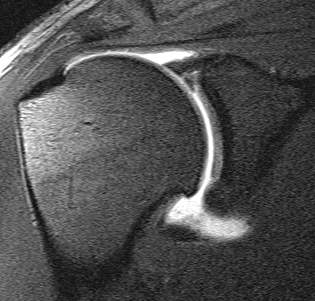
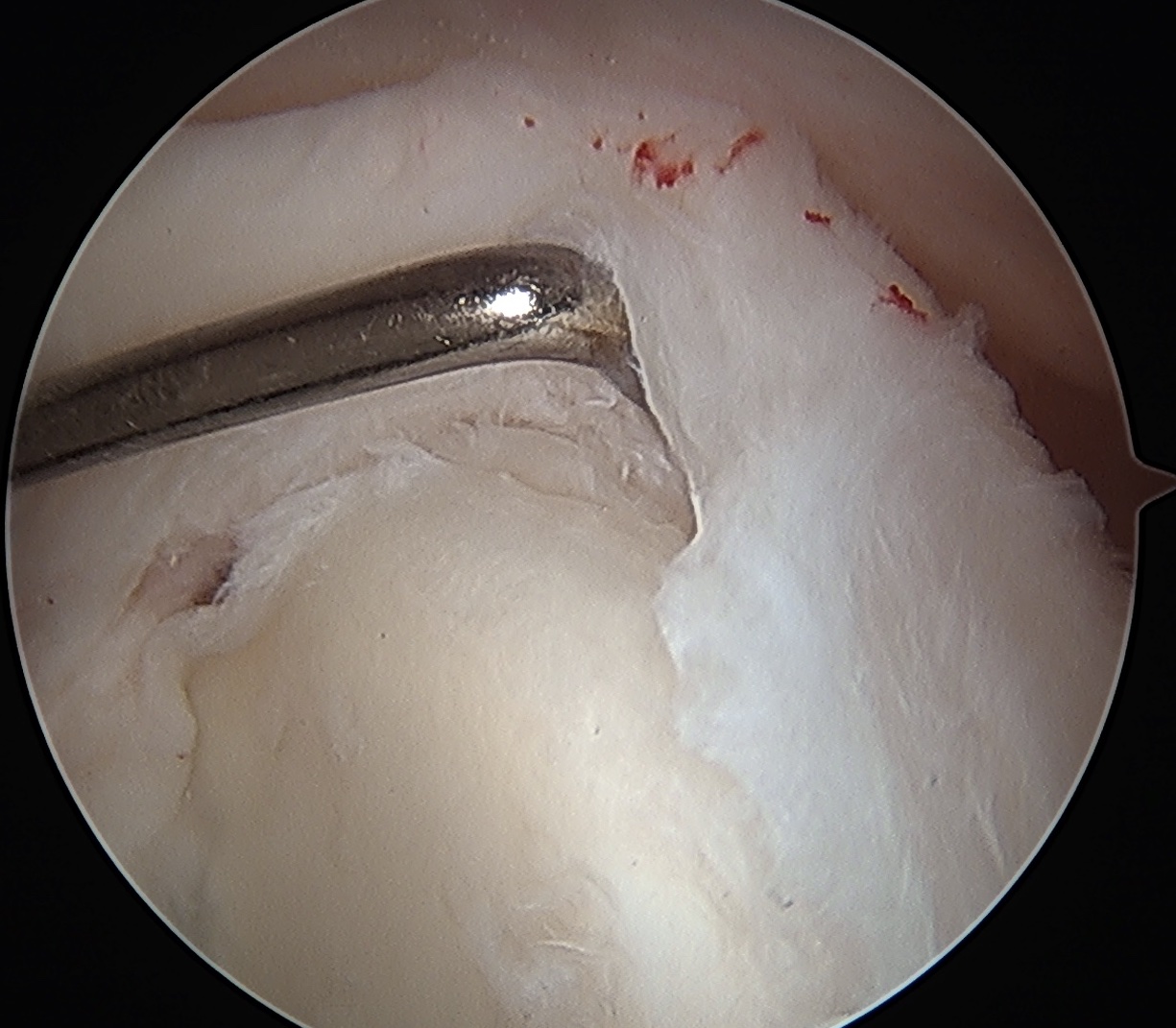
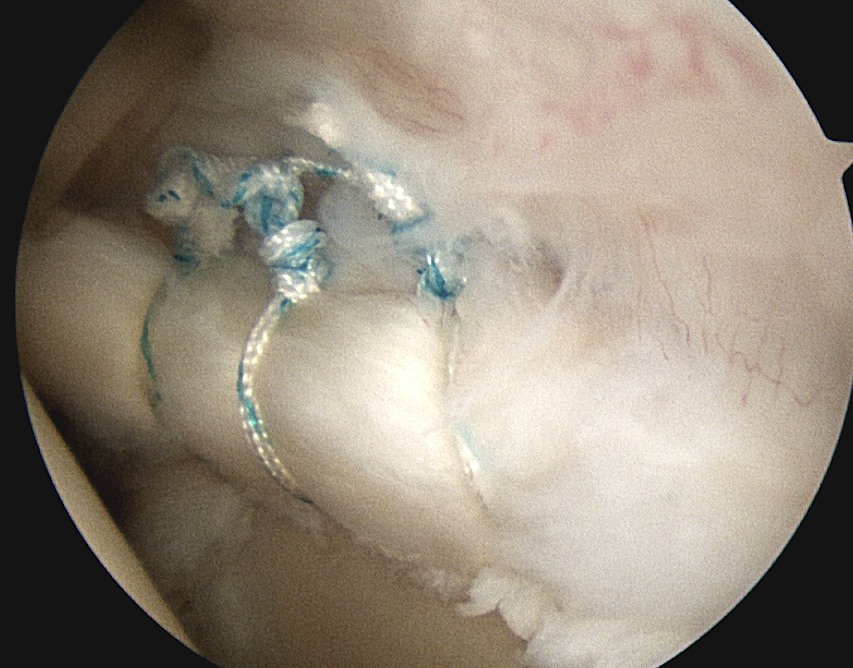
Definition
Superior labrum anterior & posterior
Injury to superior part of glenoid labrum involving region of biceps tendon insertion
Epidemiology
1. Young patients after injury / trauma
2. Older patients
- have rotator cuff tear or other pathology
- don't repair in this group
- tenotomy / tenodesis
Etiology
| Compression force | Traction on arm | Overhead motion |
|---|---|---|
| Fall on outstretched arm | Pull on arm | Throwing athlete |
| Humeral head places shear force on labrum | Grab while falling | Repetitive microtrauma |
History
Pain with overhead activities
Mimics impingement
Examination
| Speed's test | Yergason's test | O'Brien's test |
|---|---|---|
|
Resisted forward flexion at 90° Forearm supinated Pan in bicipital groove |
