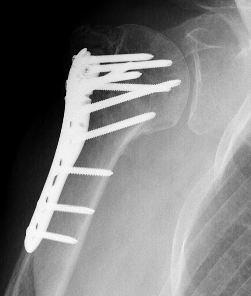
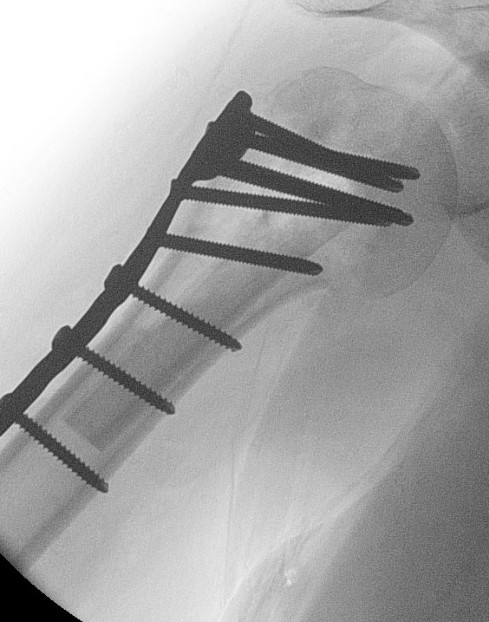
Indications
Young patients
- displaced proximal humerus fractures
Elderly patients with likely poor outcomes
- 100% displaced fractures unlikley to heal
- fracture dislocations
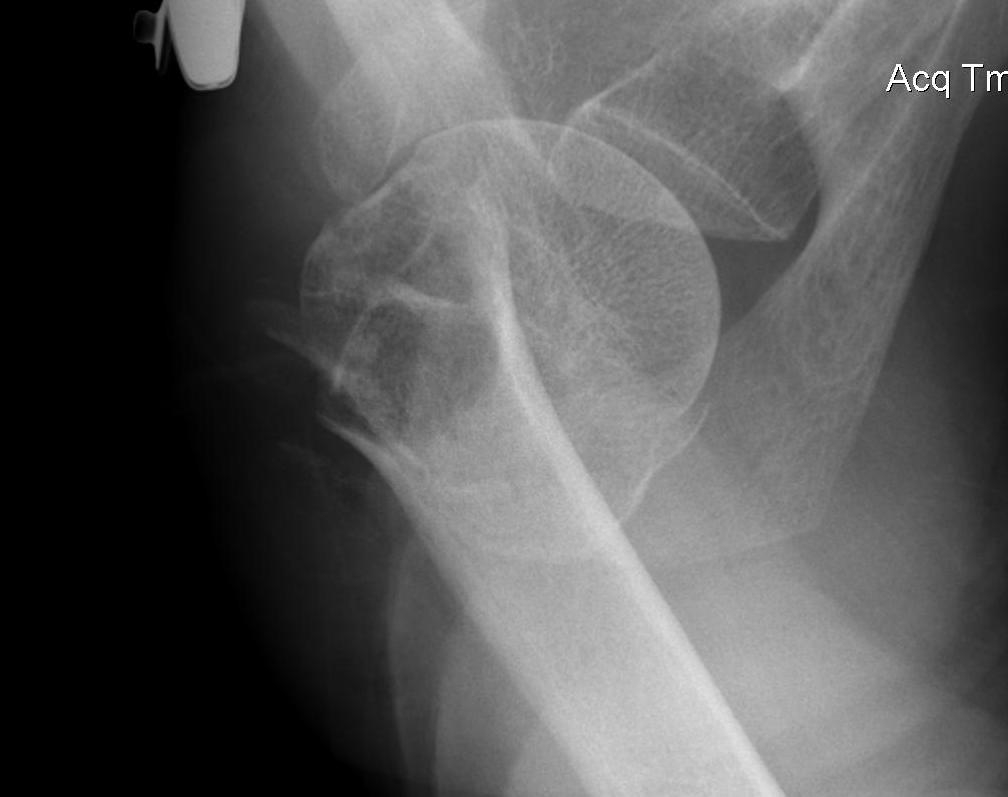
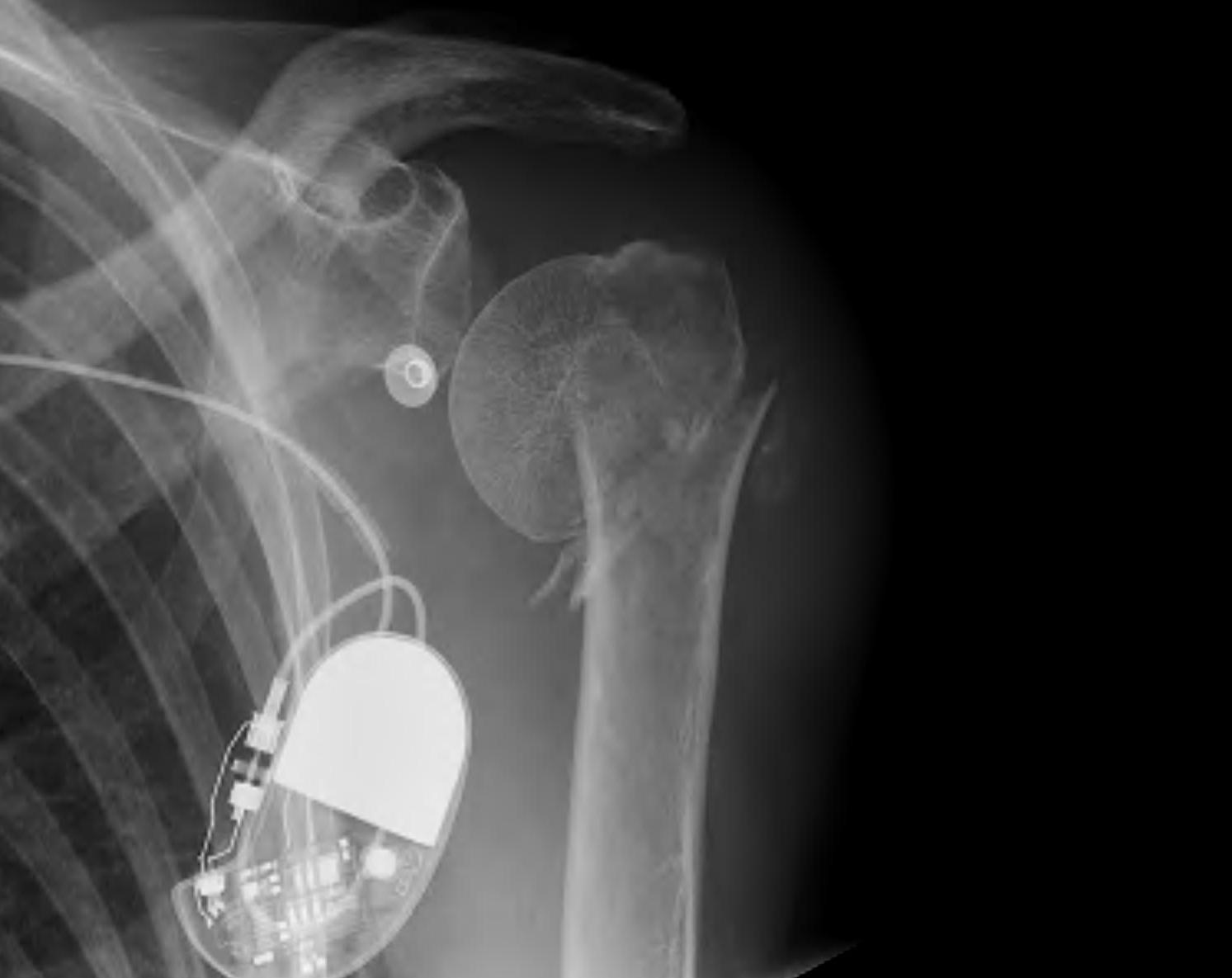
Displaced 2 part SNOH fractures in young patient
Options
ORIF with locking plate
IM nail
Hemiarthroplasty
Reverse TSA
ORIF with locking plate
