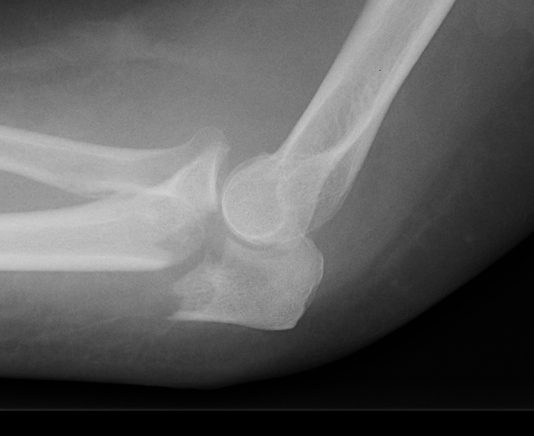
Anatomy

Proximal articular portion of the ulna
- greater sigmoid notch articulates with trochlea
- has a central bare area
- flexion / extension
Triceps insertion
- attaches to olecranon
- displaces olecranon fragment superiorly
Epidemiology
Mean age 57 years - fall from height
10% of upper limb fractures
Mayo Classification
A: Non comminuted
B: Comminuted
| Type I | Type II | Type III |
|---|---|---|
| Minimally displaced | Displaced | Trans-olecranon fracture dislocation |
| 10% | 85% | 5% |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Olecranon avulsion / triceps injury
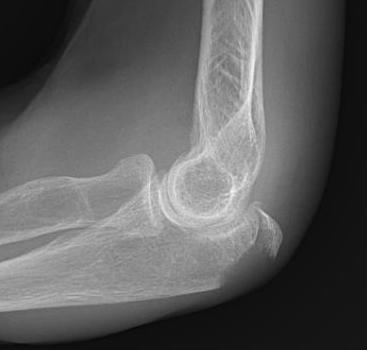
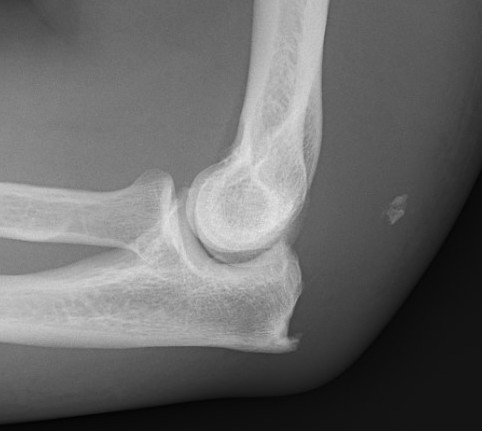
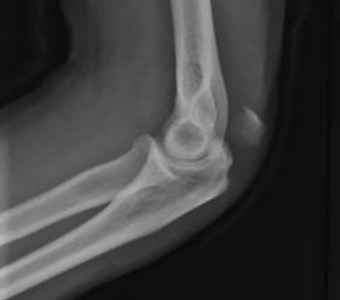
www.boneschool.com/triceps-tendon-injury
Nonoperative Management
Indications
Undisplaced fracture
Displaced fracture in patient > 70
Elderly olecranon fractures
Issue
High risk of implant failure

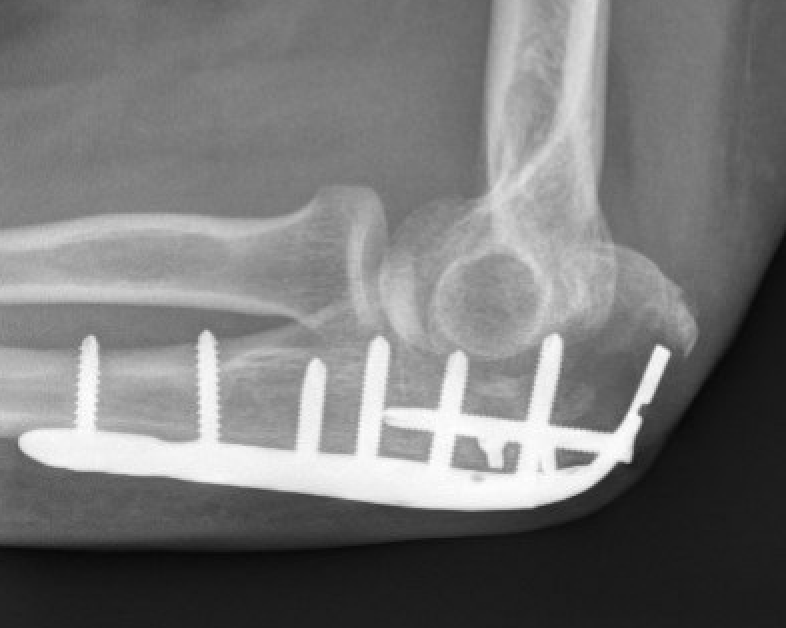
Failure of olecranon fixation in elderly patient
Results
- RCT of operative versus nonoperative management
- displaced olecranon fracture in 60 patients > 75 years
- no difference in functional scores at one year
- improved active elbow extension in operative group