Externally rotate arm with elbow 90° Resisted supination - assess pain or popping at bicipital groove |
Shoulder flexed 90o in plane of scapula Adducted 30-45o Max internal rotation / thumb down Resist downward force causes pain No pain with external rotation / thumb up |
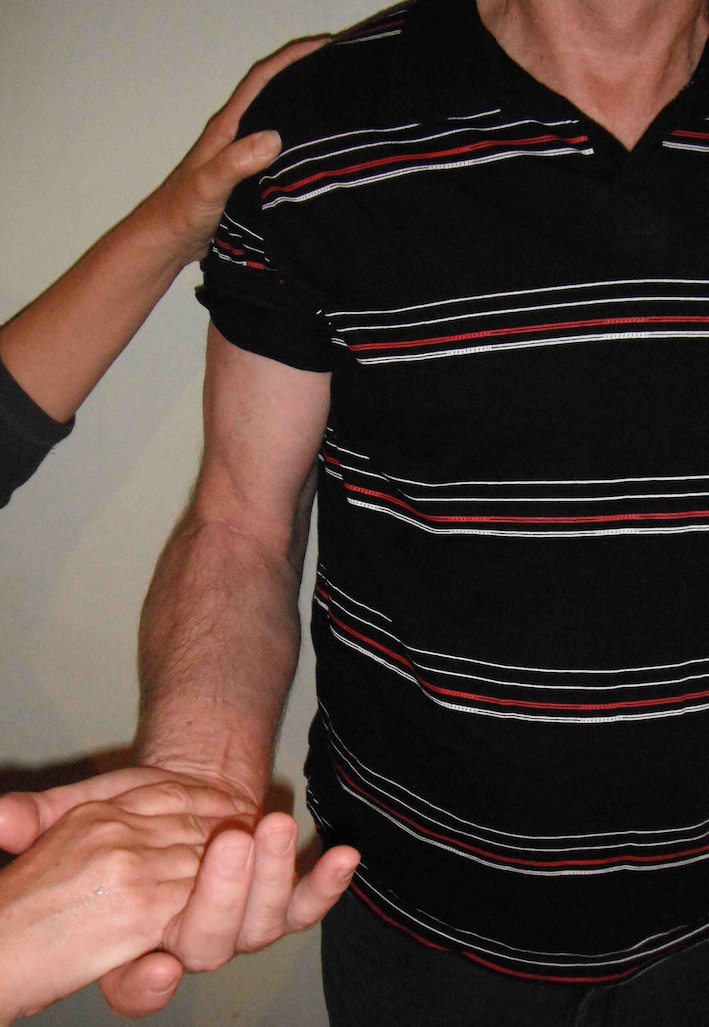 |
 |
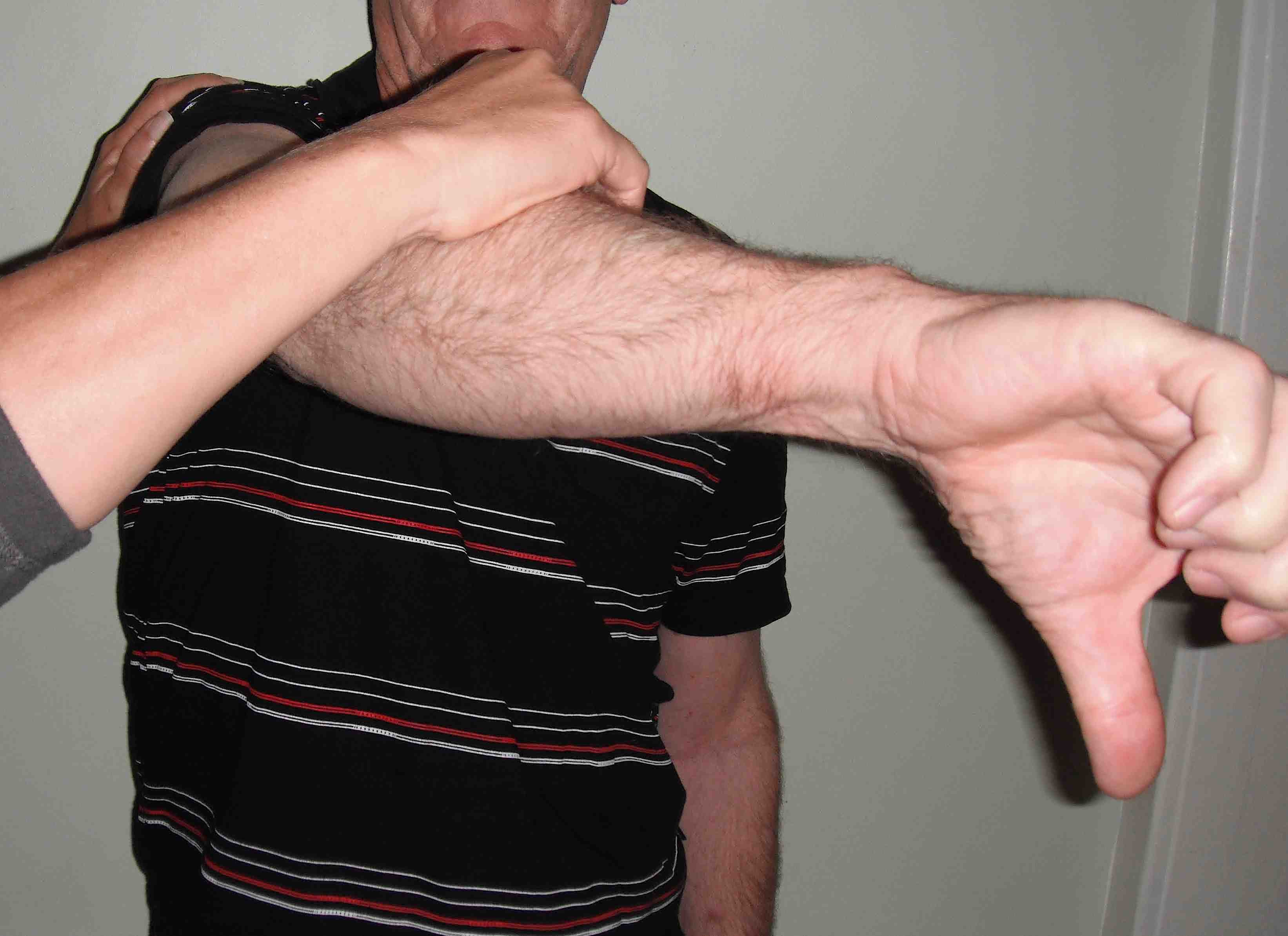 |
- systematic review of physical exam for SLAP tears
- O'Brien most sensitive
- Yergason most specifici
MRI
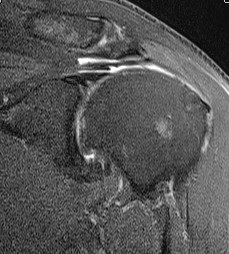

Supralabral ganglion cyst
- associated with posterior SLAP tears
- www.boneschool.com/suprascapular-nerve-compression
Arthroscopy
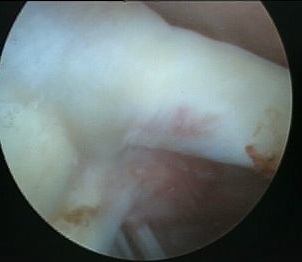
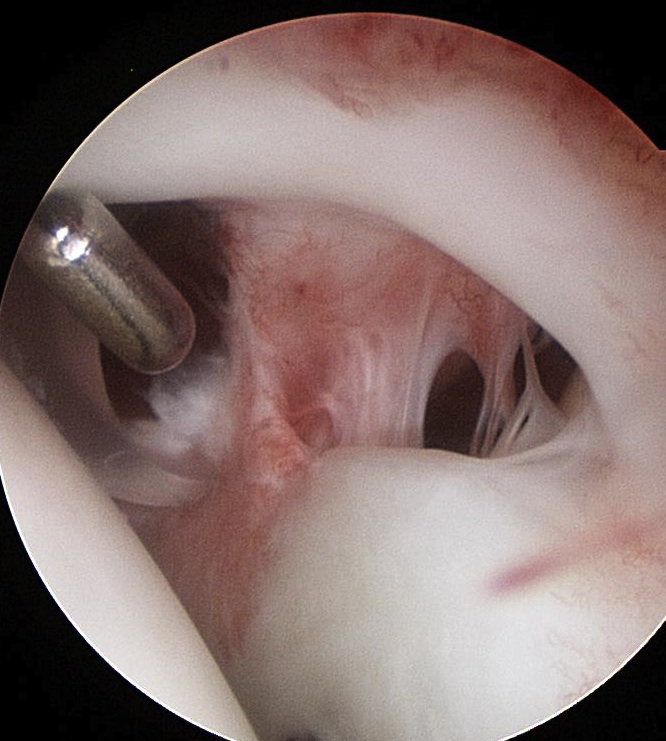
Normal insertion of superior labrum onto glenoid
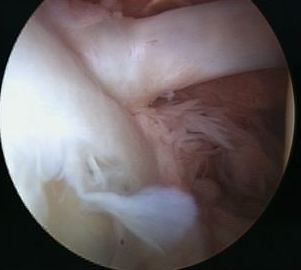
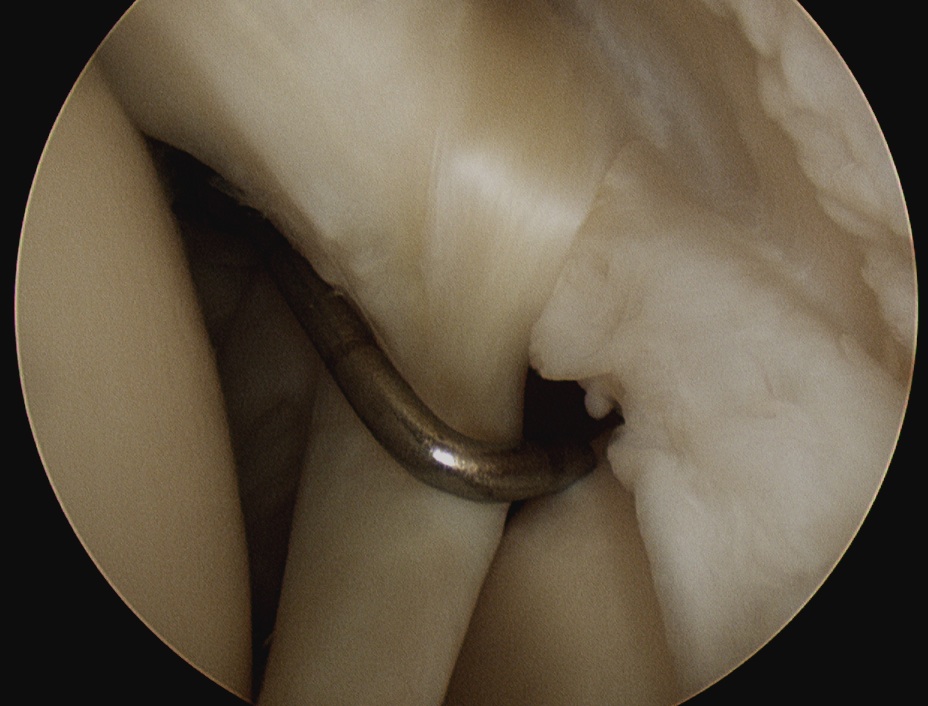
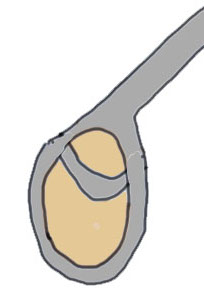
Snyder Arthroscopic Classification SLAP tears