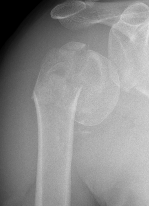

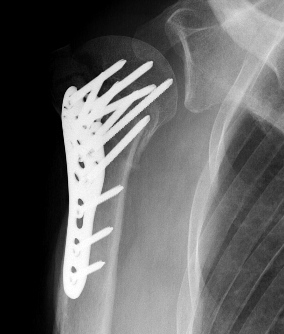
Approach
Deltoid split versus deltopectoral approach
Deltopectoral
- inter-nervous plane
- more difficult in patients with large deltoid muscle
Deltoid split
- have to expose and protect axillary nerve
- direct approach to lateral humerus for plating
Results
- RCT of deltoid split versus deltopectoral approach
- 85 patients mean age 62
- better clinical outcomes with deltopectoral approach
Xie et al Orthop Trauma Surg 2019
- systematic review of 3 RCTs and 3 prospective studies
- shorter OR times and less AVN in deltoid split
- no difference functional outcomes or complication rates
Technique
AO foundations deltopectoral approach
Vumedi ORIF 4 part SNOH deltopectoral video
Vumedi ORIF 3 part SNOH deltopectoral video
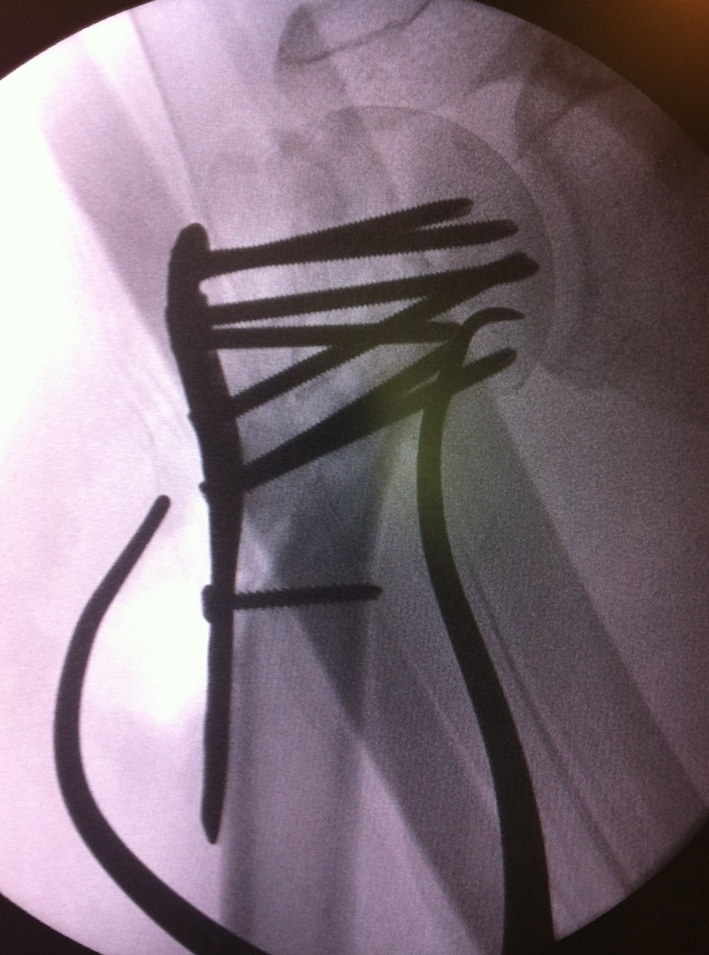
Image intensifier
- from top of patient
Beach chair / deltopectoral approach