Operative Management
Indications
Displaced fractures
- articular disruption
- extensor mechanism disruption
Options
Tension band wire (TBW)
Tension suture fixation
Olecranon plate
Olecranon excision and triceps excision


Results
- 200 olecranon fracture RCT of TBW v plate
- no difference in functional outcomes
- increased need for removal of hardware in TBW
- systematic review of TBW v plate
- 20 studies and 2000 patients
- no difference in functional outcomes
- no difference in wound breakdown or infection
- reduced loss of reduction and reoperation with plate
Tension band wire
Indication
Fracture proximal to center of rotation / midpoint of trochlea
Convert tensile distraction force of triceps into a compressive force
Issue
High rate of metal prominence / need for removal
Contra-indication
Fracture distal to center of rotation
Highly comminuted fractures
Oblique fractures
Technique



AO surgery reference olecranon TBW
Vumedi tension suture fixation video
Lateral decubitus with tourniquet
- curvilinear incision to avoid prominence of olecranon
- identify and protect ulna nerve
- reduce fracture with arm in extension
- may need to make a small drill hole in distal ulna to use bone reducing forceps
- ensure articular congruity / can release joint capsule medially and laterally to visualize
- fix with unicortical K wires
- drill hole in ulna distally
- pass 20 gauge wire and form figure of 8 wire about wires, can pass under triceps
- twist via 2 knots
Tension suture fixation

Indication
Type 2A fractures
Fracture proximal to center of rotation / midpoint of trochlea
Don't want to remove prominent wires
Technique
Vumedi olecranon suture fixation technique video
Drill hole in distal ulna
- pass sutures through drill hole
- pass sutures through medial and lateral limbs of the triceps insertion
Results
Phadnis et al Should Elbow 2020
- 168 olecranon fracture / osteotomy fixation
- TBW v suture fixation v olecranon plates
- re-operation rate: TBW 36%, plate 11%, suture group 2%
- suture group (n=41): 1 reoperation, 1 asymptomatic nonunion
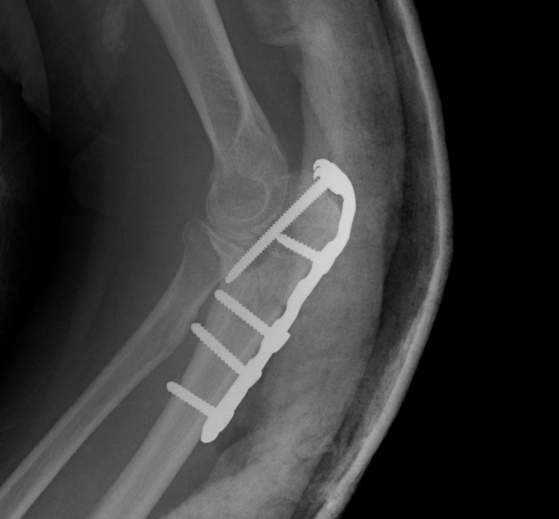
ORIF with olecranon plate
Indication
Fracture distal to center of rotation of elbow / trochlea
Technique
AO surgery reference olecranon plate
AO surgery reference olecranon plate with lag screw
Vumedi olecranon plate fixation video
Lateral decubitus with tourniquet
- curvilinear incision to avoid prominence of olecranon
- identify and protect ulna nerve
- reduce fracture with arm in extension
- ensure articular congruity
- use anatomical precontoured plate
- may want to split distal triceps to reduce proximal plate prominence



Complications

Olecranon plate nonunion
Olecranon excision and triceps advancement
Indication
Comminuted non reconstructable olecranon
Non union
Elderly
Technique
Vumedi olecranon excision and triceps advancement video