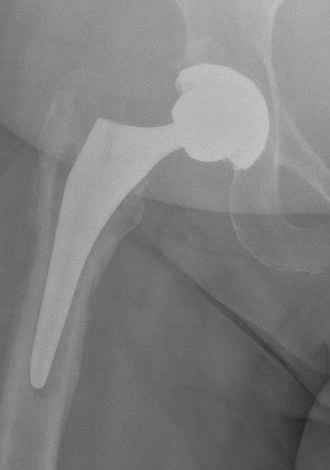
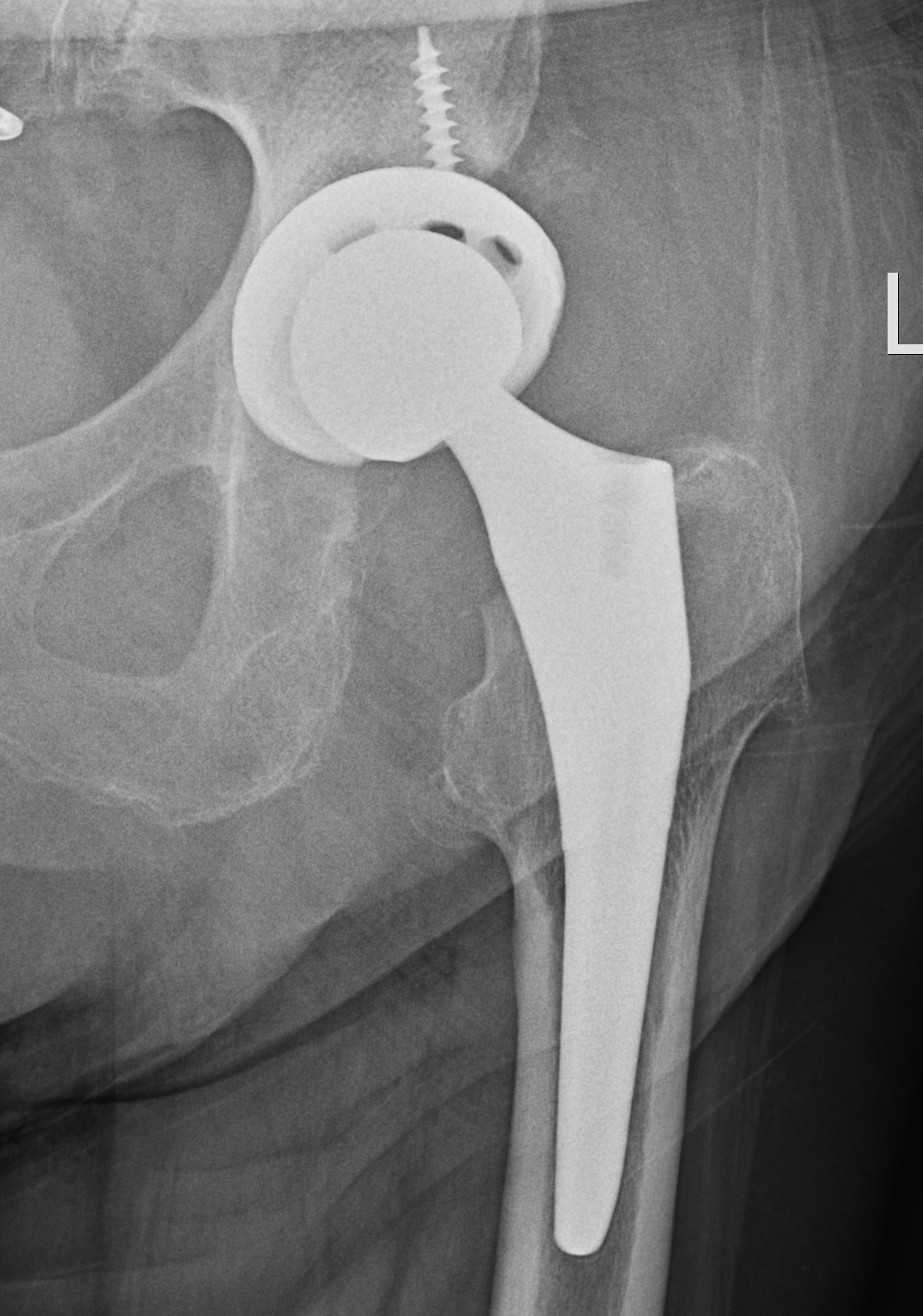
Femoral stem lysis Acetabular lysis
MRI / CT
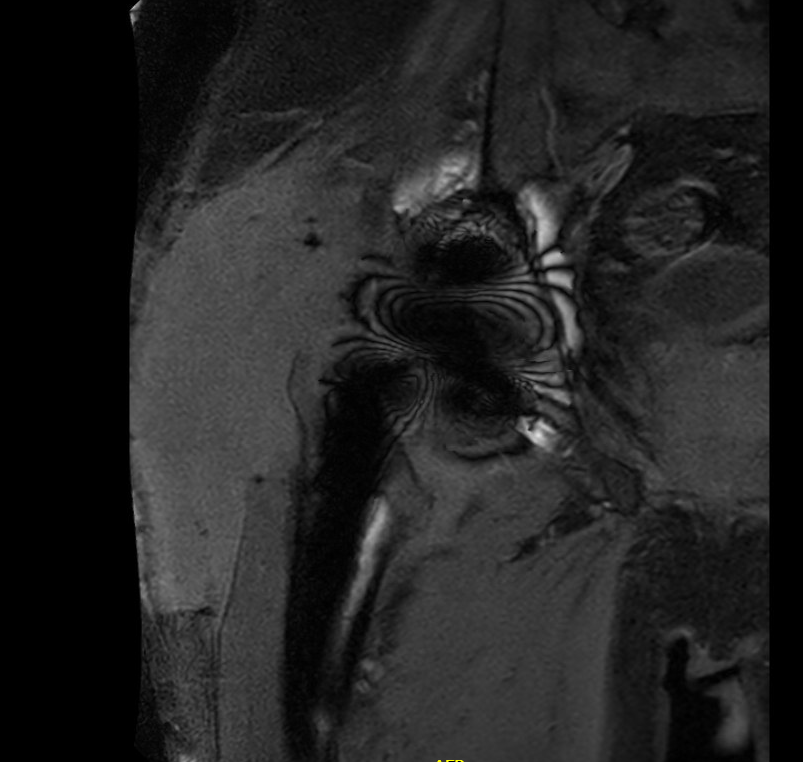
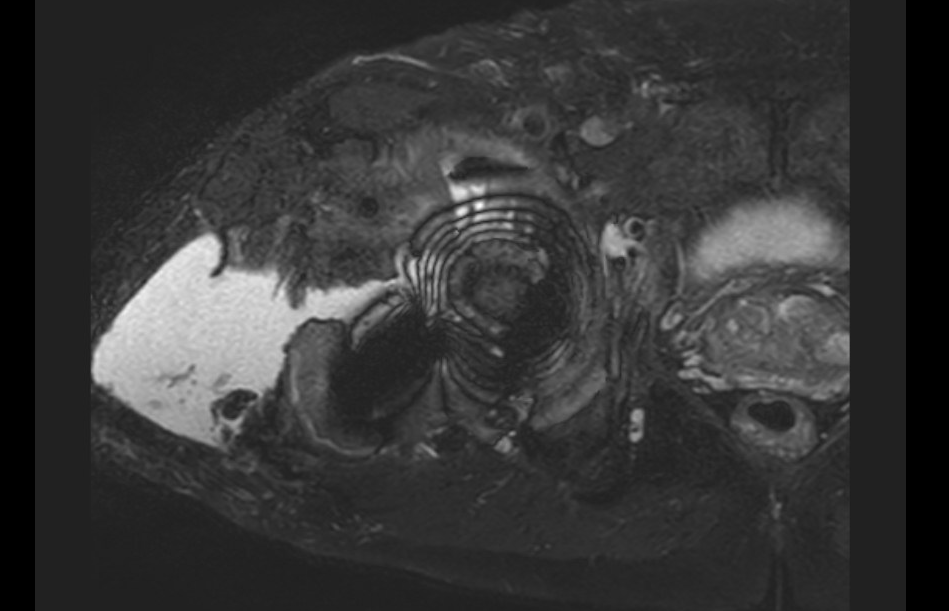
MRI demonstrating large fluid collection around THA
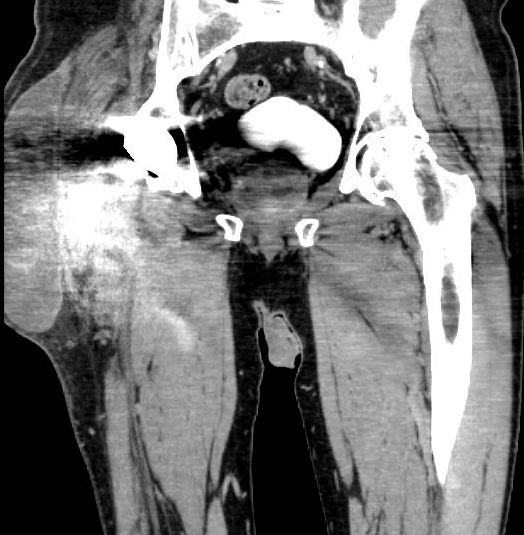
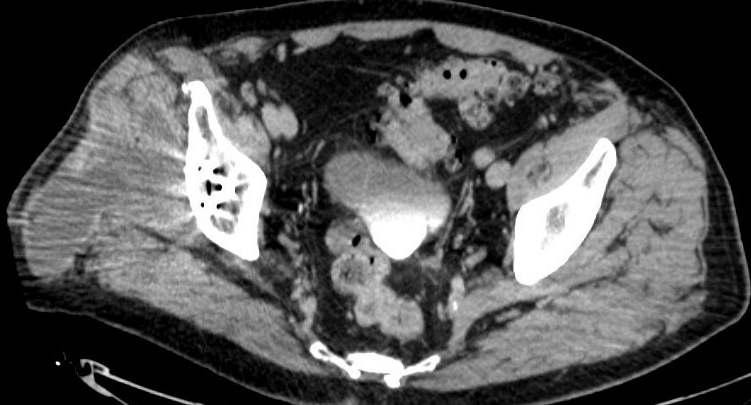
CT demonstrating large fluid collection around THA
Diagnosis
Parvizi et al J Arthroplasty 2018
- any major criteria indicates infection
- minor criteria
- score 6 or greater infected
- score 4 or 5 inconclusive
- score 3 or less not infected
- 98% sensitive
| Major criteria | Minor criteria |
|---|---|
| Sinus tract communicating with prosthesis |
Serum - CRP > 10 (2 points) - ESR > 30 (1 point) - D-dimer > 860 ng/ml (2 points)
|
| Identical pathogen identified on two cultures |