- extensile approach - release CA ligament / release proximal pectoralis major
- can release anterior deltoid insertion from lateral clavicle if needed (intra-osseous repair later)
- protect musculocutaneous nerve under conjoint, minimal retraction
- protect the axillary nerve on inferior border of SSC medially
- identify and release biceps tendon
Reduction
- identify and tag greater and lessor tuberosities with Mason Allen sutures
- reduce head onto shaft (head is displaced posteriorly) and avoid varus
- +/- fibular strut allograft
- provisionally fix with 2 mm k wires
- check provisional fixation with fluoroscopy
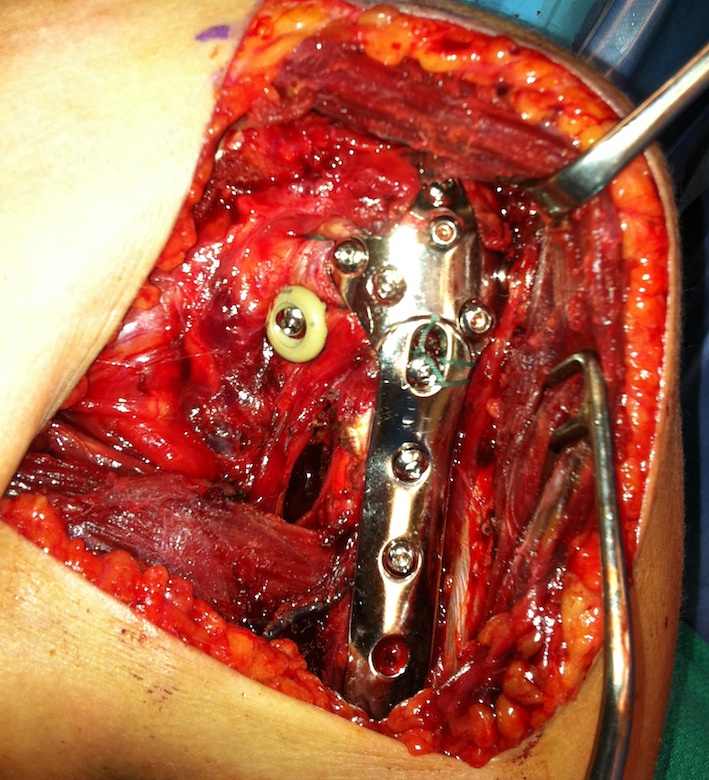
Apply plate
- lateral to biceps with single cortical screw in oblique hole
- check fluoroscopy - avoid having plate too high
- keep head out of varus to avoid cutout
- long inferomedial screws / kickstand screws
- locking screws

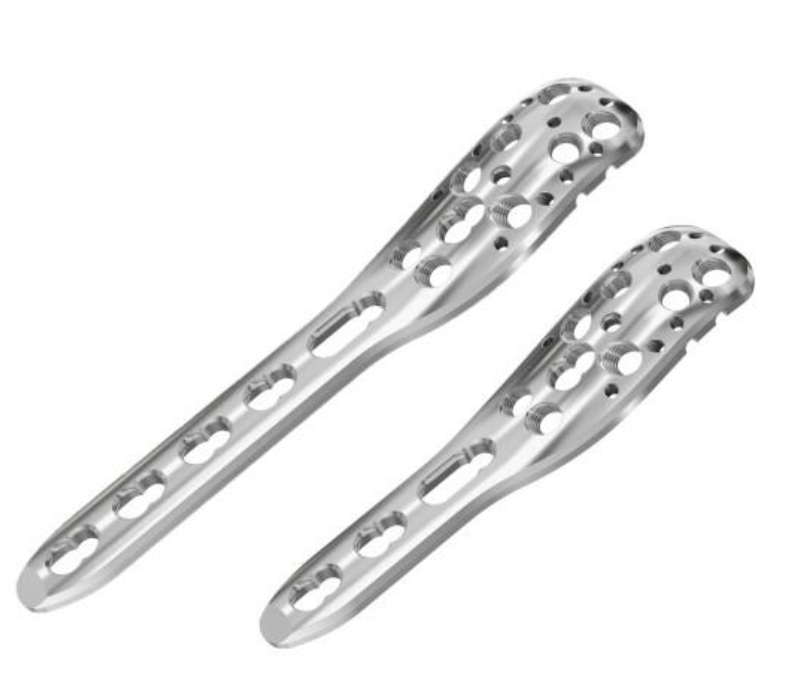
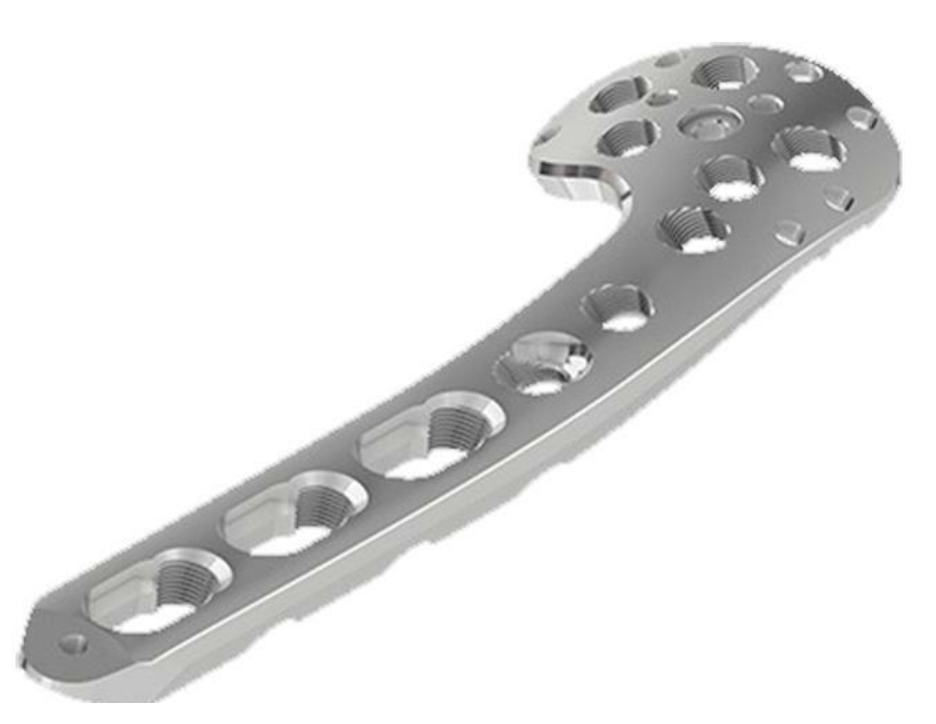
Plates