| Type 1 (10%) | Type II (40%) | Type III (30%) | Type IV |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Superior labrum frayed Labrum and biceps anchor intact |
Superior labrum and biceps anchor torn off glenoid |
Bucket handle tear of superior labrum Biceps anchor intact |
Bucket handle tear of superior labrum and biceps tendon |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
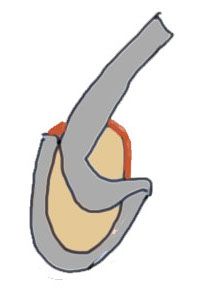 |
Multiple added variations
Type V: Type II with extension into anterior bankart lesion (not uncommon in instability)
Type VI: Type II with unstable flap
Type VII: Type II with MGHL injury
Type VIII: Type II with posterior extension
Type VI: Type II with unstable flap
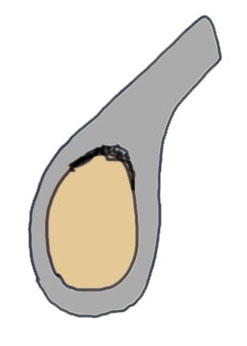
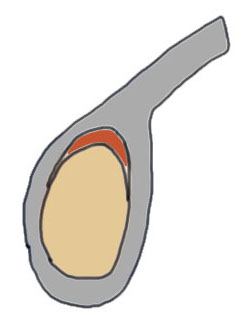
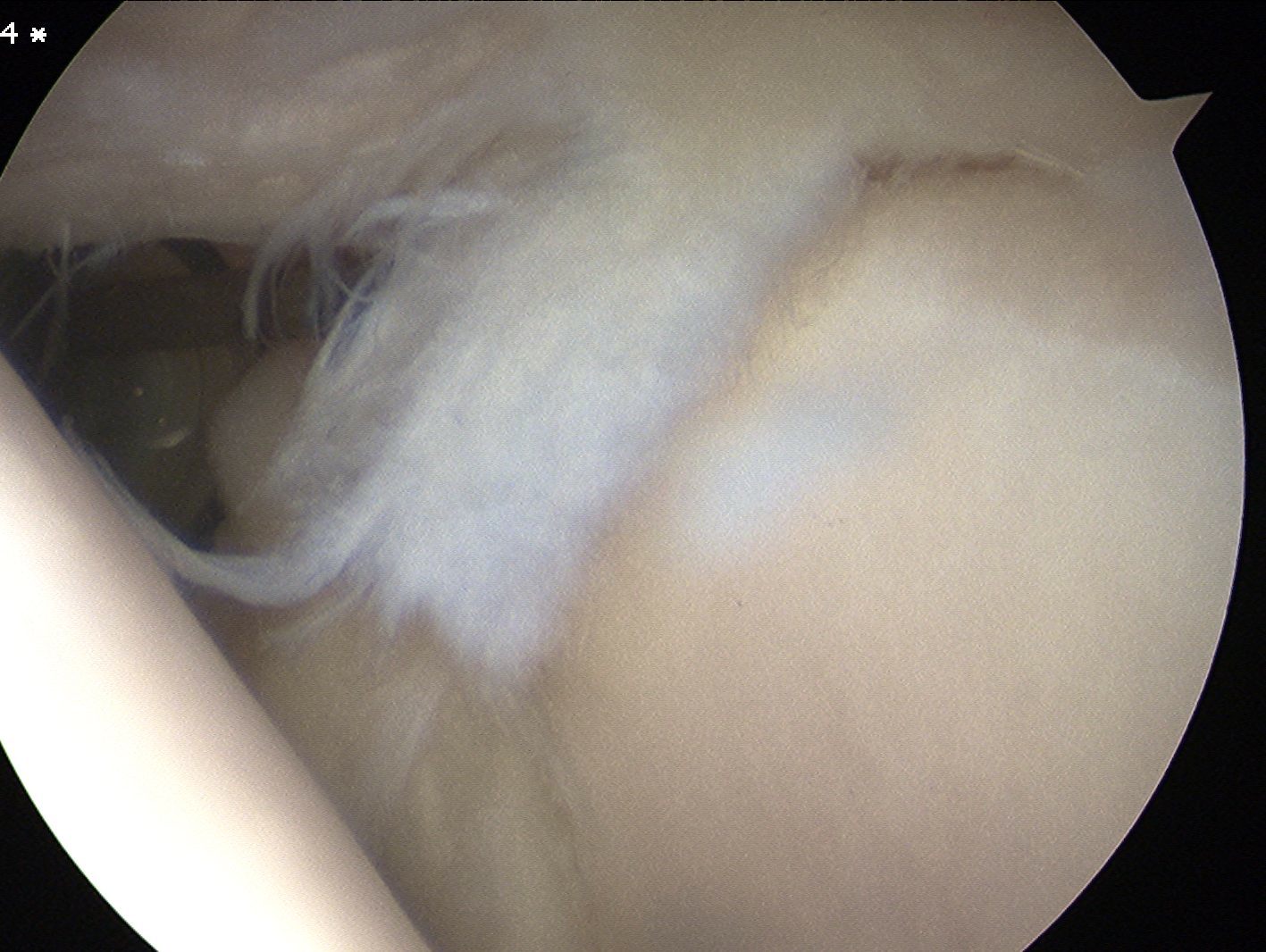
Sublabral foramen / recess
Normal variant
- recess under superior labrum
- this area of glenoid has no evidence of trauma with normal cartilage
