Etiology
| No radius fractures | Radius fractures |
|---|---|
|
Isolated DRUJ dislocation / instability - uncommon - TFCC / radioulna ligament tears |
Distal radius fractures + ulna styloid fractures + sigmoid notch fractures
|
|
Isolated ulna styloid fractures
|
Radial shaft malunion |
|
Galleazzi fractures - distal 1/3 radius with DRUJ disruption
|
|
|
Essex Lopresti fractures - fracture radial head with dislocation DRUJ
|
Anatomy of DRUJ

Articulation between the sigmoid notch of the radius and ulna head
- radius rotates around a fixed ulna
Minimal bony stability / stabiilty provided by soft tissues
- TFCC
- dorsal and palmar Radio-Ulna ligaments (thickenings of the capsule)
- inter-osseous membrane
Isolated dorsal dislocation DRUJ
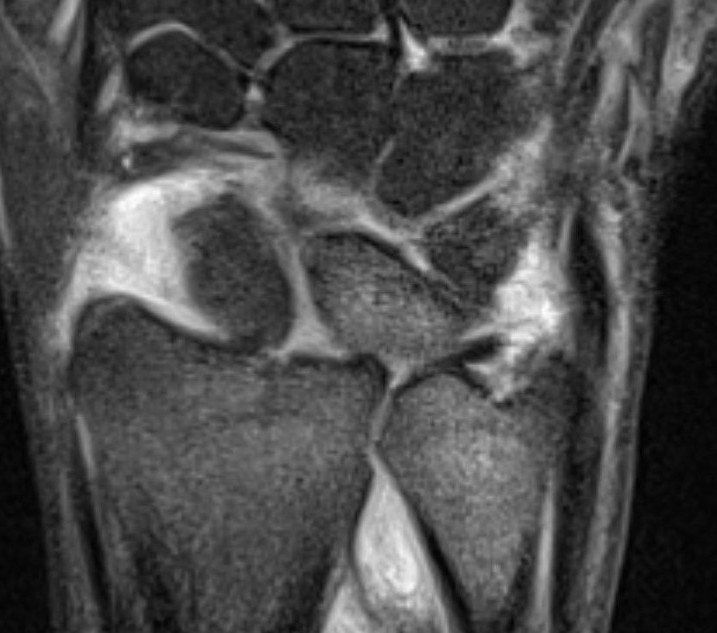
Isolated dorsal DRUJ instability with ulna sided TFCC tear
Etiology
Dorsal dislocation / instability
- hyperpronation
- tear of dorsal distal RUJ ligament + tear of TFCC
Volar dislocation very rare
Clinical
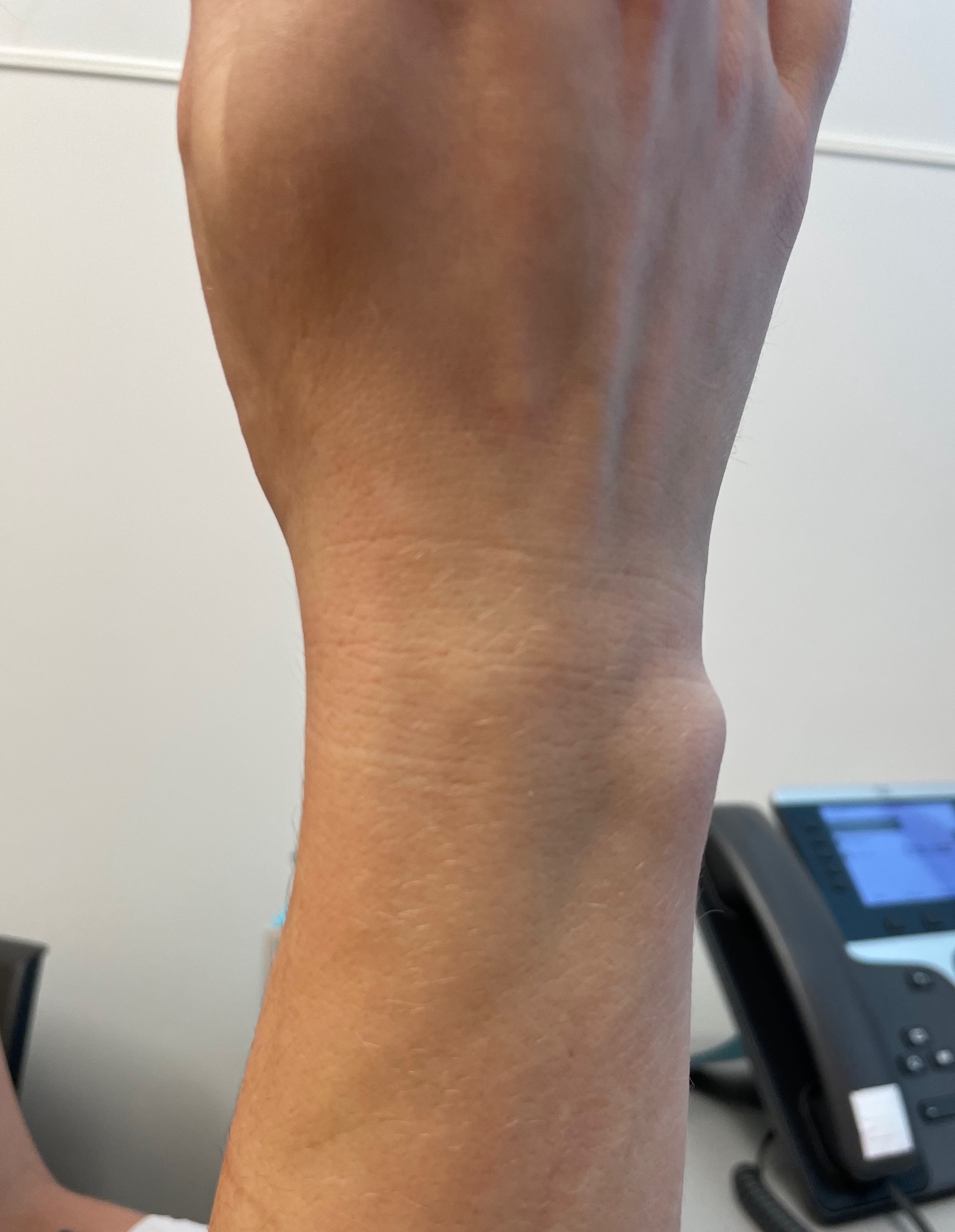
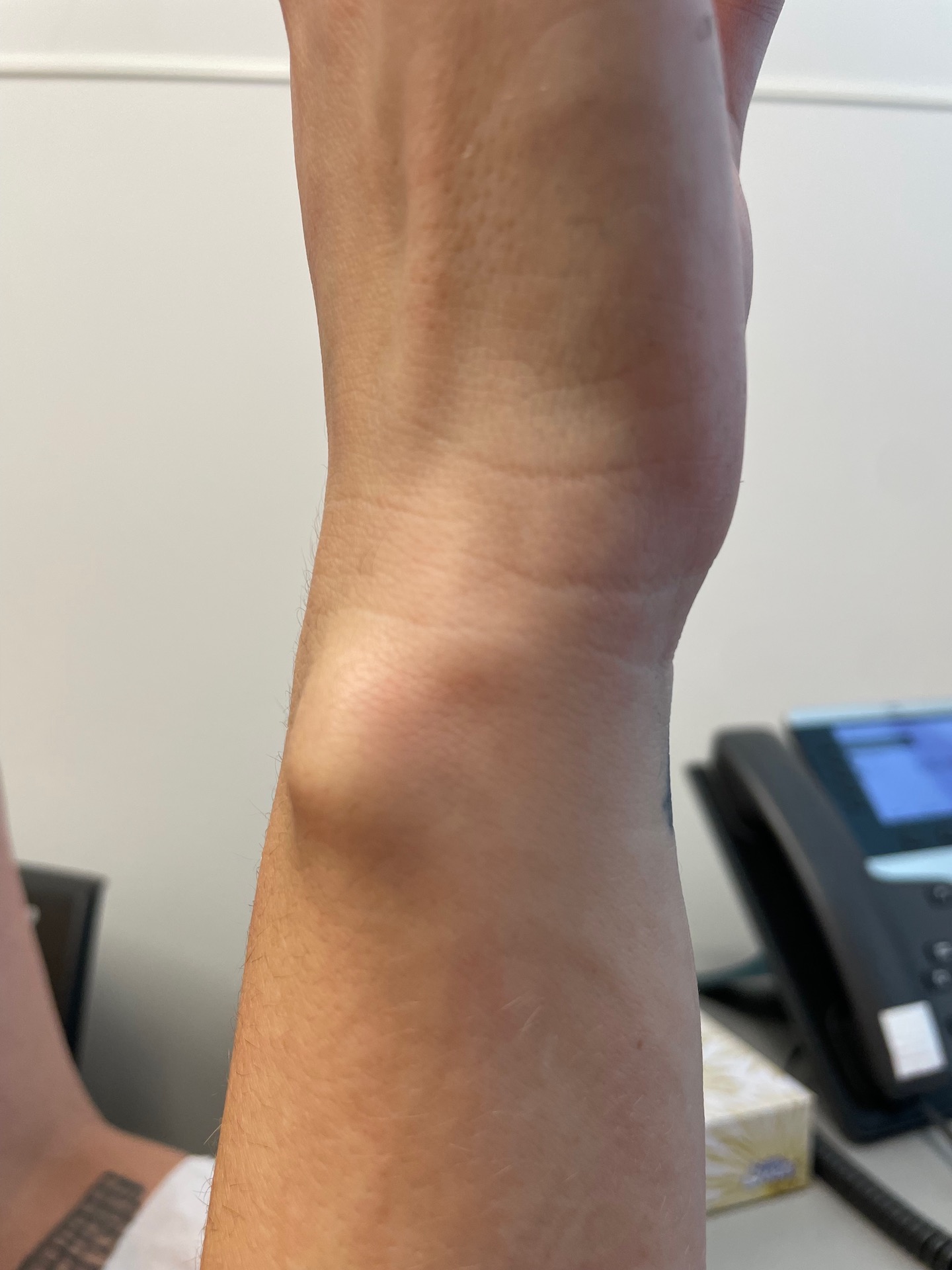
Dorsal subluxation of DRUJ in full supination
Piano key sign - wrist pronated and volar force to ulna
Ballotment test - dorsal and volar force to ulna
Xray
True lateral
- radial styloid overlies proximal scaphoid / lunate / triquetram
Dorsal subluxation of the distal ulna
CT
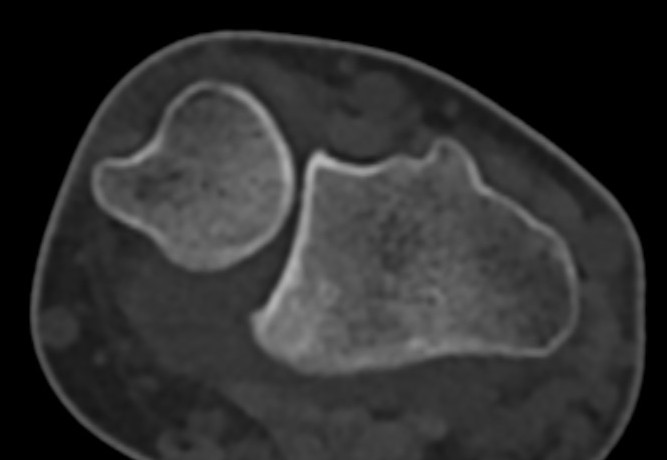