Synovial fluid - PMN > 80% (2 points) - WCC > 3000 cells uL (3 points) - synovial CRP > 6.9 mg/L (1 point) - positive alpha-defensin (3 points) - positive leukocyte esterase (3 points)
|
Blood tests
ESR > 30 - Takes 6 to 12 months to normalize post OT
CRP > 10 - takes 3 weeks to normalize post surgery
Austin et al J Arthroplasty 2008
- 116 patients with infection and 180 without
- normal ESR and CRP - 96% sensitivity for excluding infection
- elevated ESR and CRP - 56% sensitivity for diagnosing infection
Nuclear Medicine
1. Three Phase Bone Scan
- low specificity for infection
- normal study likely excludes infection
- Cemented THA - majority return to normal by 1 year but 10% can remain positive past 1 year
- Uncemented THA - can remain positive for 2 years or longer
- infection - increased blood flow / blood pool / delayed phase
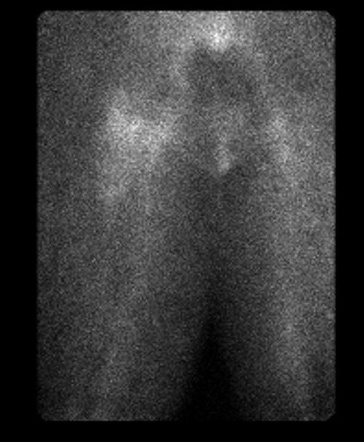
Quiescent bone scan
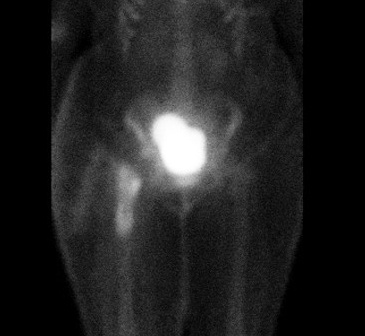
Infected THA on blood flow and blood pool