- superior labrum and biceps anchor intact and stable
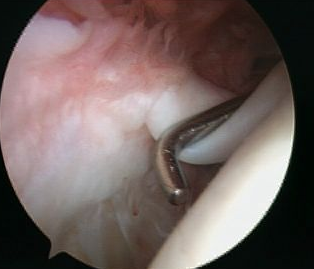
Sublabral foramen with stable biceps anchor
Nonoperative management
Physiotherapy
Activity modification
Cortisone injections
Results
- nonoperative treatment of SLAP tears
- physiotherapy and up to 2 cortisone injections
- 85% improved
- RCT of SLAP repair v tenodesis v sham surgery (120 patients)
- no difference in groups at 2 years
Operative management
Options
SLAP repair
SLAP repair + Biceps tenodesis - arthroscopic suprapectoral or open infrapectoral
Biceps tenotomy
Management Algorithm
| Type I | Type II | Type III | Type IV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Debride labrum | Repair | Debride labrum | Repair |
| Biceps tenodesis / tenotomy | Biceps tenodesis / tenotomy |
Results
SLAP Repair v Tenodesis
Sandler et al Arthrosc Sports Med Rehab 2022
- systematic review of SLAP repair v tenodesis
- 4 studies and 270 patients
- similar outcome scores but slightly higher satisfaction rates with biceps tenodesis
- higher return to sport and lower reoperation rate with biceps tenodesis
Abdul-Rassoul et al Orthop J Sports Med 2019
- systematic review of return to sport
- return to sport SLAP repair: 80%
- return to sport biceps tenodesis: 85%
Biceps tenodesis in overhead athletes
- systematic review of biceps tenodesis in overhead athletes
- 8 articles and 100 athletes
- return to play 70%
Tenodesis v tenotomy
- RCT of tenotomy v tenodesis
- no difference in outcomes / cramping / supination strength
- increased cosmetic deformity / popeye in tenotomy (33%) versus tenodesis (10%)
SLAP and anterior labral tear in young patient with instability (Type V)

Bitar et al Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 2024
- patients with recurrent anterior instability with SLAP + Bankart