Dorsal subluxation of the distal ulna
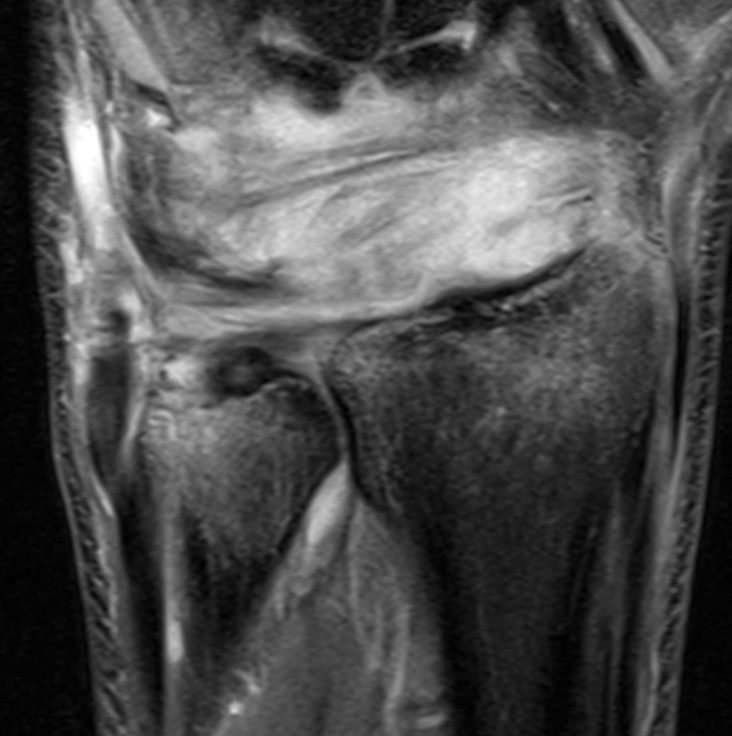
MRI
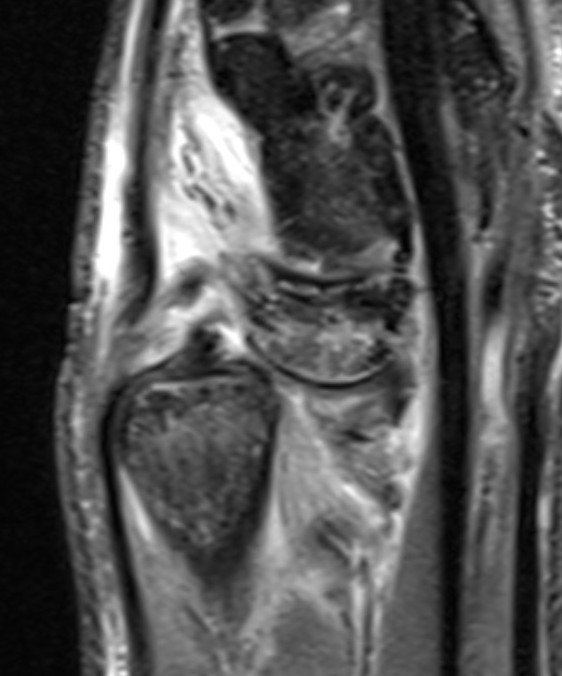
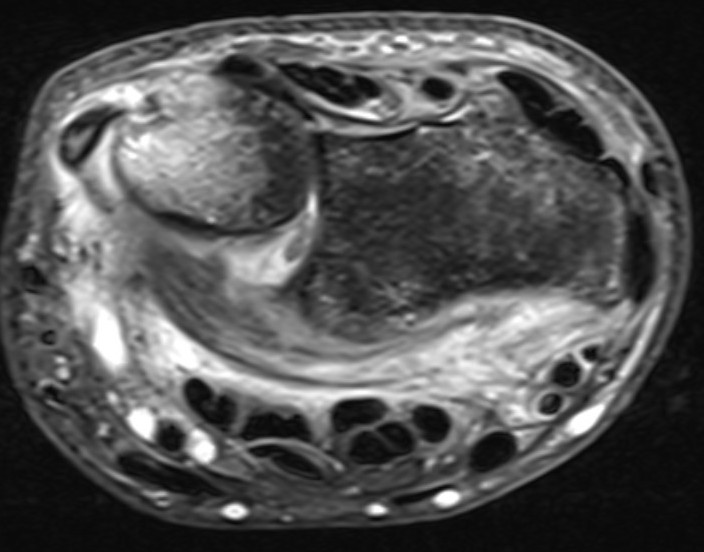
MRI demonstrating dorsal distal ulna subluxation associated with significant ligament disruption
Acute DRUJ instability
Closed reduction
- dorsal dislocation: cast in supination
- volar dislocation: cast in pronation
Failure closed reduction / unstable DRUJ
- open reduction
- repair TFCC / ulna styloid process
- +/- dorsal capsule repair / imbrication
- +/- K wire fixation
Technique
Dorsal approach
- 5/6 approach / bed of EDM
- interval between EDM and ECU
- open capsule
- sutures in TFCC
- suture over capsule / +/- suture anchors / +/- pass through drill holes in base ulna styloid