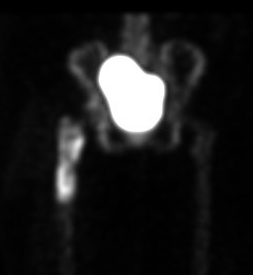
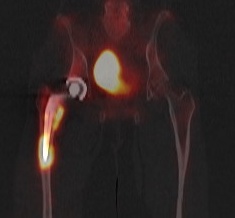
Infected THA on delayed phase
Indium 111 Labelled White cell scan + bone scan
- 64% sensitive and 78% specific for diagnosis THA infection
PET scan / [18F]Fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET)
Kwee et al Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008
- meta-analysis 11 studies and 600 patients
- 82% sensitive and 87% specific
Fluid Aspiration
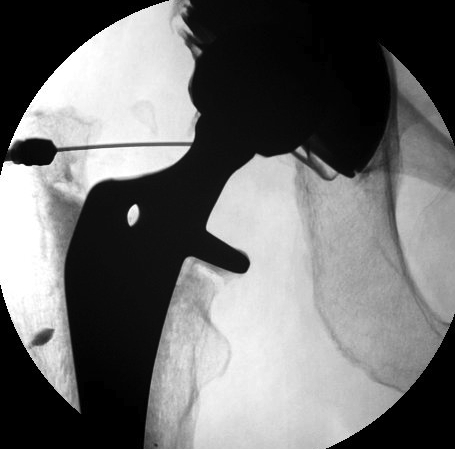
Cell count
- WCC > 3450 uL3 91% sensitive and 93% specific
- neutrophil > 78% was 95% sensitive and 87% specific
Leukocyte esterase (neutrophil enzyme)
- 81% sensitivity and 100% specificity
Culture
- sensitivity 82% and specificity 91%
Tissue specimens
Intra-operative gram stain - low sensitivity
Intra-operative swabs - less sensitivity than tissue specimens
Fresh frozen section
- > 5 neutrophils per high-powered field
- in at least 5 separate microscopic fields
- sensitivity of the interface membrane 83%, specificity was 98%
- sensitivity pseudocapsule 42%, specificity was 98%
Tissue culture
Gold standard
- same microbe on two different samples
- multiple specimens best to avoid contaminants (5 - 6)
- PCR can increase diagnosis
Sonification
Using ultrasound to remove and culture biofilm from removed prostheses
- more accurate than intra-operative tissue specimens
- especially in setting of pre-operative antibiotics
- tissue specimen: sensitivity 61% and specificity 99%
- sonificate-fluid: sensitivity 79% and specificity 99%
- 14 cases of PJI were detected by sonicate-fluid culture but not by prosthetic-tissue culture
- patients receiving antimicrobial therapy within 14 days before surgery
- sensitivities of periprosthetic tissue 45%
- sensitivity of sonicate-fluid culture 75%