- Bankart repair versus Bankart repair + SLAP repair
- 45 in each group
- no difference in recurrence or functional outcome between two groups
- systematic review of Type V SLAP tears
- Bankart repair versus Bankart repair + SLAP repair
- no difference
Rotator cuff tears and SLAP tears
- RCT patients with SLAP and rotator cuff tears > 50 years old
- tenotomy v SLAP repair with associated rotator cuff repair
- improved ROM and functional scores in tenotomy group
Arthroscopic SLAP repair
Vumedi arthroscopic SLAP repair video
Vumedi arthroscopic SLAP repair video 2
Technique
Beachchair
- anterior portal for suture passage / superior glenoid debridement
- lateral portal to insert anchors
- anterior to supraspinatus tendon / portal of Wilminton (posterior infraspinatus transrotator cuff)
- debride superior glenoid to bleeding bone
- anchor repair
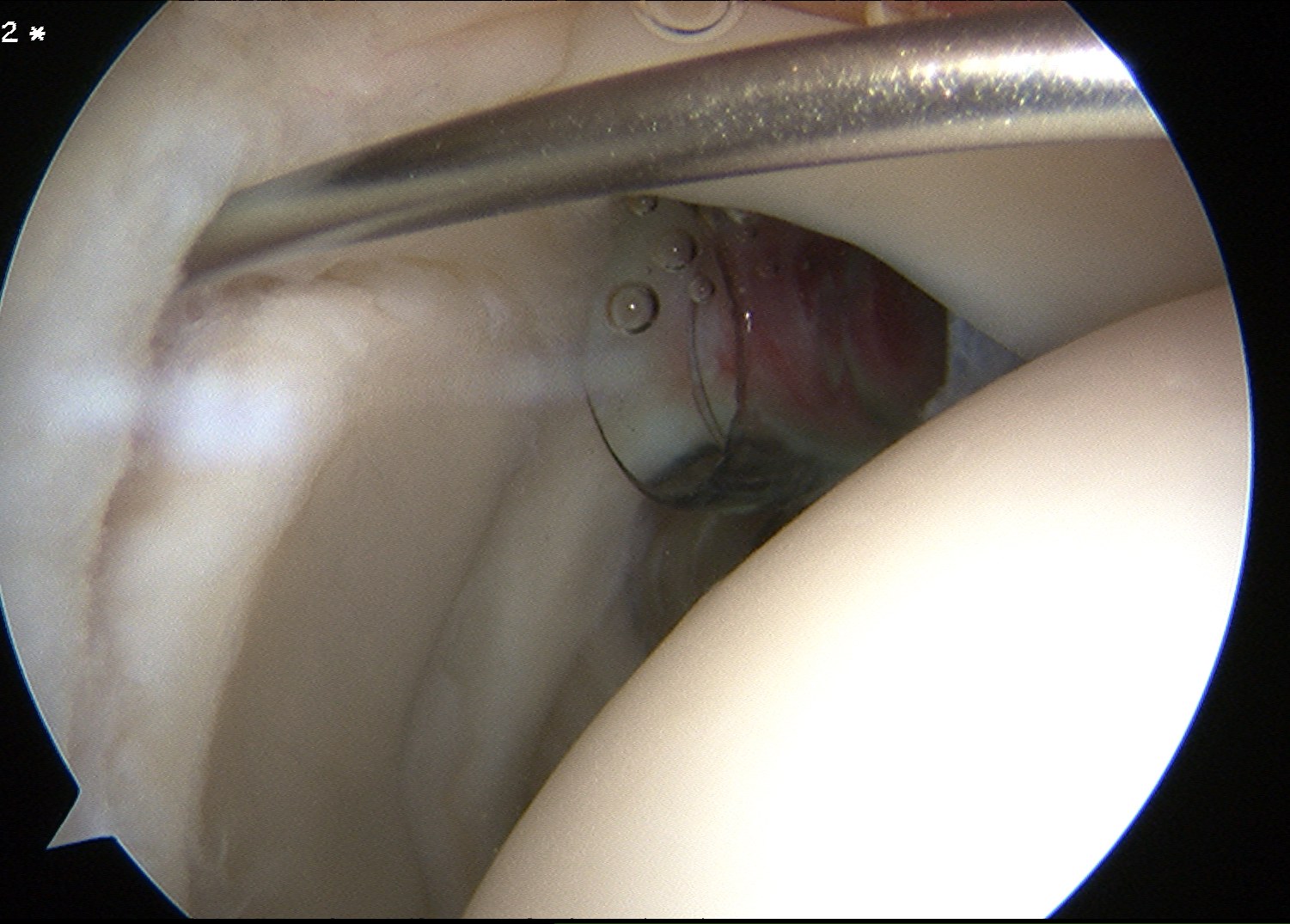
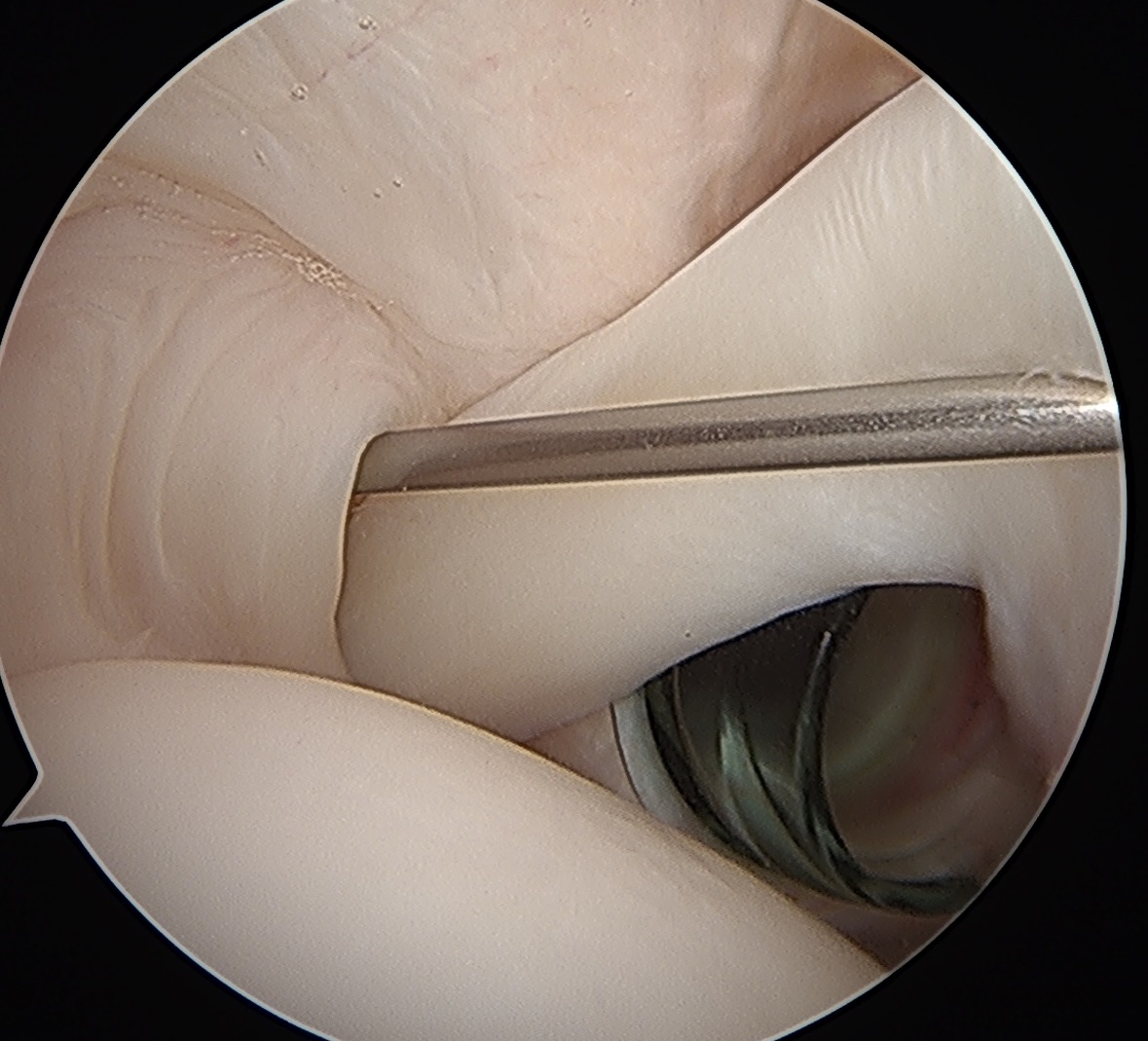