Synthes 3.5 mm LCP Proximal humeral plate surgical technique PDF
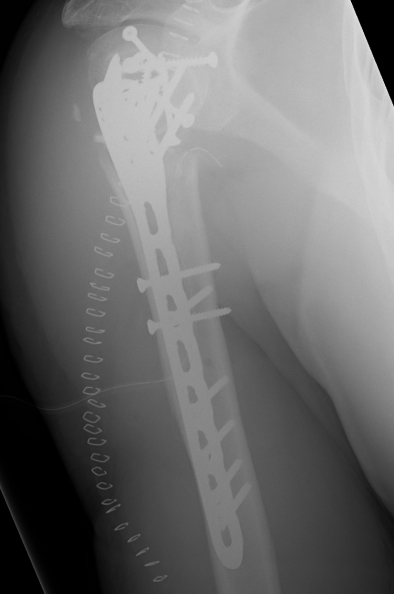
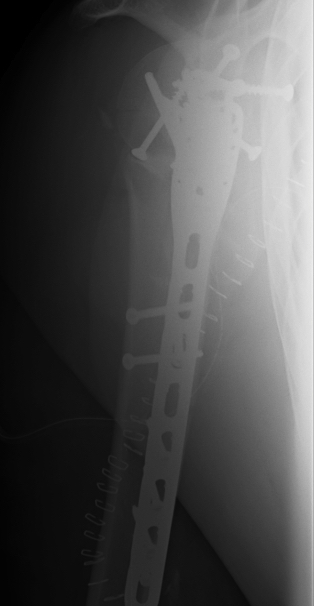
Long proximal humerus plates
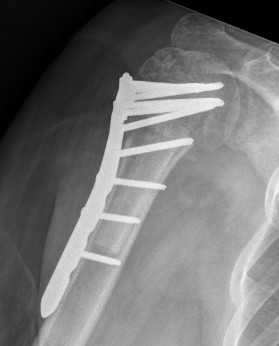
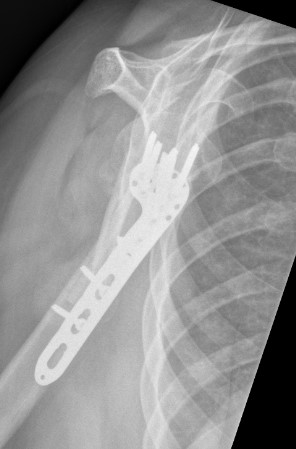

Synthes 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular proximal humerus plate surgical technique PDF
Fibular strut allograft
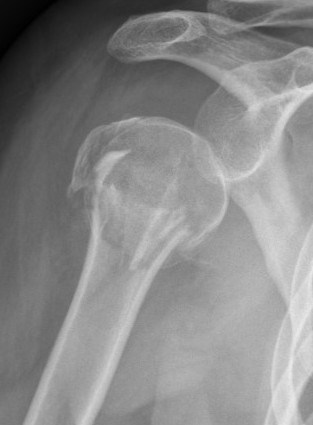
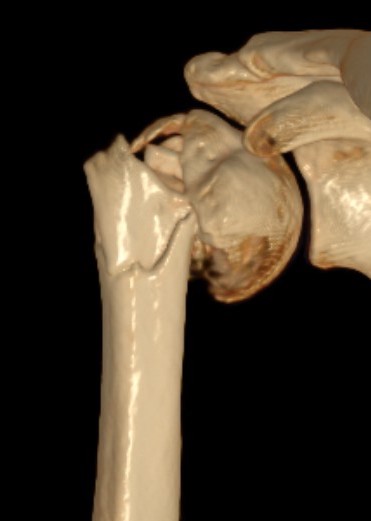