- dorsal capsule repair / imbrication
- +/- k wire
Results
- RCT of 40 patients with TFCC tear and DRUJ instability
- TFCC transosseous repair v TFCC repair + capsular repair
- better grip strength with additional capsular repair
Yeh et al BMC Musculoskeletal 2024
- 225 patients with DRUJ instability treated with TFCC repair
- 135 stable after TFCC repair: recurrent instability 4%
- 95 cases unstable after TFCC repair and treated with dorsal capsule imbrication: recurrent instability 1%
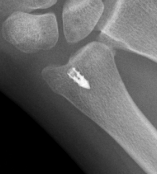
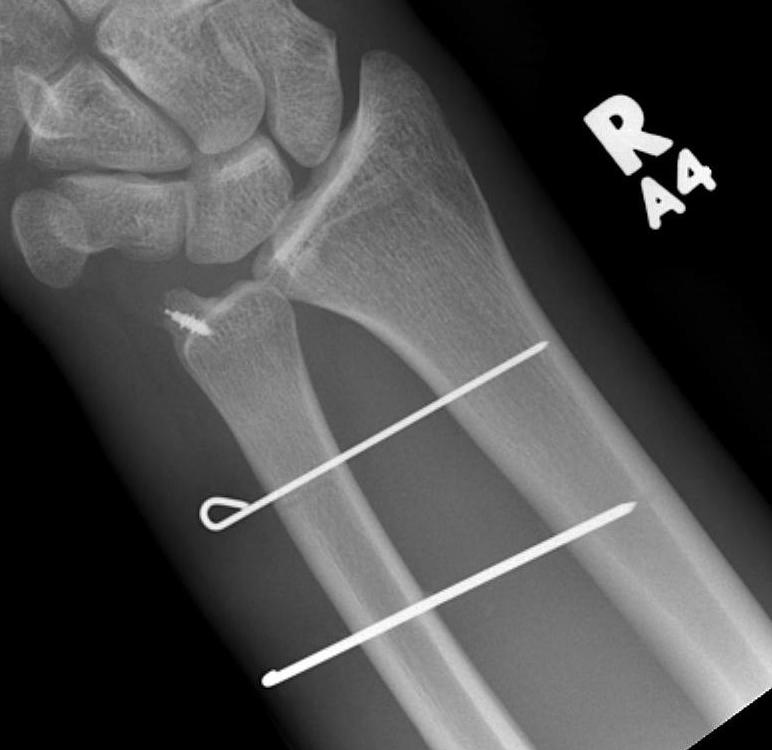
Chronic / recurrent DRUJ instability
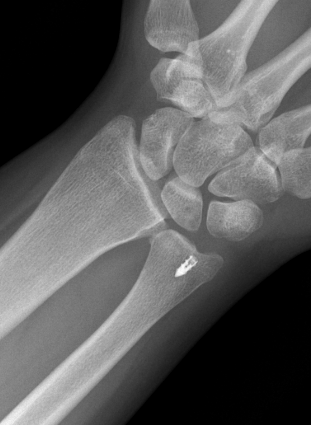