Trans-rotator cuff portal and portal anterior to leading edge supraspinatus

SLAP repair + arthroscopic suprapectoral biceps tenodesis
Technique
Vumedi arthroscopic suprapectoral biceps tenodesis video
Beach chair
- tag biceps tendon with high strength suture and release
- repair superior labrum with one or two anchors
- anchor biceps tendon into bicipital groove
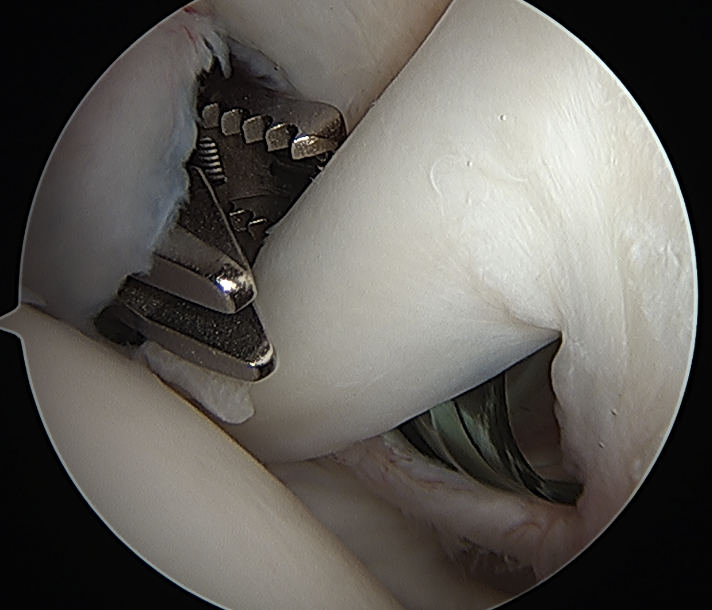
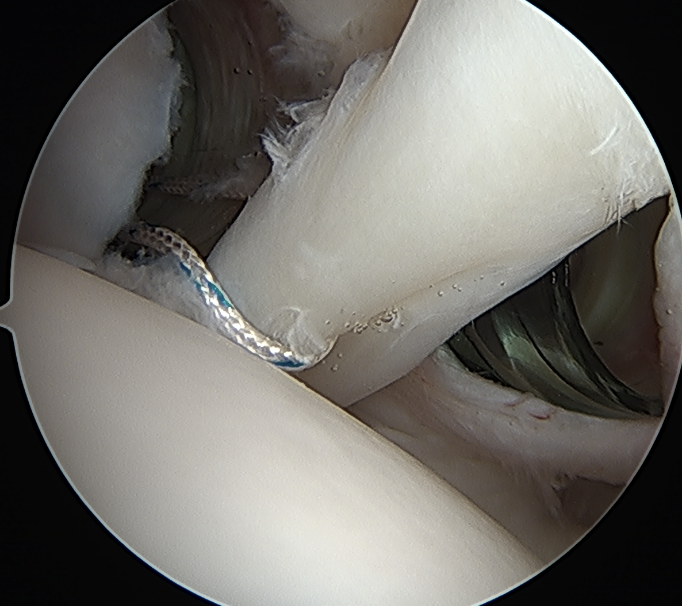
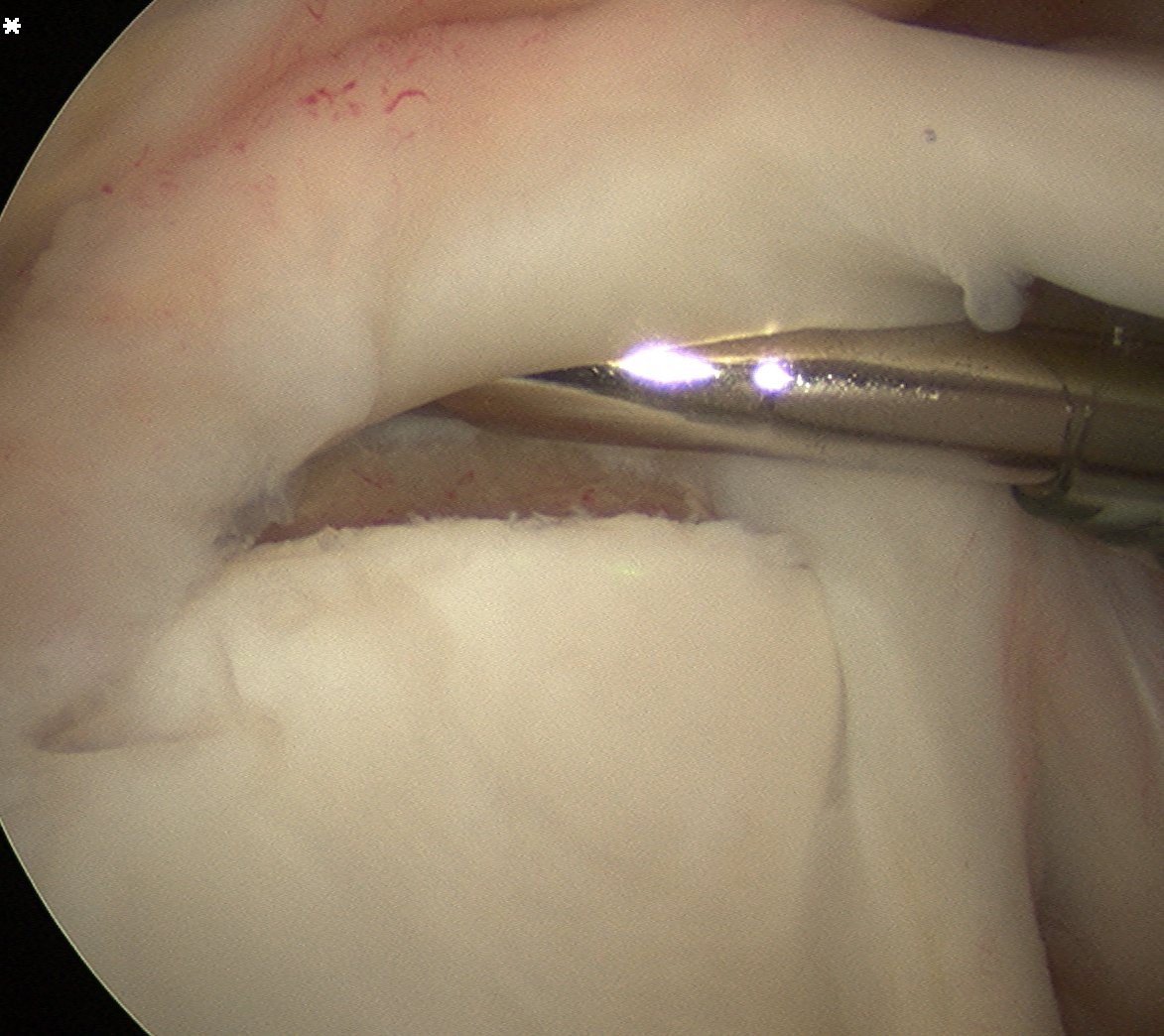
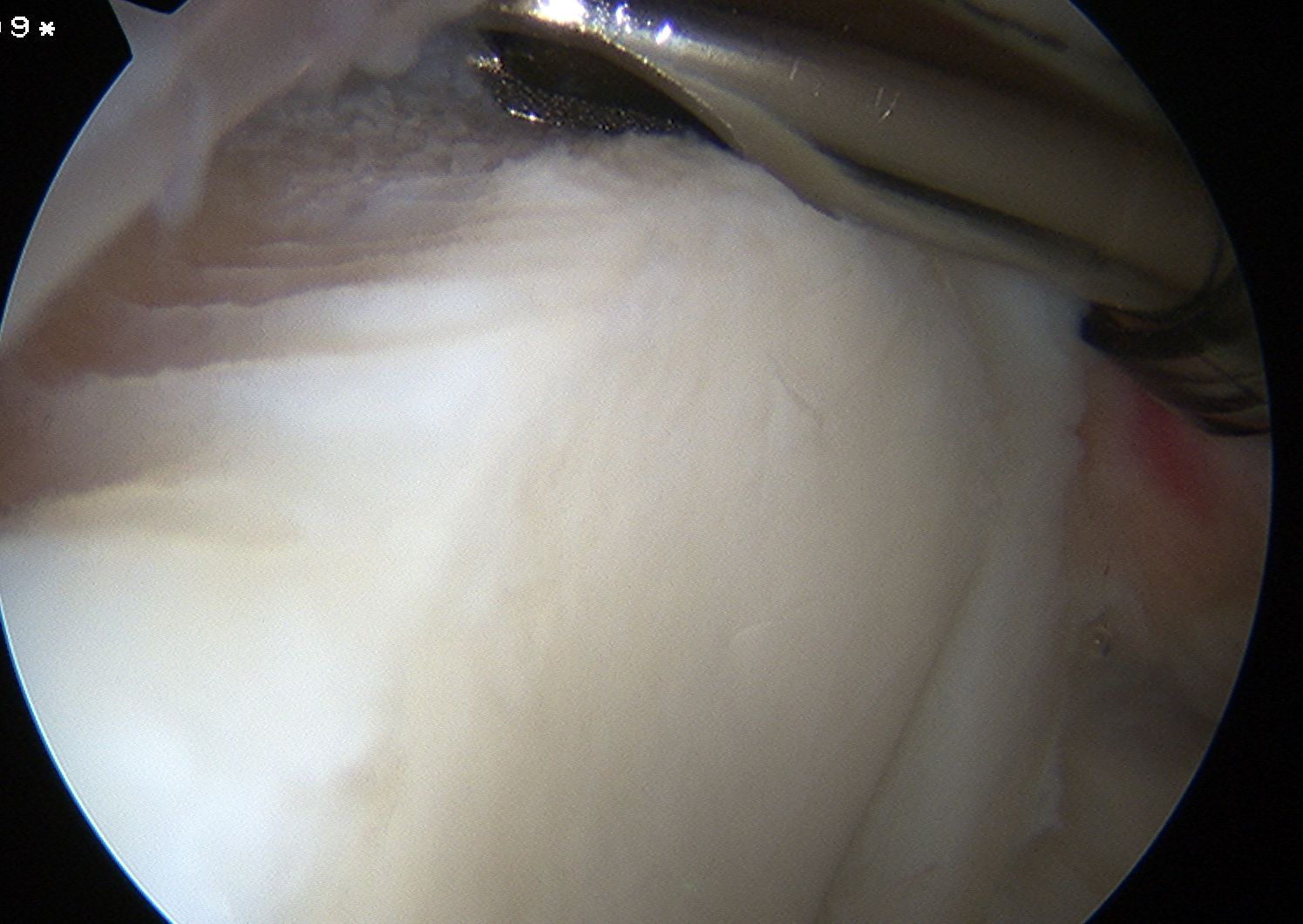
Tag biceps through portal just anterior to supraspinatus tendon
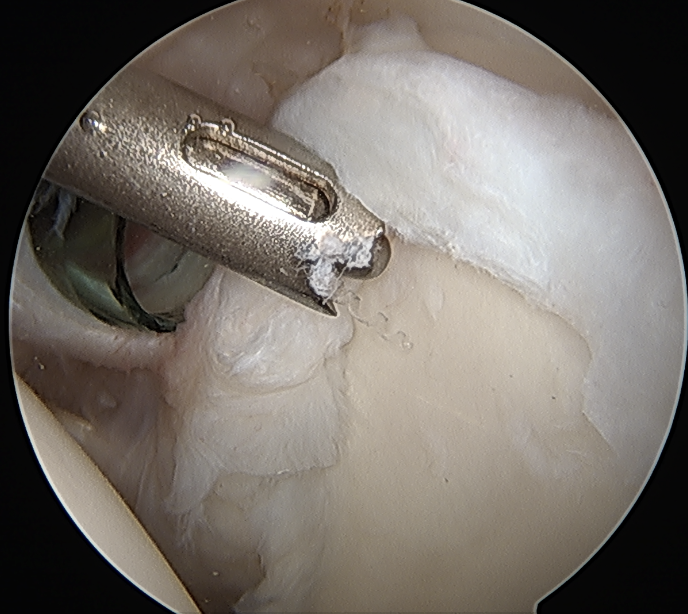
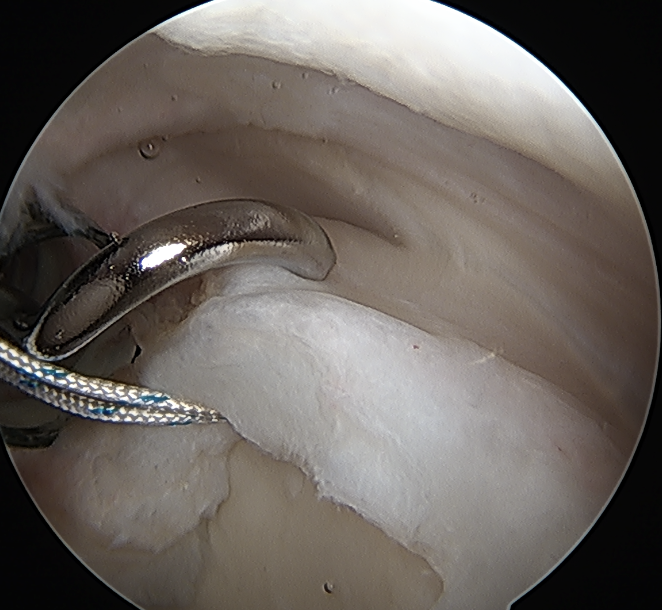
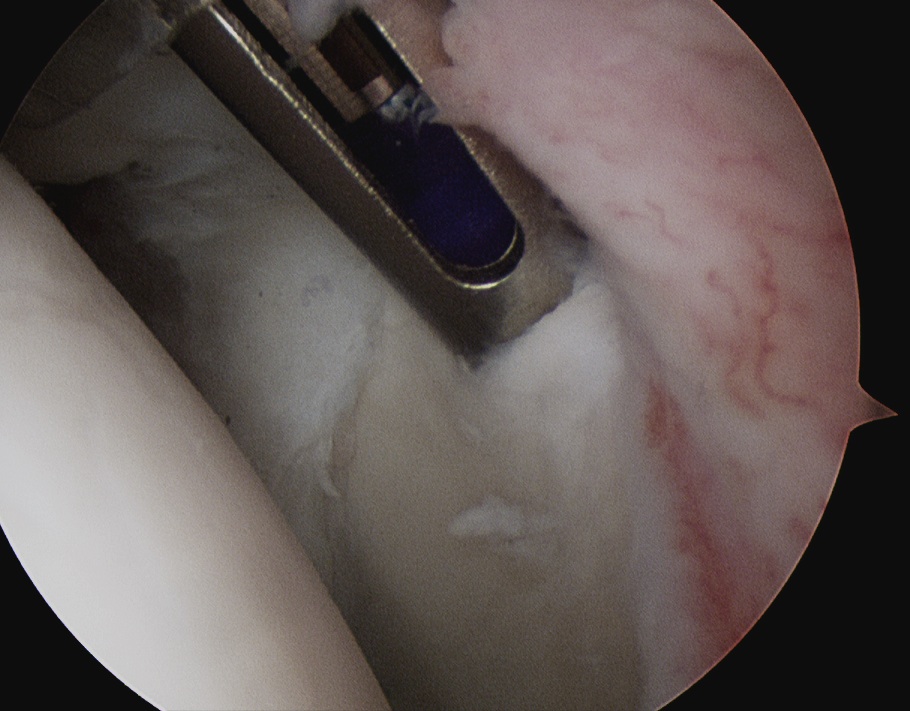
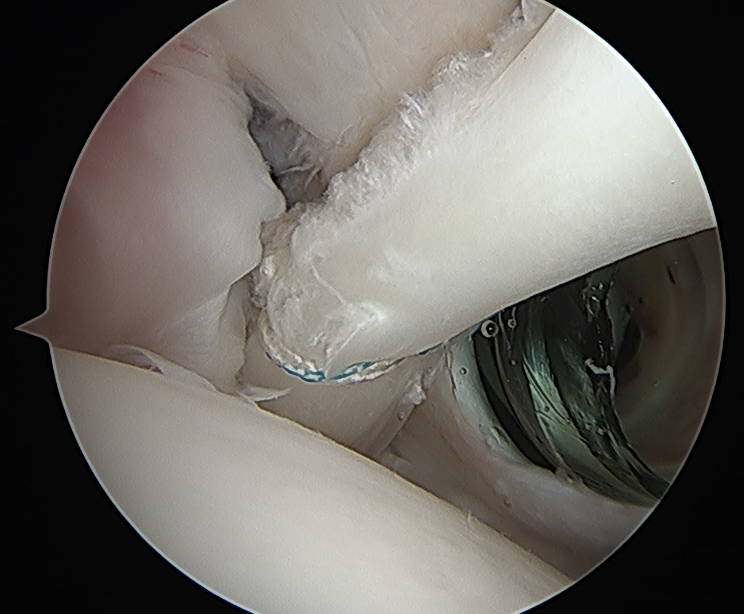
Release biceps and perform superior labral repair
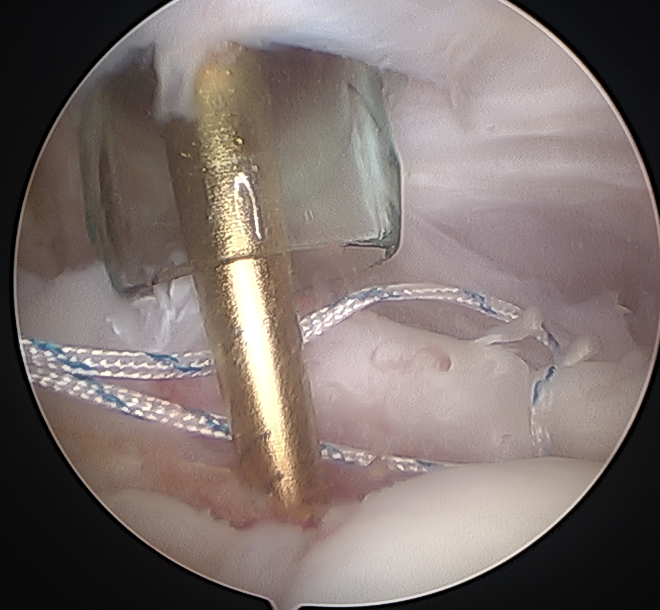
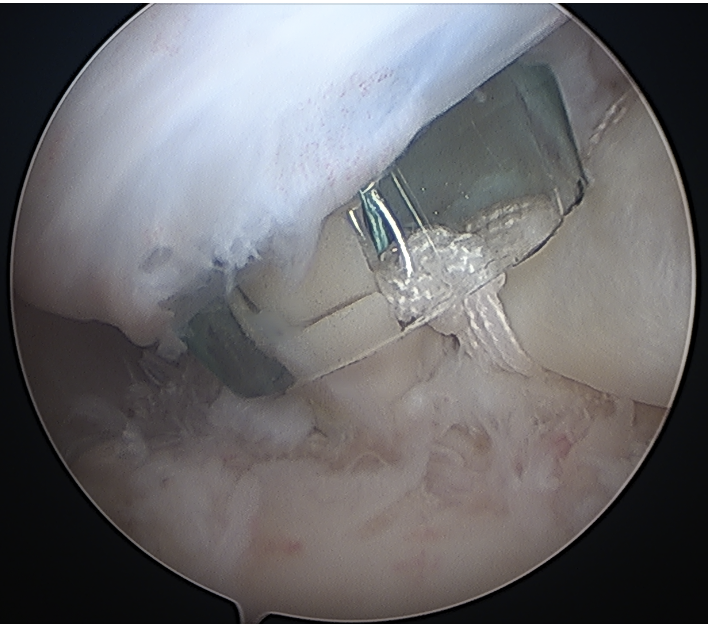
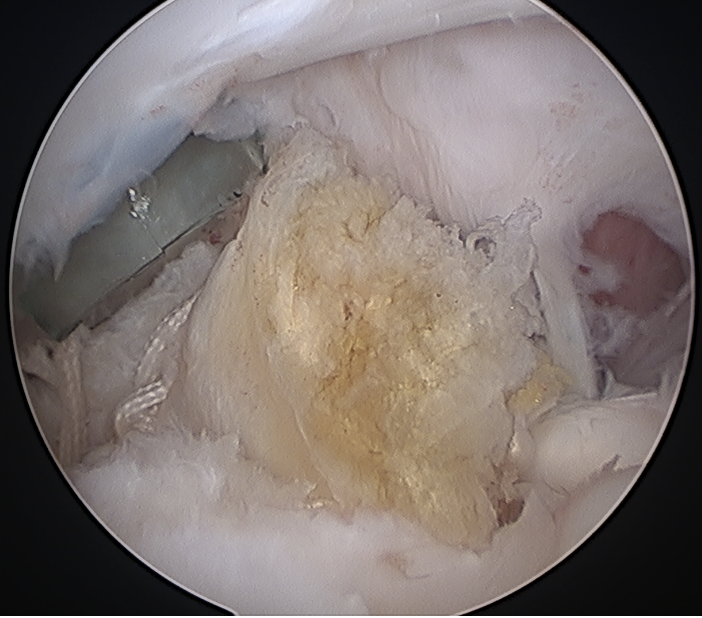