Technique
Vumedi fibular strut allograft video
Results
- 80 patients RCT ORIF +/- fibular strut allograft
- no significant differences
Nie et al J Orthop Surg Res 2022
- systematic review of fibular strut allograft for augmentation SNOH ORIF
- 8 studies and 600 patients
- fibula strut associated lower complications and better outcomes
Complications
Kavuri et al Indian J Orthop 2018
- systematic review of locking plate fixation proximal humerus fractures
- 57 studies and 3400 patients
- intraarticular screw penetration 10%
- varus collapse 7%
- subacromial impingement 5%
- avascular necrosis 5%
- adhesive capsulitis 4%
- nonunion 2%
- deep infection 1%
- reoperation 14%.
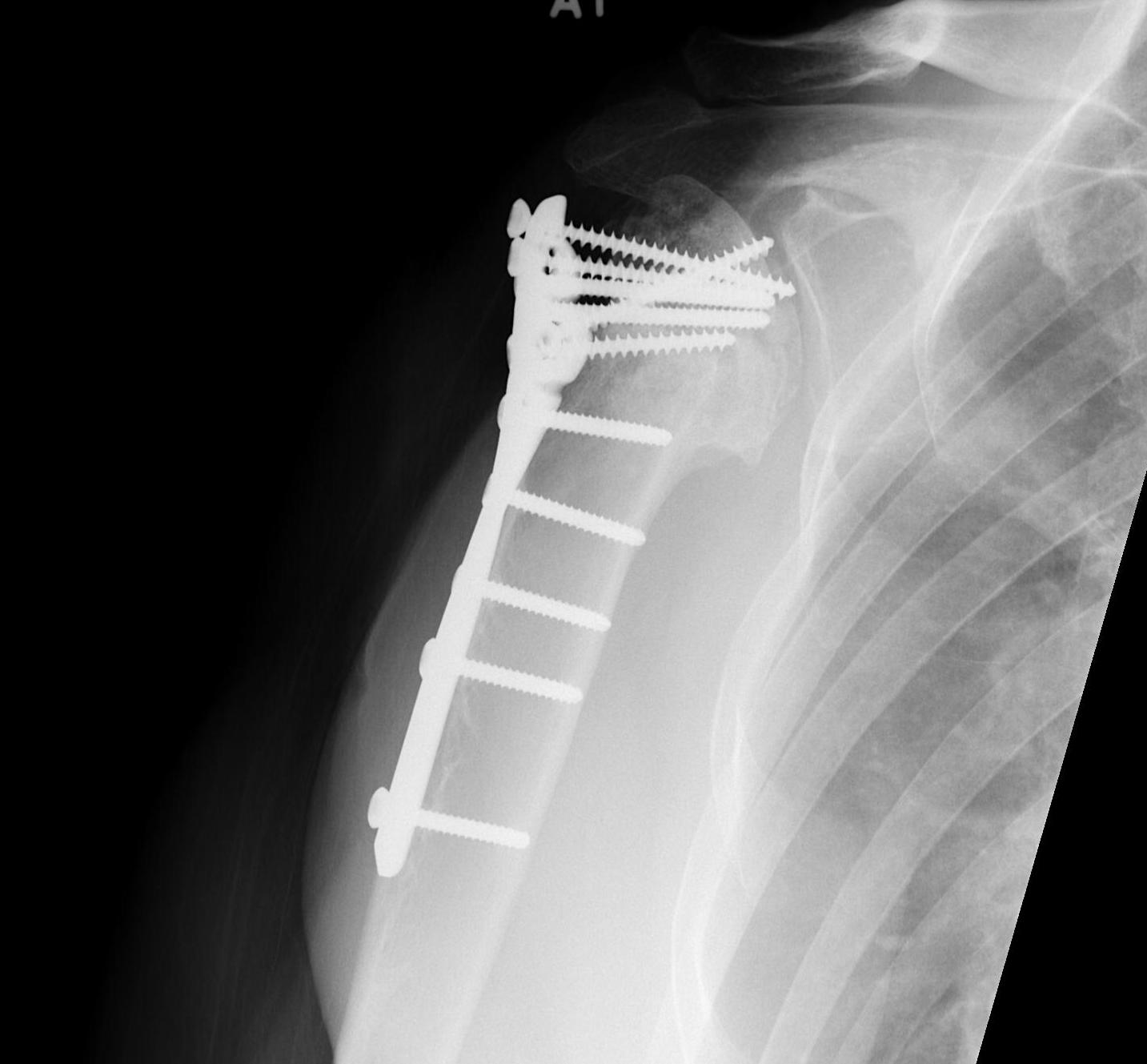
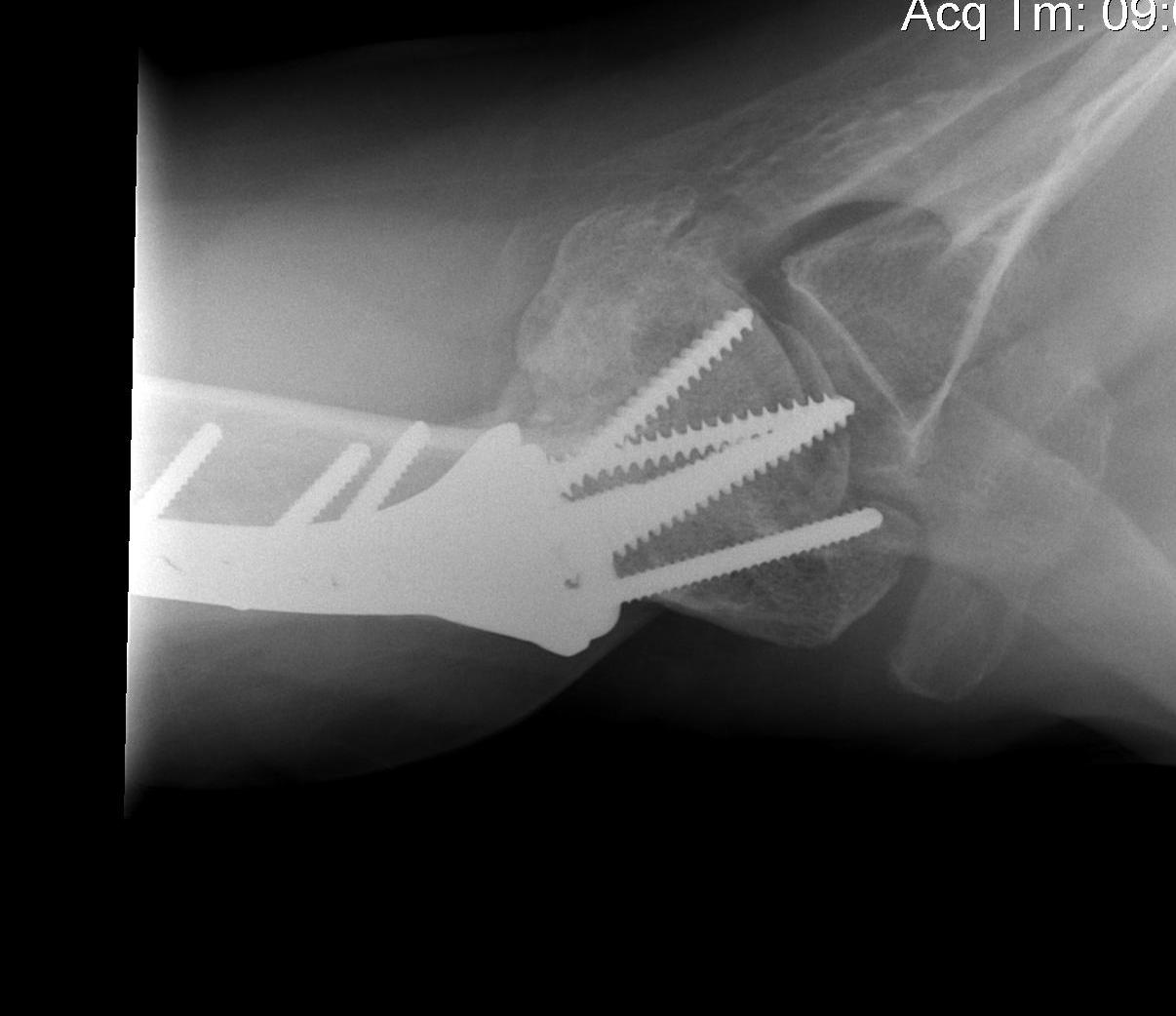
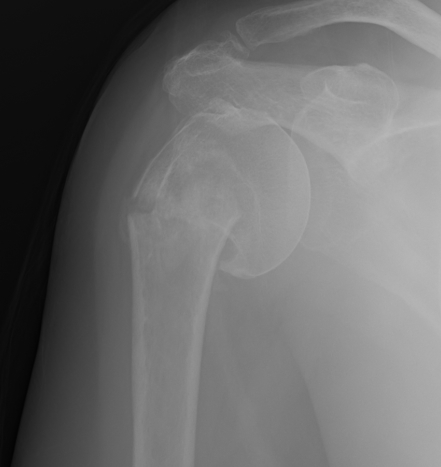
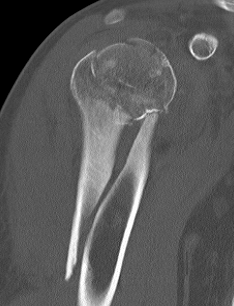
Avascular necrosis
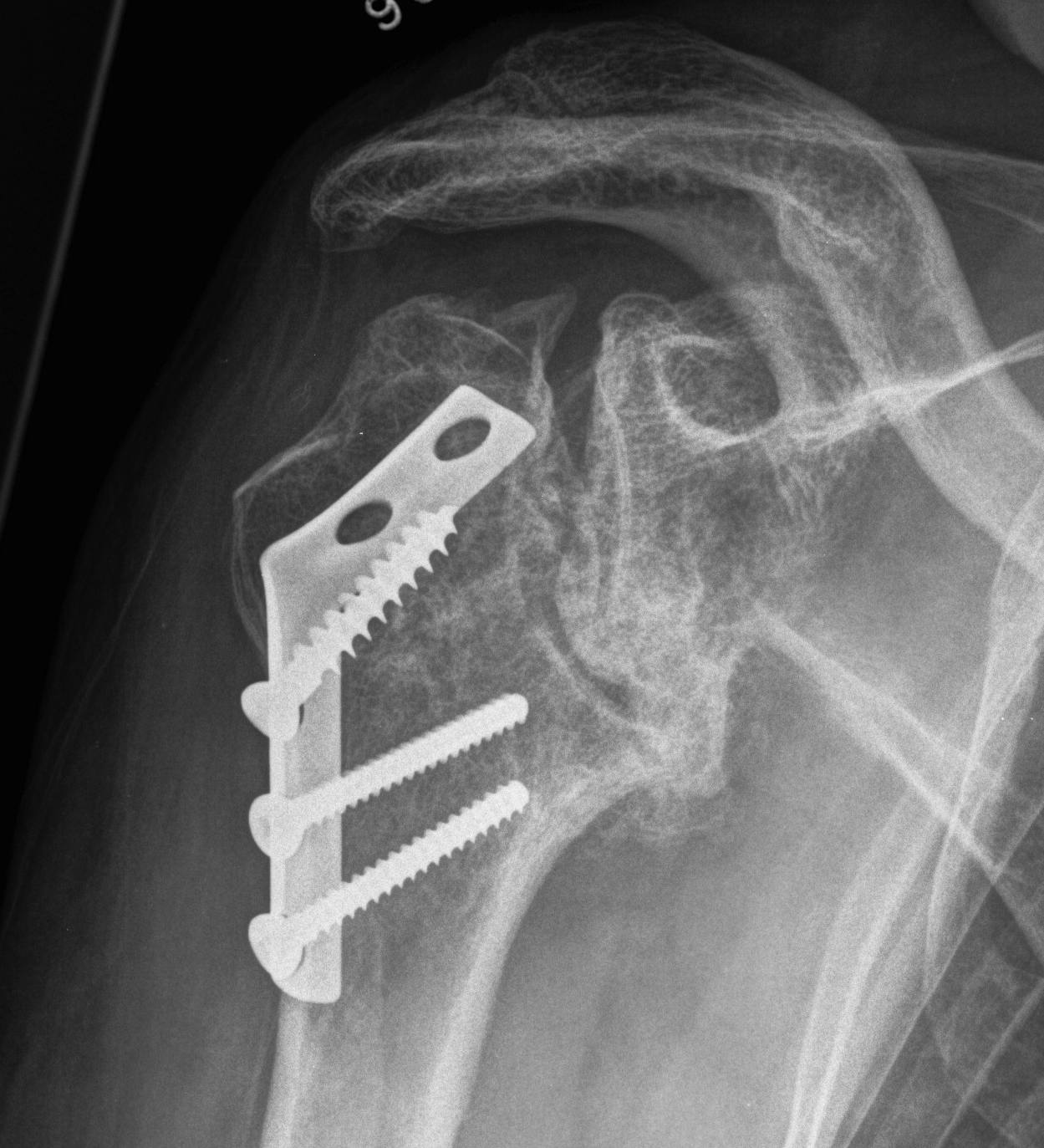
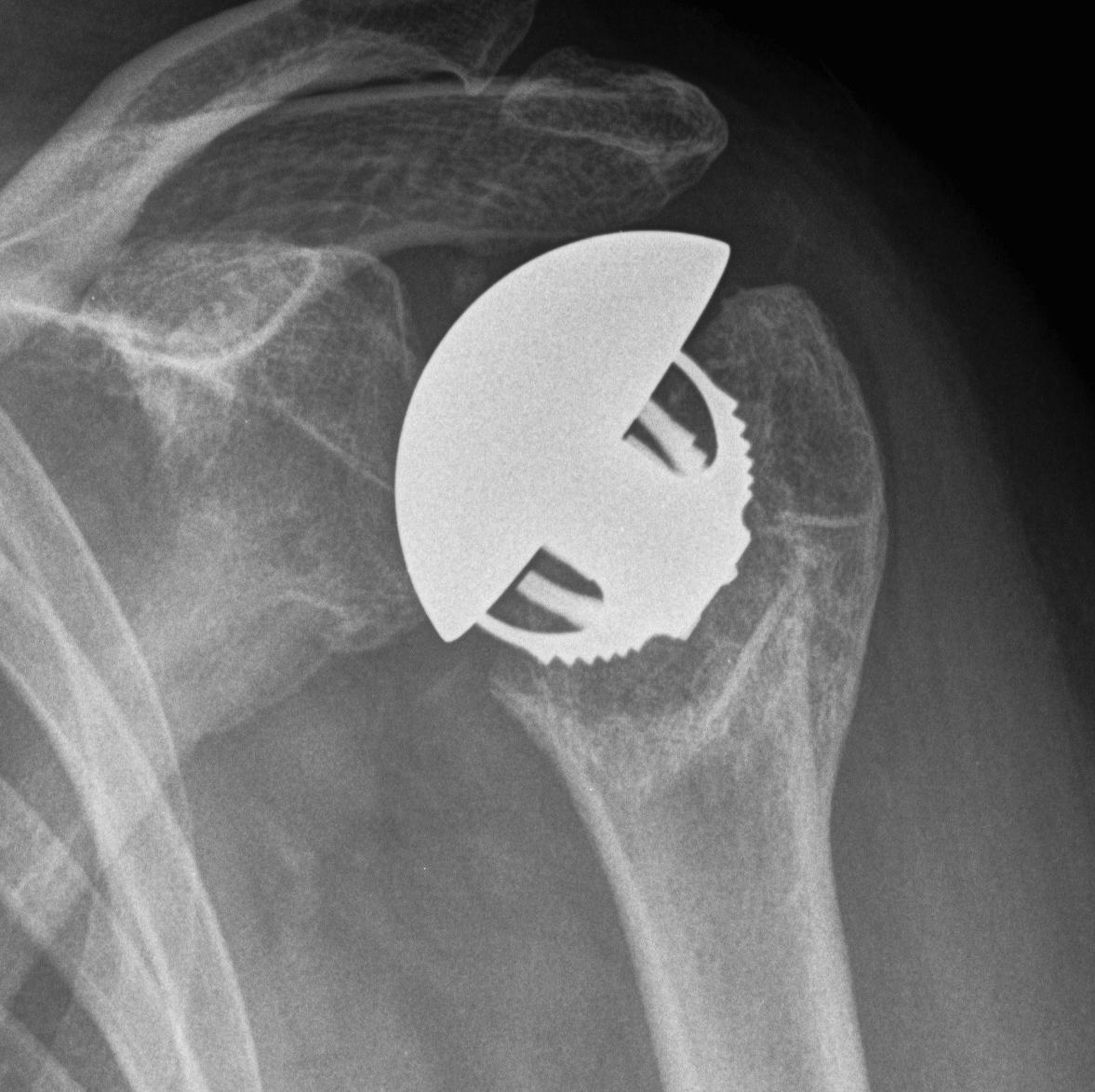
Avascular necrosis