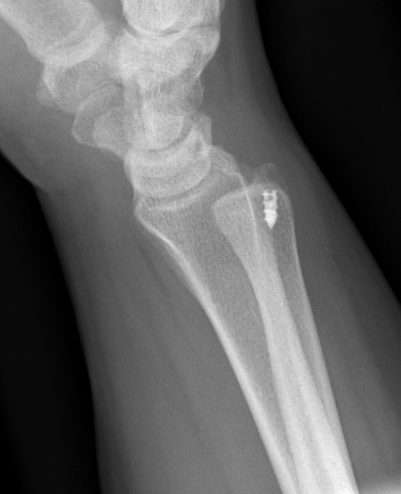
Recurrent DRUJ instability after TFCC repair
Management
Radioulnar ligament reconstruction / Adams-Berger ligament reconstruction
Technique
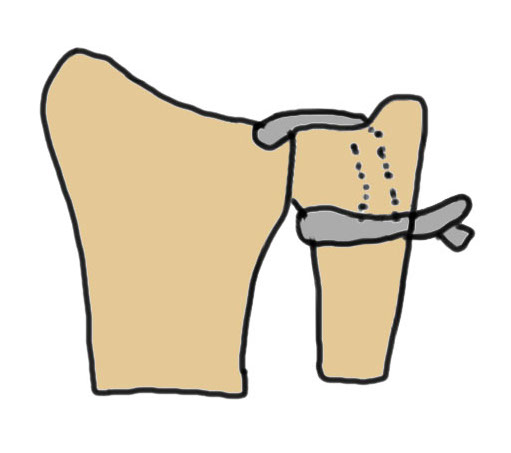
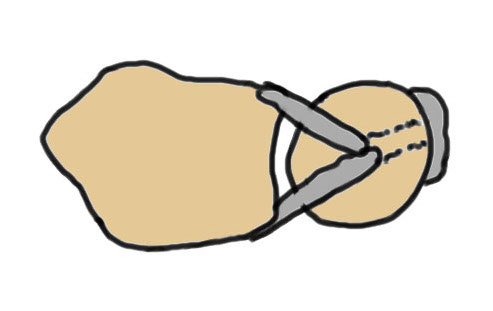
Vumedi DRUJ ligament reconstruction video
Vumedi arthroscopic DRUJ ligament reconstruction video
Results
Gillis et al J Wrist Surg 2019
- 95 cases of Adam-Berger reconstruction for DRUJ instability
- 91% stable DRUJ
- 76% no or mild pain
Isolated ulna styloid fractures with DRUJ instability
Classification ulna styloid process fractures
| Type 1: Tip fracture | Type 2: Base fracture |
|---|---|
|
Stable DRUJ
|
DRUJ potentially unstable |
 |