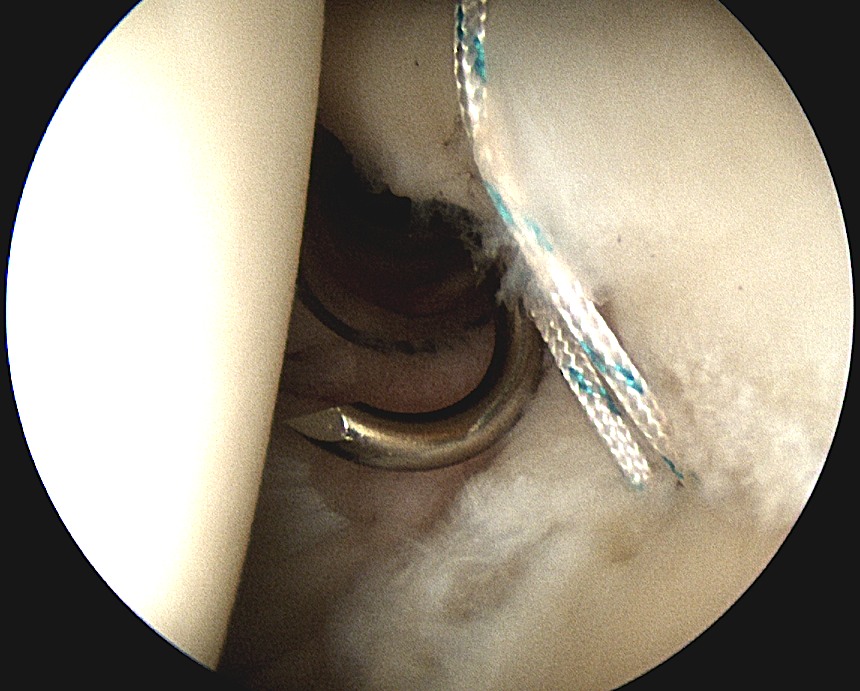
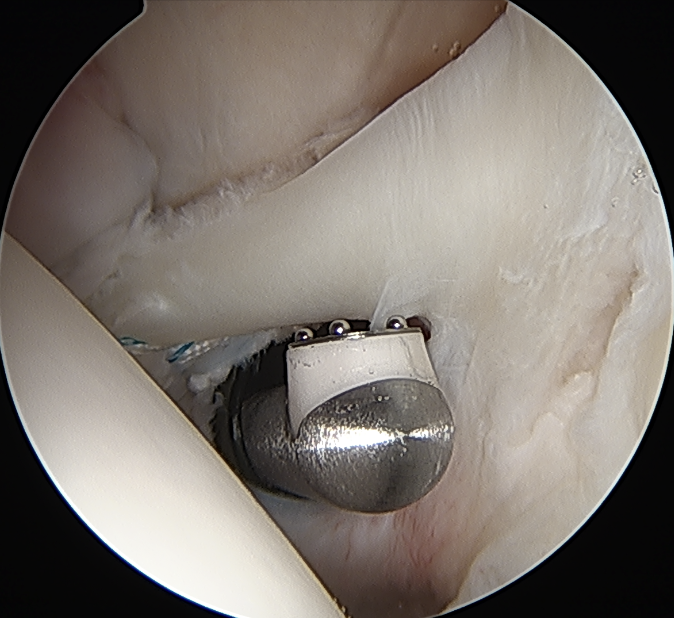
Anchor biceps tendon into bicipital groove
Open subpectoral biceps tenodesis
Technique
Vumedi open subpectoral tenodesis video
Arthrex subpectoral biceps tenodesis video using biceps button
Arthrex subpectoral biceps tenodesis surgical technique PDF
Beachchair
- arthroscopic biceps tendon release
- SLAP repair
- open approach to biceps
- incision centered on humerus below pectoralis tendon
- retract deltoid laterally / elevate pectoralis tendon / conjoint tendon medially
- find biceps tendon / shorten to 2cm of tendon / suture
- anchor biceps tendon
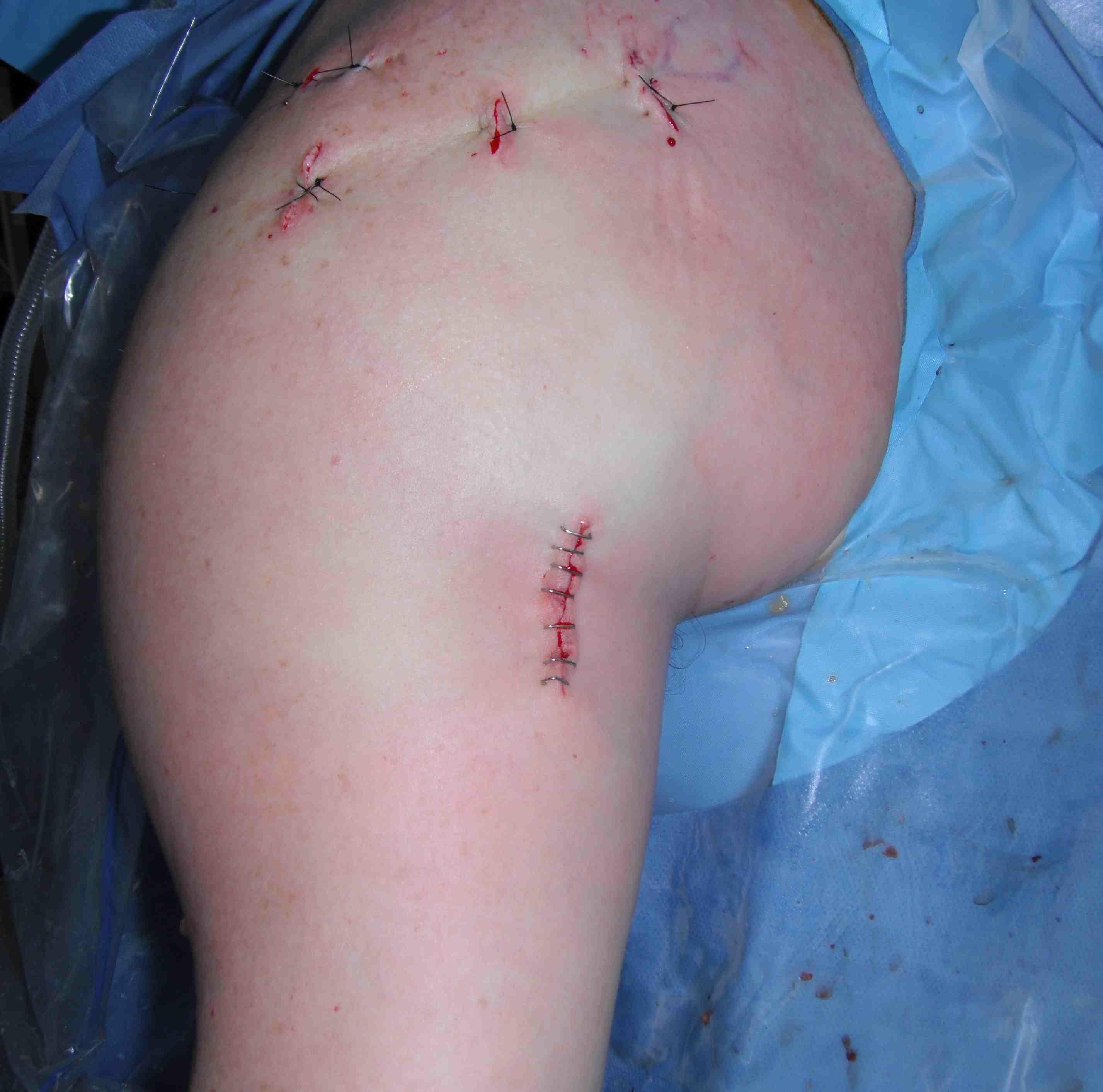
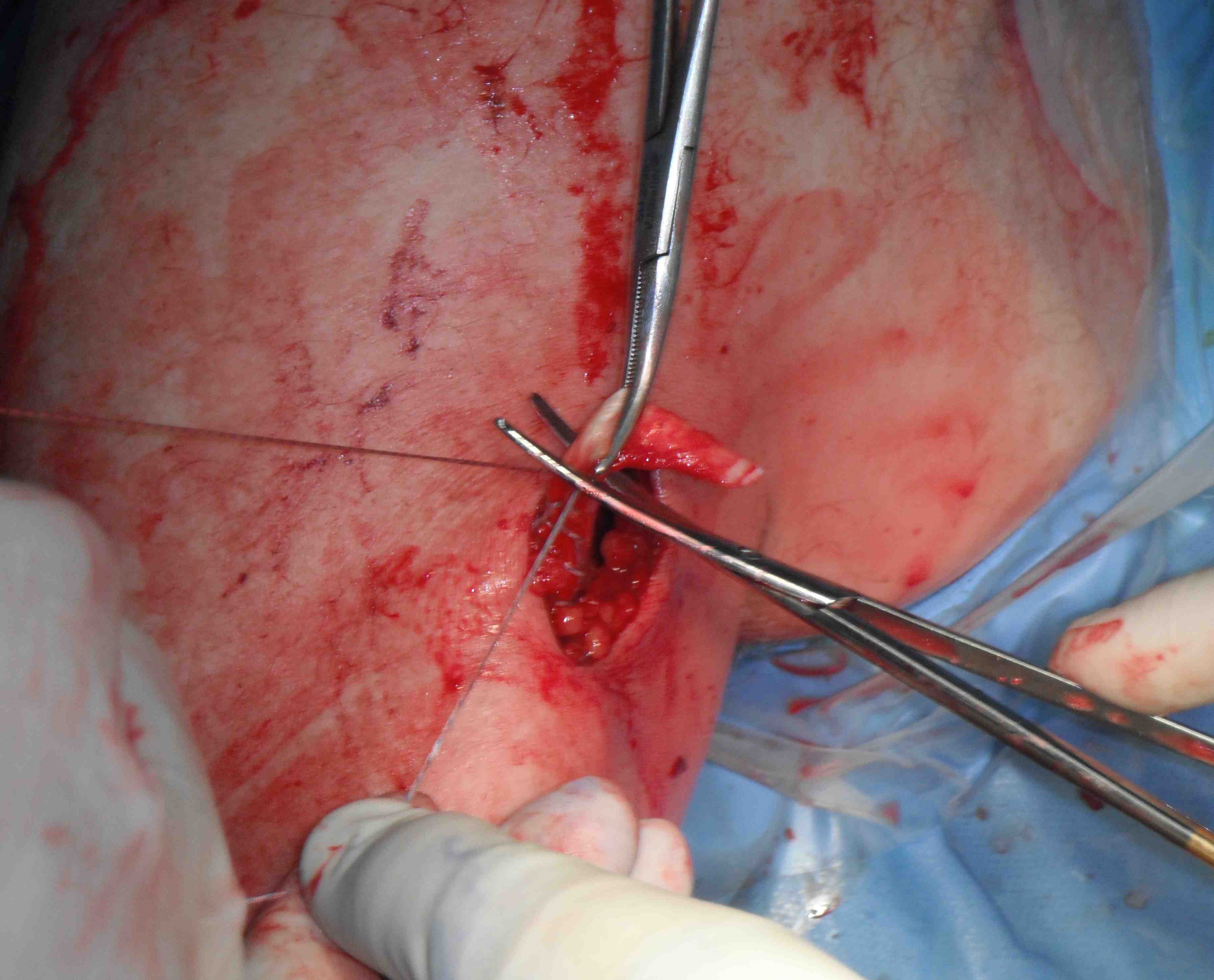
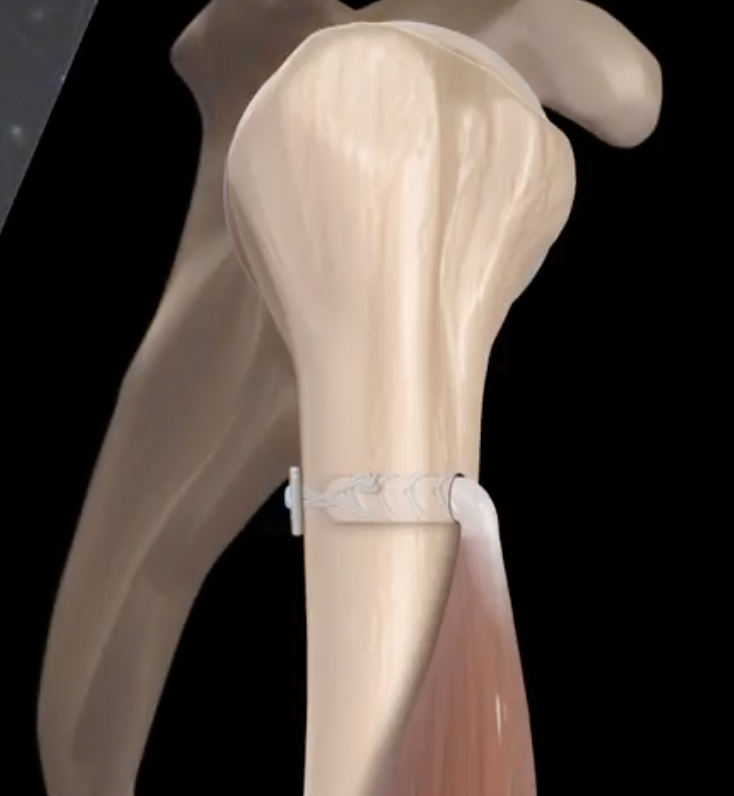
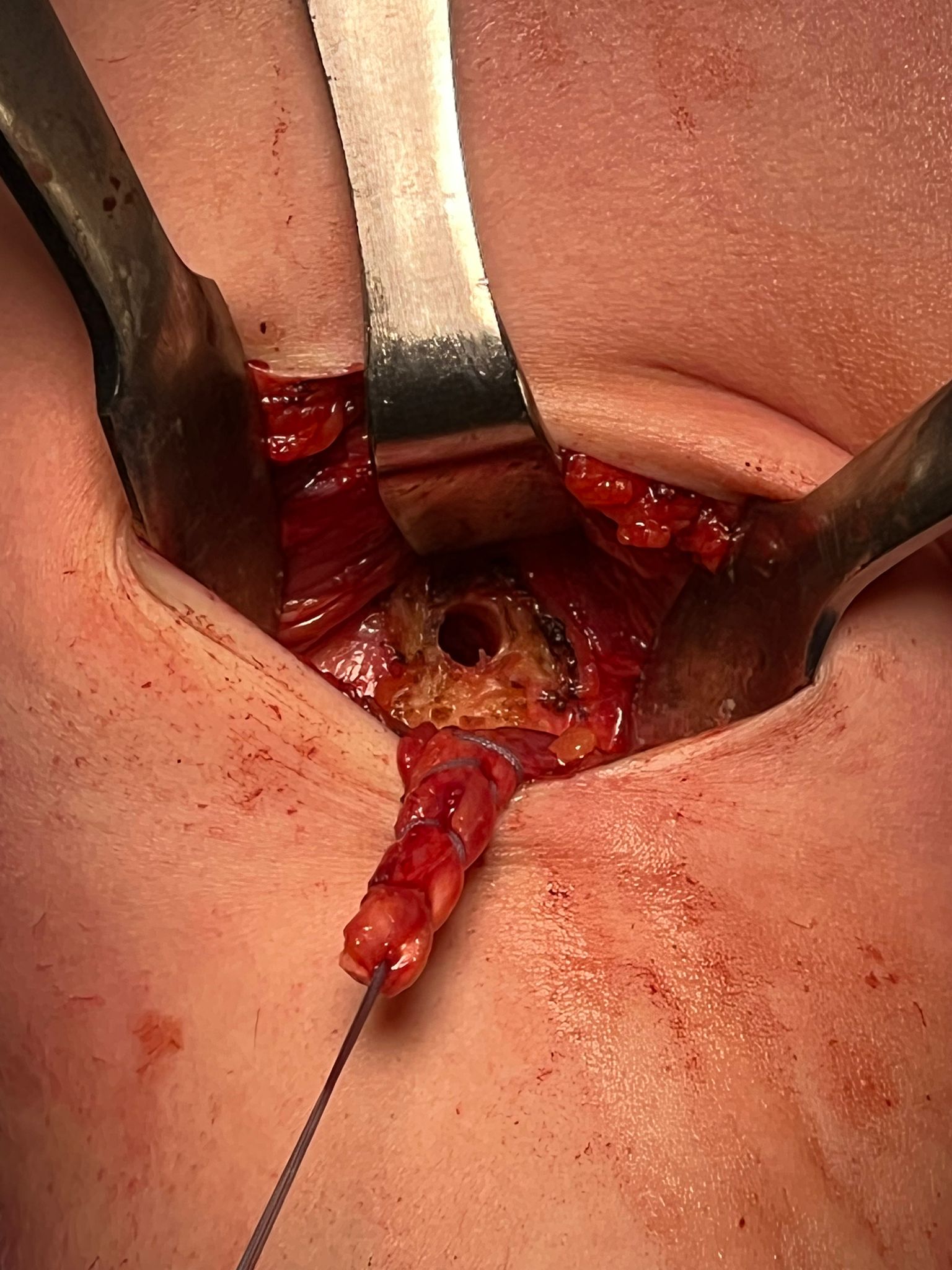
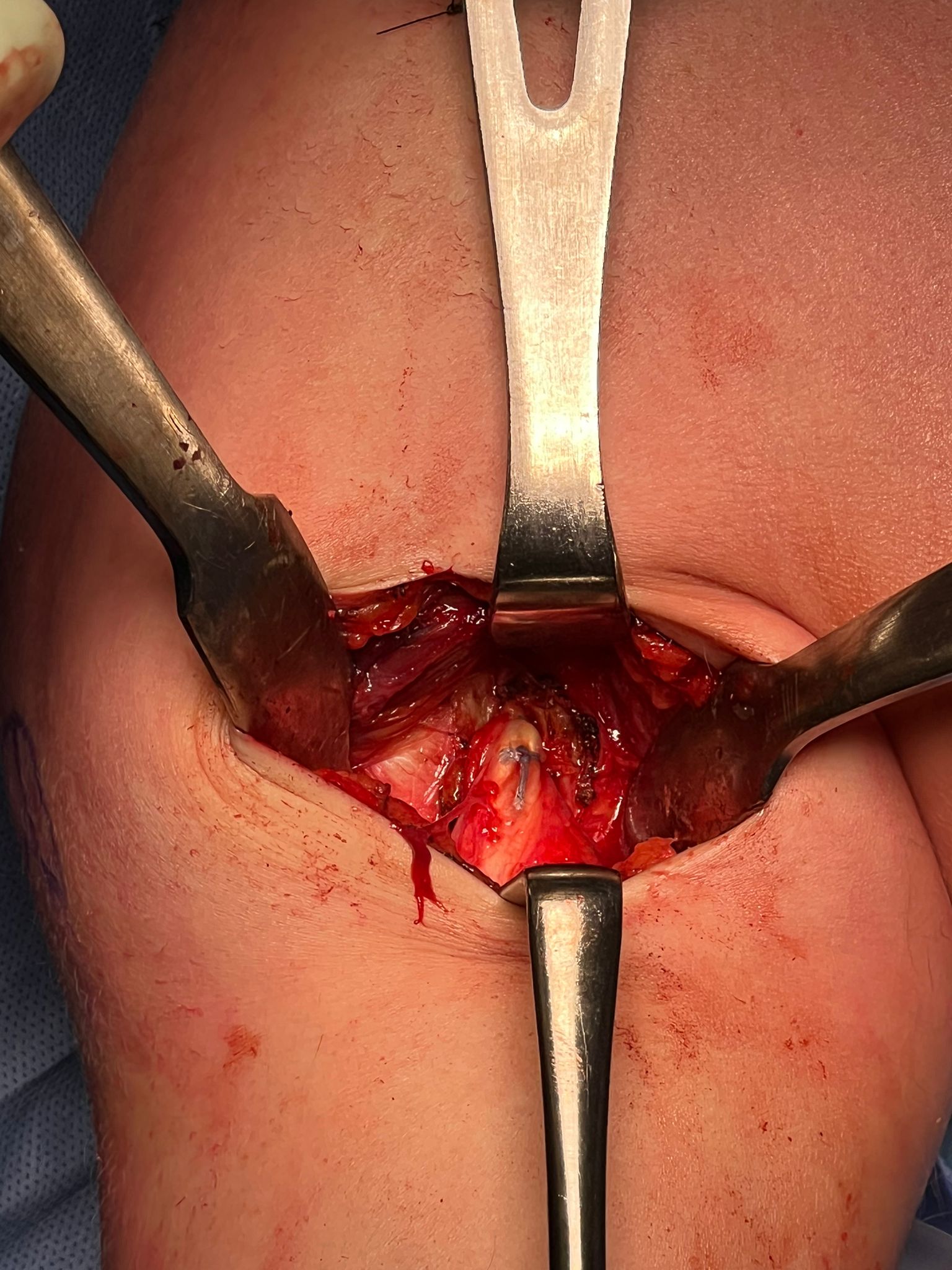
Bicortical open subpectoral biceps tenodesis using Arthrex Biceps Button