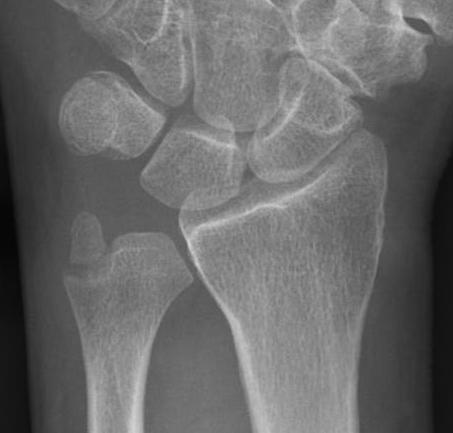 |
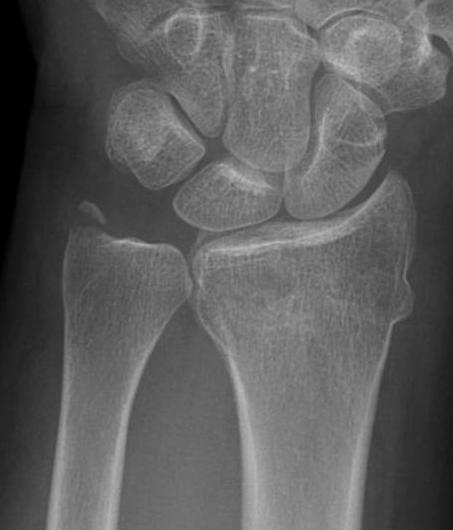
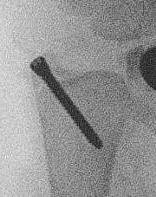
Ulna styloid process fracture and acute DRUJ instability
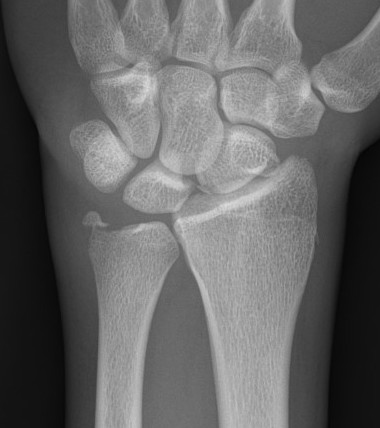
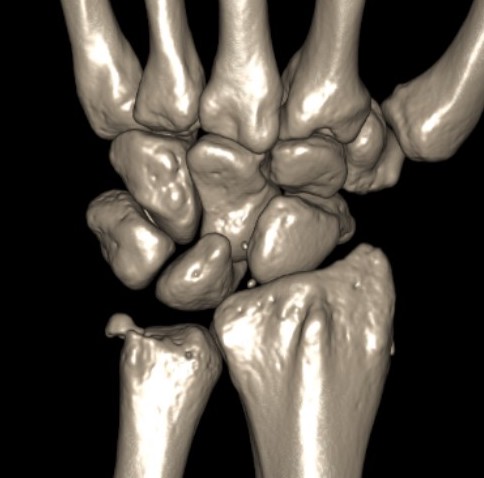
Ulna styloid fracture with TFCC injury
Management
Closed reduction
- dorsal dislocation: cast in supination
- volar dislocation: cast in pronation
Failure closed reduction / unstable DRUJ
- ulna styloid ORIF
- +/- capsule repair
- +/- K wire fixation
Technique
AO surgery ulna styloid fracture screw fixation
AO surgery ulna styloid TBW fixation
Galeazzi fracture
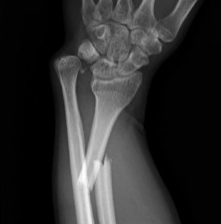
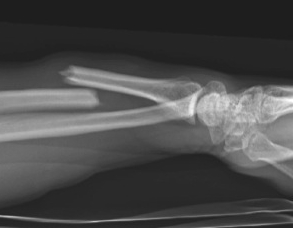
Galeazzi fracture with DRUJ disruption
Incidence of DRUJ instability after radius ORIF
Rettig et al J Hand Surg Am 2001
- 40 patients with Galeazzi fracture dislocations
- DRUJ instability after radius ORIF
- Type 1: radius fracture < 7.5 cm to articular surface: 55% DRUJ instability
- TYpe II: radius fracture > 7.5 cm to articular surface: 6% DRUJ instability


www.boneschool.com/galeazzi-fracture
Distal radius fracture with DRUJ instability
Management
DRUJ instability after distal radius fracture ORIF
- 100 cases of DRUJ instability after distal radius ORIF
- 50 treated with arthroscopic capsular repair
- 50 treated in cast
- better outcomes with capsular repair
www.boneschool.com/distal-radius-fractures
Radial malunion / Non anatomical ORIF of BBFF
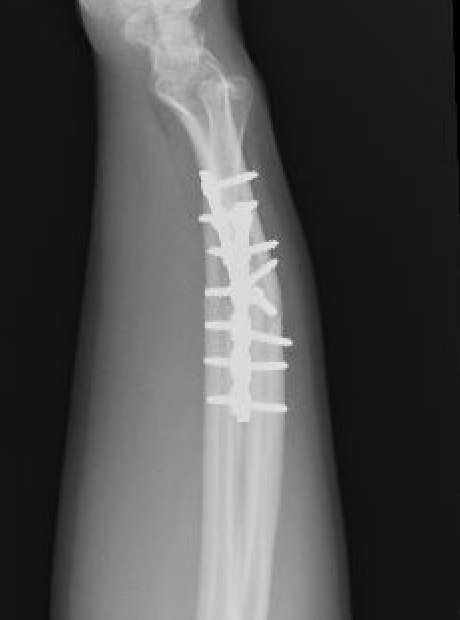
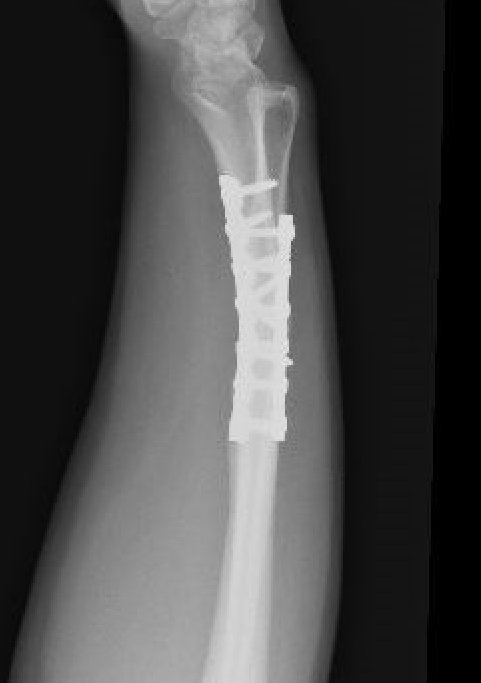
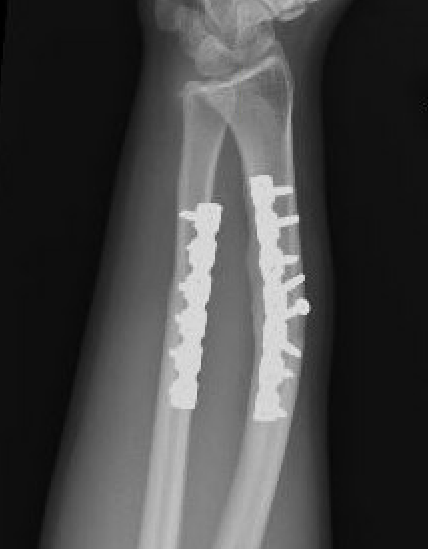
Radial malunion after ORIF of BBFF
Etiology
Non operative management of BBFF
Non anatomical ORIF of BBFF
Bone loss radius
Radius short
Lengthening radius difficult
Ulna shortening
Radius angulated / rotated
Radial osteotomy
TFCC repair +/- TFCC reconstruction
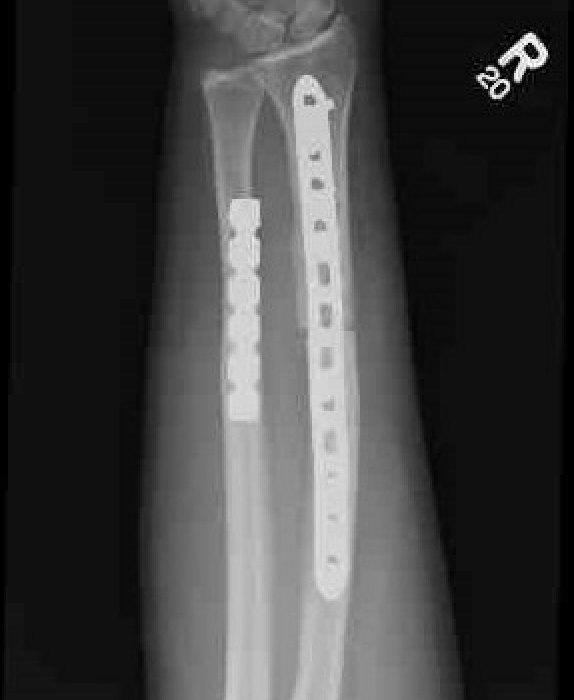
Essex-Lopresti injury
Definition
Early
- fracture radial head with dislocation DRUJ
- Essex-Lopresti variant - radial neck fracture with dislocation DRUJ
Late
- excision of radial head without replacement
